Related Research Articles
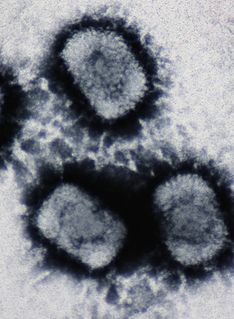
Cowpox is an infectious disease caused by the cowpox virus. The virus, part of the genus Orthopoxvirus, is closely related to the vaccinia virus. The virus is zoonotic, meaning that it is transferable between species, such as from cat to human. The transferral of the disease was first observed in dairymaids who touched the udders of infected cows and consequently developed the signature pustules on their hands. Cowpox is more commonly found in animals other than bovines, such as rodents. Cowpox is similar to, but much milder than, the highly contagious and often deadly smallpox disease. Its close resemblance to the mild form of smallpox and the observation that dairy farmers were immune to smallpox inspired the modern smallpox vaccine, created and administered by English physician Edward Jenner.

The smallpox vaccine was the first vaccine to be developed against a contagious disease. In 1796, the British doctor Edward Jenner demonstrated that an infection with the relatively mild cowpox virus conferred immunity against the deadly smallpox virus. Cowpox served as a natural vaccine until the modern smallpox vaccine emerged in the 20th century. From 1958 to 1977, the World Health Organization conducted a global vaccination campaign that eradicated smallpox, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. Although routine smallpox vaccination is no longer performed on the general public, the vaccine is still being produced to guard against bioterrorism and biological warfare.

Vaccinia virus is a large, complex, enveloped virus belonging to the poxvirus family. It has a linear, double-stranded DNA genome approximately 190 kbp in length, which encodes approximately 250 genes. The dimensions of the virion are roughly 360 × 270 × 250 nm, with a mass of approximately 5–10 fg. The vaccinia virus is the source of the modern smallpox vaccine, which the World Health Organisation used to eradicate smallpox in a global vaccination campaign in 1958–1977. Although smallpox no longer exists in the wild, vaccinia virus is still studied widely by scientists as a tool for gene therapy and genetic engineering.

Eczema vaccinatum is a rare severe adverse reaction to smallpox vaccination.
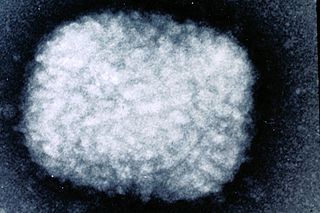
Poxviridae is a family of viruses. Humans, vertebrates, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are currently 83 species in this family, divided among 22 genera, which are divided into two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include smallpox.
The Modified Vaccinia Ankara (MVA) is an attenuated vaccine of a poxvirus. It was licensed and used as a poxvirus vaccine in Bavaria and is a vector for vaccination against non-poxvirus diseases.
Orthopoxvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Poxviridae and subfamily Chordopoxvirinae. Vertebrates, including mammals and humans, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species are in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include smallpox, cowpox, horsepox, camelpox, and monkeypox. The most widely known member of the genus is Variola virus, which causes smallpox. It was eradicated globally by 1977, through the use of Vaccinia virus as a vaccine. The most recently described species is the Alaskapox virus, first isolated in 2015.

Ceragenix Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is a biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Denver, Colorado that develops prescription therapies based on a platform of proprietary surface active technologies—skin Barrier Repair Technology (BRT) and Cerageninis, a new class of broad spectrum anti-infectives. The company discovers, develops and commercializes anti-infective drugs based on its proprietary class of compounds, Ceragenins. Active against a range of gram positive and gram negative bacteria, these agents are being developed as anti-infective medical device coatings and as therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant organisms.

Eczema herpeticum is a rare but severe disseminated infection that generally occurs at sites of skin damage produced by, for example, atopic dermatitis, burns, long-term usage of topical steroids or eczema. It is also known as Kaposi varicelliform eruption, Pustulosis varioliformis acute and Kaposi-Juliusberg dermatitis.

Aphidicolin is a tetracyclic diterpene antibiotic isolated from the fungus, Cephalosporum aphidicola with antiviral and antimitotic properties. Aphidicolin is a reversible inhibitor of eukaryotic nuclear DNA replication. It blocks the cell cycle at early S phase. It is a specific inhibitor of DNA polymerase Alpha and Delta in eukaryotic cells and in some viruses and an apoptosis inducer in HeLa cells. Natural aphidicolin is a secondary metabolite of the fungus Nigrospora oryzae.

Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) is a DNA poxvirus that causes the human skin infection molluscum contagiosum. Molluscum contagiosum affects about 200,000 people a year, about 1% of all diagnosed skin diseases. Diagnosis is based on the size and shape of the skin lesions and can be confirmed with a biopsy, as the virus cannot be routinely cultured. Molluscum contagiosum virus is the only species in the genus Molluscipoxvirus. MCV is a member of the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae of family Poxviridae. Other commonly known viruses that reside in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae are variola virus and monkeypox virus.
Rabbitpox is a disease of rabbits caused by a virus of the genus Orthopoxvirus in the family Poxviridae, and closely related to vaccinia virus. Rabbitpox was first isolated at the Rockefeller Institute in New York in 1933, following a series of epidemics in the laboratory rabbits. It is an acute disease only known to infect laboratory rabbits as no cases have been reported in wild rabbits; it also cannot infect humans.
In enzymology, a mRNA guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
ACAM2000 is a smallpox vaccine manufactured by Sanofi Pasteur Biologics Co. of Cambridge Massachusetts.

Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by one of two virus variants, Variola major and Variola minor. The agent of variola virus (VARV) belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980. The risk of death after contracting the disease was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often those who survived had extensive scarring of their skin, and some were left blind.
Generalized vaccinia is a cutaneous condition that occurs 6–9 days after vaccination, characterized by a generalized eruption of skin lesions, and caused by the vaccinia virus.

Progressive vaccinia is a rare cutaneous condition caused by the vaccinia virus, characterized by painless, but progressive, necrosis and ulceration.

The Yaba monkey tumor virus is a type of poxvirus. The first case of the virus was obtained from a colony of rhesus monkeys in Yaba, Lagos, Nigeria. The virus caused the formation of tumors on the bodies of the monkeys. From these tumors the virus was isolated and determined to be its own species of virus. It is a species of the Yatapoxvirus genus and is closely related to the tanapox. The virus gets its name from the suburb of Yaba, Lagos.
Analgecine is an analgesic extract that is approved for the treatment of back pain and neuralgia in China.
B13R is a protein expressed by vaccinia virus.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.