Related Research Articles

The Romani people, also known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan people group, traditionally nomadic itinerants living mostly in Europe, as well as diaspora populations in the Americas.

The Dom are a people with origins in the Indian subcontinent which through ancient migrations are found scattered across the Western Asia, North Africa, Caucasus, Central Asia, Eastern Anatolia Region and still parts of the Indian subcontinent. The traditional language of the Dom is Domari, an endangered Indo-Aryan language, thereby making the Dom an Indo-Aryan ethnic group. They have been associated with other traditionally itinerant ethnic groups, called the Rom/Roma/Romani people and Lom people: the three groups have been said to have separated from each other or, at least, to share a similar history. Specifically, the ancestors of the Dom, the Domba left the Indian subcontinent sometime between late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages.

The Lom people, also known as Bosha by non-Loms or Armenian Romani or Caucasian Romani, are an ethnic group in historic Armenia. Their Lomavren language is a mixed language, combining Indo-Aryan and Armenian.
The Kawliya, Qawliya or Awaz, Keche-Hjälp, also known as Zott and Ghorbati, is a community in Iraq of Indian origin, estimated to number over 60,000 people. Today they speak mostly Arabic, while their ethnolect is a mixture of Persian, Kurdish and Turkish, only spoken by the older generations. The largest tribes are the Bu-Baroud, Bu-Swailem, Bu-Helio, Bu-Dakhil, Bu-Akkar, Bu-Murad, Bu-Thanio, Bu-Shati, Al-Farahedah, Al-Mtairat, Bu-Khuzam, Bu-Abd, Bu-Nasif, Bu-Delli and Al-Nawar. Their main occupation is entertainment, and also small trades.
Domari is an Indo-Aryan language, spoken by Dom people scattered across the Middle East. The language is reported to be spoken mainly in Turkey and the Levant. Based on the systematicity of sound changes, we know with a fair degree of certainty that the names Domari and Romani derive from the Indo-Aryan word ḍom. The language itself actually derives from an Indo-Aryan language. The Arabs referred to them as nawar/qurbaṭ as they were a nomadic people that originally immigrated to the Middle East from Indian subcontinent.
The Romani people, also referred to depending on the sub-group as Roma, Sinti or Sindhi, or Kale are an Eurasian ethnic group, who live primarily in Europe. They originated in Indian subcontinent and left sometime between the 1st century AD - 2nd century AD, as merchants, and settled in Roman Egypt, eventually settling in Europe, the Byzantine Empire.
The Garachi, also spelled Karachi or Karaci, are a group of the Romani people living in Azerbaijan. Little research has been done on the Garachi, and most of what is known about them is based on the works of the 19th-century Russian scholars Kerope Patkanov and Jean-Marie Chopin.
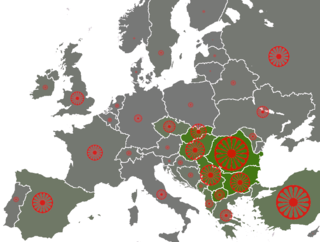
The Roma people have several distinct populations, the largest being the Roma and the Iberian Calé or Caló, who reached Anatolia and the Balkans about the early 12th century, from a migration out of the Indian subcontinent beginning about 1st century - 2nd century AD. They settled in the areas of present-day Turkey, Greece, Serbia, Romania, Croatia, Moldova, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Hungary, Albania, Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Czech Republic, Slovenia and Slovakia, by order of volume, and Spain. From the Balkans, they migrated throughout Europe and, in the nineteenth and later centuries, to the Americas. The Roma population in the United States is estimated at more than one million.
Nawar is an Arabic term for several sedentary communities used primarily in Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, and Palestine. The term, regarded as derogatory, is used by Arabs for several diverse ethnic groups. They have historically been called "Gypsies", though as a whole they only have economic activities and lifestyle in connection with the Romani, possibly having distant linguistical relationship; only the Dom people have a clear connection with the Roma. The Dom people are especially known as Nawar.

Bilal is a Lebanese singer of Nawari descent, who is notable for singing not only in Arabic, but mainly in Domari, his native language.
Zott is the Arabic term for gypsies, Romani people and Dom people. The Zott were musicians who migrated in great numbers from northern India to the Middle East about 1000 years ago. Their name was later applied to any itinerant entertainer of Indian origin, and came to be the common name of the Dom people in the Middle East, as English gypsy or tinker with contemptuous connotations. The Al-Qamus Al-Muhit glosses the term as equivalent to Nawar.

The ethnic groups in the Middle East refers to the peoples that reside in West Asia as well as Egypt in North Africa, a transcontinental region commonly known as the Middle East. The region has historically been a crossroad of different cultures. Since the 1960s, the changes in political and economic factors have significantly altered the ethnic composition of groups in the region. While some ethnic groups have been present in the region for millennia, others have arrived fairly recently through immigration. The largest ethnic groups in the region are the Arabs, Kurds, Persians, and Turks, but there are dozens of other ethnic groups which have hundreds of thousands, if not millions, of members.

The Romani people are also known by a variety of other names; in English as gypsies or gipsies and Roma, in Greek as γύφτοι (gíftoi) or τσιγγάνοι (tsiggánoi), in Central and Eastern Europe as Tsingani, in France as gitans besides the dated bohémiens, manouches, in Italy as zíngari and gitani, in Spain as gitanos, and in Portugal as ciganos.

It is estimated that there are one million Romani people in the United States, occasionally known as American Gypsies. Though the Romani population in the United States has largely assimilated into American society, the largest concentrations are in Southern California, the Pacific Northwest, Texas and the Northeast as well as in cities such as Chicago and St. Louis.
The Domari-speaking community in Syria, commonly identified as Dom and Nawar, is estimated to number 100–250,000 or 250–300,000 people. The vast majority is sedentary. There are semi-nomadic groups, some moving outside the country. In Aleppo, the Dom community is probably the largest, while they are reported to live in Damascus, Homs and Latakia as well. The community is highly marginalised in society, and they are referred to as Qurbāṭ and Qarač in the northern part, and Nawar elsewhere. These terms are used for various groups that mainly share socio-economic profile. The community is divided into clans.
Romani people in Libya speak the Domari language. They immigrated to the territory of the present day Libya from South Asia, particularly from India, in Byzantine times. Romani people self-segregated themselves for centuries from the dominant culture of Libya, who view Romani as dishonorable though clever. Historically, Gypsies in Libya have provided musical entertainment as weddings and other celebrations. The Romani people or Gypsies in Libya include subgroups like Nawar, Halebi and Ghagar.
Romani people in Egypt speak the Romani language. They migrated to the territory of the present day Egypt from South Asia, particularly from India, during the Roman Egypt times and mixed with the local Egyptians population in the South for more than 2000 years. Romani people self-segregated themselves for centuries from the dominant culture of Egypt, who view Romani as dishonorable though clever. Historically, Romani in Egypt have provided musical entertainment at weddings and other celebrations, singing Egyptian traditional songs in return for money. The Romani people in Egypt include subgroups like Nawar, Halebi and Ghagar.
Some reports suggest the existence of Romani people in Morocco. Thomas (2000) states that "Xoraxane or Muslim Gypsies have been reported in Morocco. It is suspected that Kalo Gypsies from Spain have migrated to Morocco for business reasons. However no government statistics can substantiate this supposition. Similarly, it may be true that French speaking Gypsies or Manouche may have in the past or still today traveled and worked in Morocco but there is no evidence of this at the moment." Phillips (2001) mentions rather speculatively that "Some Kali or Gitan are probably in Morocco." The available reports are not sufficiently precise to confirm the Romani identity or even existence of such groups, but in the event that they exist and are of Romani origin, they would have immigrated to the territory of the present day Morocco ultimately from South Asia, and proximately from Spain and/or Algeria.
Romani people in Algeria historically included Gitanos who migrated there along with other Spanish people in the late 19th century, during the French colonial period; most of these left for France following Algeria's independence in 1962, resulting in a large community in the South of France. Ratcliffe (1933) describes a Gitano encampment on the heights above Algiers, whose Catholic inhabitants sold lace and mended chairs. Notable descendants of the Gitanos who used to live in Algeria include the film-maker Tony Gatlif and the footballer André-Pierre Gignac.
Romani people in Sudan speak the Domari language. They immigrated to the territory of the present day Sudan from South Asia, particularly from India, in Byzantine times. Romani people self-segregated themselves for centuries from the dominant culture of Sudan, who view Romani as dishonorable though clever. Historically, Gypsies in Sudan have provided musical entertainment as weddings and other celebrations. The Romani people or Gypsies in Sudan include subgroups like Nawar, Halebi and Ghagar.
References
- ↑ "Kuri Journal - Dom of North Africa - An Overview". Domresearchcenter.com. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
- ↑ Phillips, David J. (2 August 2017). Peoples on the Move: Introducing the Nomads of the World. William Carey Library. ISBN 9781903689059 . Retrieved 2 August 2017– via Google Books.
- ↑ Berland, Joseph C. (2004). Customary Strangers: New Perspectives on Peripatetic Peoples in the Middle East, Africa, and Asia. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 0-89789-771-4 . Retrieved 2013-10-28.