
A Doppler radar is a specialized radar that uses the Doppler effect to produce velocity data about objects at a distance. It does this by bouncing a microwave signal off a desired target and analyzing how the object's motion has altered the frequency of the returned signal. This variation gives direct and highly accurate measurements of the radial component of a target's velocity relative to the radar.

Millimeter-wave cloud radars, also denominated cloud radars, are radar systems designed to monitor clouds with operating frequencies between 24 and 110 GHz. Accordingly, their wavelengths range from 1 mm to 1.11 cm, about ten times shorter than those used in conventional S band radars such as NEXRAD.

Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type. Modern weather radars are mostly pulse-Doppler radars, capable of detecting the motion of rain droplets in addition to the intensity of the precipitation. Both types of data can be analyzed to determine the structure of storms and their potential to cause severe weather.
The National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL) is a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) weather research laboratory under the Office of Oceanic and Atmospheric Research. It is one of seven NOAA Research Laboratories (RLs).

The Aggie Doppler Radar (ADRAD) is a Doppler weather radar located on the roof of the Eller Oceanography & Meteorology Building on the Texas A&M University campus in College Station, Texas.

A lightning detector is a device that detects lightning produced by thunderstorms. There are three primary types of detectors: ground-based systems using multiple antennas, mobile systems using a direction and a sense antenna in the same location, and space-based systems.

Doppler on Wheels is a fleet of X-band and C-band radar trucks managed by the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and previously maintained by the Center for Severe Weather Research (CSWR) in Boulder, Colorado, led by principal investigator (PI) Joshua Wurman, with the funding largely provided by the National Science Foundation (NSF). The DOW fleet and its associated Mobile Mesonets and deployable weather stations (Pods) were Lower Atmospheric Observing Facilities (LAOF) "National Facilities" supporting a wide variety NSF-sponsored research. They are now included in the NSF's "Community Instruments and Facilities" (CIF) program led by PI Karen Kosiba.

Joshua Michael Aaron Ryder Wurman is an American atmospheric scientist and inventor noted for tornado, tropical cyclone, and weather radar research.

The Verification of the Origins of Rotation in Tornadoes Experiment are field experiments that study tornadoes. VORTEX1 was the first time scientists completely researched the entire evolution of a tornado with an array of instrumentation, enabling a greater understanding of the processes involved with tornadogenesis. A violent tornado near Union City, Oklahoma was documented in its entirety by chasers of the Tornado Intercept Project (TIP) in 1973. Their visual observations led to advancement in understanding of tornado structure and life cycles.

OU-PRIME was an advanced Doppler weather radar. It was completed in January 2009 after a ten-month construction period and commissioned on April 4, 2009. It is operated by the Advanced Radar Research Center (ARRC) at the University of Oklahoma (OU). The radar was manufactured by Enterprise Electronics Corporation to provide OU students and faculty a platform for research and education in the field of radar meteorology. This C-band polarimetric radar has some of the highest resolution data of any C-band weather radar in the United States.

The Chengdu University of Information Technology, formerly the Chengdu Meteorological College (成都气象学院), is a provincial public university in Chengdu, Sichuan, China. The university is co-sponsored by the China Meteorological Administration and the Sichuan Provincial People's Government.

During the early evening of Friday, May 31, 2013, a very large and powerful tornado occurred over rural areas of Central Oklahoma. This rain-wrapped, multiple-vortex tornado was the widest tornado ever recorded and was part of a larger weather system that produced dozens of tornadoes over the preceding days. The tornado initially touched down at 6:03 p.m. Central Daylight Time (2303 UTC) about 8.3 miles (13.4 km) west-southwest of El Reno, rapidly growing in size and becoming more violent as it tracked through central portions of Canadian County. Remaining over mostly open terrain, the tornado did not impact many structures; however, measurements from mobile weather radars revealed extreme winds up to 135.0 m/s within the vortex. These are among the highest observed wind speeds on Earth, just slightly lower than the wind speeds of the 1999 Bridge Creek–Moore tornado. As it crossed U.S. 81, it had grown to a record-breaking width of 2.6 miles (4.2 km), beating the previous width record set in 2004. Turning northeastward, the tornado soon weakened. Upon crossing Interstate 40, the tornado dissipated around 6:43 p.m. CDT (2343 UTC), after tracking for 16.2 miles (26.1 km), it avoided affecting the more densely populated areas near and within the Oklahoma City metropolitan area.
The following is a glossary of tornado terms. It includes scientific as well as selected informal terminology.
Jeffrey W. Frame is an American atmospheric scientist known for being lit and modeling studies of severe convective storms and for teaching meteorology. He was a scientist for VORTEX2 and other field research programs.
Yvette Richardson is an American meteorologist with substantial contributions on tornado dynamics, tornadogenesis, the environments of tornadoes, supercells, and severe convection, and radar observations of these. She was a principal investigator (PI) of VORTEX2.
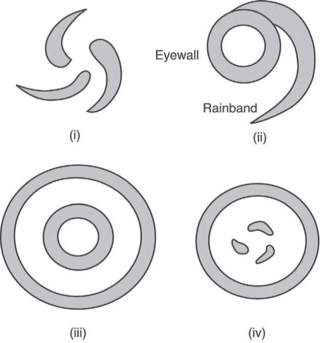
The Hurricane Rainband and Intensity Change Experiment (RAINEX) is a project to improve hurricane intensity forecasting via measuring interactions between rainbands and the eyewalls of tropical cyclones. The experiment was planned for the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season. This coincidence of RAINEX with the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season led to the study and exploration of infamous hurricanes Katrina, Ophelia, and Rita. Where Hurricane Katrina and Hurricane Rita would go on to cause major damage to the US Gulf coast, Hurricane Ophelia provided an interesting contrast to these powerful cyclones as it never developed greater than a category 1.

NOAA's 10 cm Doppler Weather Radar was a 10 cm wavelength S-band Doppler Weather Radar commonly referred to as NSSL Doppler, and was used to track severe weather and related meteorological phenomena. The radar became operational soon after its donation, collecting its first data in May 1971. Data was collected on magnetic tapes and processed on a NASA computer post event due to the lack of real-time capability at the time.

Roger M. Lhermitte was a French meteorologist who "pioneered the development of meteorological Doppler radar." His career extended from the 1950s until his death where he made numerous contributions to the field of Radar Meteorology resulting in over 100 publications and numerous patents.

Project NIMROD was a meteorological field study of severe thunderstorms and their damaging winds conducted by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It took place in the Greater Chicago area from May 15 to June 30, 1978. Data collected was from single cell thunderstorms as well as mesoscale convective systems, such as bow echoes. Using Doppler weather radars and damage clues on the ground, the team studied mesocyclones, downbursts and gust fronts. NIMROD was the first time that microbursts, very localized strong downdrafts under thunderstorms, were detected; this helped improve airport and public safety by the development of systems like the Terminal Doppler Weather Radar and the Low-level windshear alert system.

The Rapid X-band Polarimetric Radar, commonly abbreviated as RaXPol, is a mobile research radar designed and operated by the University of Oklahoma, led by Howard Bluestein. RaXPol often collaborates with adjacent mobile radar projects, such as Doppler on Wheels and SMART-R. Unlike its counterparts, RaXPol typically places emphasis on temporal resolution, and as such is capable of surveilling the entire local atmosphere in three dimensions in as little as 20 seconds, or a single level in less than 3 seconds.
















