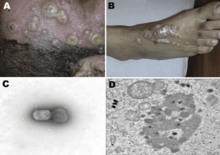
Cowpox is an infectious disease caused by the cowpox virus (CPXV). It presents with large blisters in the skin, a fever and swollen glands, historically typically following contact with an infected cow, though in the last several decades more often from infected cats. The hands and face are most frequently affected and the spots are generally very painful.

Orf is a farmyard pox, a type of zoonosis. It causes small pustules in the skin of primarily sheep and goats, but can also occur on the hands of humans. A pale halo forms around a red centre. It may persist for several weeks before crusting and then either resolves or leaves a hard lump. There is usually only one lesion, but there may be many, and they are not painful. Sometimes there are swollen lymph glands.

Milking is the act of removing milk from the mammary glands of cattle, water buffalo, humans, goats, sheep, and, more rarely, camels, horses, and donkeys. Milking may be done by hand or by machine, and requires the animal to be currently or recently pregnant. The milker may refer either to the animal that produces the milk or the person who milks said animal.

A somatic cell count (SCC) is a cell count of somatic cells in a fluid specimen, usually milk. In dairying, the SCC is an indicator of the quality of milk—specifically, its low likeliness to contain harmful bacteria, and thus its high food safety. White blood cells (leukocytes) constitute the majority of somatic cells in question. The number of somatic cells increases in response to pathogenic bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus, a cause of mastitis. The SCC is quantified as cells per milliliter. General agreement rests on a reference range of less than 100,000 cells/mL for uninfected cows and greater than 250,000 for cows infected with significant pathogen levels. Several tests like the PortaSCC milk test and The California mastitis test provide a cow-side measure of somatic cell count. The somatic cell count in the milk also increases after calving when colostrum is produced.
Orthopoxvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Poxviridae and subfamily Chordopoxvirinae. Vertebrates, including mammals and humans, and arthropods serve as natural hosts. There are 12 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include smallpox, cowpox, horsepox, camelpox, and mpox. The most widely known member of the genus is Variola virus, which causes smallpox. It was eradicated globally by 1977, through the use of Vaccinia virus as a vaccine. The most recently described species is the Alaskapox virus, first isolated in 2015.

Brucella melitensis is a Gram-negative coccobacillus bacterium from the Brucellaceae family. The bacterium causes ovine brucellosis, along with Brucella ovis. Humans can become infected if they have contact with an infected animal or its byproducts. Animals acquire B. melitensis by venereal transmission. The organism is found in blood, urine, milk, and semen. It is zoonotic, unlike B. ovis, causing Malta fever or localized brucellosis in humans.

Camelpox is a disease of camels caused by the camelpox virus (CMPV) of the family Poxviridae, subfamily Chordopoxvirinae, and the genus Orthopoxvirus. It causes skin lesions and a generalized infection. Approximately 25% of young camels that become infected will die from the disease, while infection in older camels is generally more mild. Although rare, the infection may spread to the hands of those that work closely with camels.

Sheeppox is a highly contagious disease of sheep caused by a poxvirus different from the benign orf. This virus is in the family Poxviridae and genus Capripoxvirus. Sheeppox virus (SPV) is the most severe of all the animal pox diseases and can result in some of the most significant economic consequences due to poor wool and leather quality.

Lumpy skin disease (LSD) is an infectious disease in cattle caused by a virus of the family Poxviridae, also known as Neethling virus. The disease is characterized by fever, enlarged superficial lymph nodes, and multiple nodules on the skin and mucous membranes, including those of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Infected cattle may also develop edematous swelling in their limbs and exhibit lameness. The virus has important economic implications since affected animals tend to have permanent damage to their skin, lowering the commercial value of their hide. Additionally, the disease often results in chronic debility, reduced milk production, poor growth, infertility, abortion, and sometimes death.

Fowlpox is the worldwide disease of poultry caused by viruses of the family Poxviridae and the genus Avipoxvirus. The viruses causing fowlpox are distinct from one another but antigenically similar, possible hosts including chickens, turkeys, quail, canaries, pigeons, and many other species of birds. There are two forms of the disease. The first is spread by biting insects and wound contamination, and causes lesions on the comb, wattles, and beak. Birds affected by this form usually recover within a few weeks. The second is contracted by inhalation or ingestion of the virus via dust or aerosols, leading to the 'diphtheritic form' of the disease, in which diphtheritic membranes form in the mouth, pharynx, larynx, and sometimes the trachea. The prognosis for this form is poor.

Bovine papillomaviruses (BPV) are a paraphyletic group of DNA viruses of the subfamily Firstpapillomavirinae of Papillomaviridae that are common in cattle. All BPVs have a circular double-stranded DNA genome. Infection causes warts of the skin and alimentary tract, and more rarely cancers of the alimentary tract and urinary bladder. They are also thought to cause the skin tumour equine sarcoid in horses and donkeys.

The United States raw milk debate concerns issues of food safety and claimed health benefits of raw milk, and whether authorities responsible for regulating food safety should prohibit sale of raw milk for consumption.
Variola caprina is a contagious viral disease caused by Goatpox virus, a pox virus that affects goats. The virus usually spreads via the respiratory system, and sometimes spreads through abraded skin. It is most likely to occur in crowded stock. Sources of the virus include cutaneous lesions, saliva, nasal secretions and faeces. There are two types of the disease: the papulo-vesicular form and the nodular form. The incubation period is usually 8–13 days, but it may be as short as four days.

Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious and sometimes fatal viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including domestic and wild bovids. The virus causes a high fever lasting two to six days, followed by blisters inside the mouth and near the hoof that may rupture and cause lameness.

Streptococcus canis is a group G beta-hemolytic species of Streptococcus. It was first isolated in dogs, giving the bacterium its name. These bacteria are characteristically different from Streptococcus dysgalactiae, which is a human-specific group G species that has a different phenotypic chemical composition. S. canis is important to the skin and mucosal health of cats and dogs, but under certain circumstances, these bacteria can cause opportunistic infections. These infections were known to afflict dogs and cats prior to the formal description of the species in Devriese et al., 1986. However, additional studies revealed cases of infection in other mammal species, including cattle and even humans. Instances of mortality from S. canis in humans are very low with only a few reported cases, while actual instances of infection may be underreported due to mischaracterizations of the bacteria as S. dysgalactiae. This species, in general, is highly susceptible to antibiotics, and plans to develop a vaccine to prevent human infections are currently being considered.
Caprine arthritis encephalitis virus (CAEV) is a retrovirus which infects goats and cross-reacts immunologically with HIV, due to being from the same family of viruses. CAEV cannot be transmitted to humans, including through the consumption of milk from an infected goat. There is no evidence that CAEV can cure HIV in humans.

Bovine mastitis is the persistent, inflammatory reaction of the udder tissue due to physical trauma or microorganisms infections. Mastitis, a potentially fatal mammary gland infection, is the most common disease in dairy cattle in the United States and worldwide. It is also the most costly disease to the dairy industry. Milk from cows suffering from mastitis has an increased somatic cell count. Prevention and control of mastitis requires consistency in sanitizing the cow barn facilities, proper milking procedure and segregation of infected animals. Treatment of the disease is carried out by penicillin injection in combination with sulphar drug.
Capripoxvirus is a genus of viruses in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae and the family Poxviridae. Capripoxviruses are among the most serious of all animal poxviruses. All CaPV are notifiable diseases to the OIE. Sheep, goat, and cattle serve as natural hosts. These viruses cause negative economic consequences by damaging hides and wool and forcing the establishment of trade restrictions in response to an outbreak. The genus consists of three species: sheeppox virus (SPPV), goatpox virus (GTPV), and lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV). They share no serological relationship with camel pox, horse pox, or avian poxes. Capripoxviruses for sheeppox and goatpox infect only sheep and goat respectively. However, it is probable that North American relatives, the mountain goat and mountain sheep, may be susceptible to the strains but has not been experimentally proven. Lumpy skin disease virus affects primarily cattle, but studies have been shown that giraffes and impala are also susceptible to LSDV. Humans cannot be infected by Capripoxviruses.
Pseudocowpox is a disease caused by the Paravaccinia virus or Pseudocowpox virus, a virus of the family Poxviridae and the genus Parapoxvirus. Humans can contract the virus from contact with livestock infected with Bovine papular stomatitis and the disease is common among ranchers, milkers, and veterinarians. Infection in humans will present with fever, fatigue, and lesion on the skin.

A dry cow refers to a dairy cow that is in a stage of their lactation cycle where milk production ceases prior to calving. This part of their lactation cycle is referred to as the cows dry period and typically last between 40 and 65 days. Dry cows are typically divided into two groups: far-off and close-up. Once the cow has entered this stage, producers will seal the cows teat while following a veterinarian recommended, dry cow therapy for their herd. This dry period is a critical part of their lactation cycle and is important for the cows health, the newborn calf and future milk production, as it allows the cow time to rest, eat and prepare for birth. During this time, the cow will produce colostrum for the newly born calf.