
École Centrale de Nantes, or Centrale Nantes, is a grande école – a French engineering school – established in 1919 under the name of Institut Polytechnique de l'Ouest. It provides Bachelor, Graduate, Master, and PhD Programmes based on the latest scientific and technological developments and the best management practices.

The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, nonprofit research and higher education facility dedicated to the study of marine science and engineering.

The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. With an annual budget of about $9.9 billion, the NSF funds approximately 25% of all federally supported basic research conducted by the United States' colleges and universities. In some fields, such as mathematics, computer science, economics, and the social sciences, the NSF is the major source of federal backing.

The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) is a public research university in Sai Kung District, New Territories, Hong Kong. Founded in 1991, it was the territory's third institution to be granted university status, and the first university without any precursory existence upon its formation. It occupies a 60-hectare (150-acre) seaside site in Tai Po Tsai, Clear Water Bay Peninsula, and has established a satellite campus in Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.

The Statewide California Earthquake Center (SCEC) is a collaboration of more than 1,000 scientists across 100 research institutions focused primarily on conducting research on earthquakes in Southern California and elsewhere by gathering data, conducting theoretical studies, and performing computer simulations; integrate information into a comprehensive, physics-based understanding of earthquake phenomena; and communicate that understanding to end-users and society at large as useful knowledge for reducing earthquake risk and improving community resilience.

The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH) is a public research university in Huntsville, Alabama. The university is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools and comprises eight colleges: arts, humanities & social sciences; business; education; engineering; honors; nursing; science; and graduate. The university's enrollment is approximately 10,000. It is part of the University of Alabama System and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities: Very High Research Activity".
A testbed is a platform for conducting rigorous, transparent, and replicable testing of scientific theories, computing tools, and new technologies.

The U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command Army Research Laboratory is the foundational research laboratory for the United States Army under the United States Army Futures Command (AFC). DEVCOM ARL conducts intramural and extramural research guided by 11 Army competencies: Biological and Biotechnology Sciences; Humans in Complex Systems; Photonics, Electronics, and Quantum Sciences; Electromagnetic Spectrum Sciences; Mechanical Sciences; Sciences of Extreme Materials; Energy Sciences; Military Information Sciences; Terminal Effects; Network, Cyber, and Computational Sciences; and Weapons Sciences.
The Center for Analysis and Prediction of Storms (CAPS) was established at the University of Oklahoma in 1989 as one of the first eleven National Science Foundation Science and Technology Centers. Located at the National Weather Center in Norman, Oklahoma, its mission is the development of techniques for the computer-based prediction of high-impact local weather, such as individual spring and winter storms, with the NEXRAD (WSR-88D) Doppler weather radar serving as a key data source.

The Cyprus Institute is a non-profit research and educational institution with a scientific and technological orientation. It was formally established in 2005, and started operations in 2007.
The National Institute of Aerospace (NIA) is a non-profit research and graduate education institute headquartered in Hampton, Virginia, near NASA's Langley Research Center.
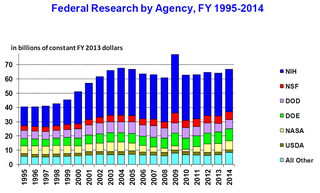
The science policy of the United States is the responsibility of many organizations throughout the federal government. Much of the large-scale policy is made through the legislative budget process of enacting the yearly federal budget, although there are other legislative issues that directly involve science, such as energy policy, climate change, and stem cell research. Further decisions are made by the various federal agencies which spend the funds allocated by Congress, either on in-house research or by granting funds to outside organizations and researchers.

The Center for Neurotechnology (CNT) is an Engineering Research Center funded by the National Science Foundation, develops devices to restore the body's capabilities for sensation and movement. The center is based at the University of Washington. Its core partner organizations are the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and San Diego State University.
Engineering Research Centers (ERC) are university-led institutions developed through the National Science Foundation (NSF) Directorate of Engineering. While ERCs are initially funded by the NSF, they are expected to be self-sustaining within 10 years of being founded. The Engineering Research Centers program was originally developed in 1984 with the mission of removing disparity between academic and industrial engineering applications. In this way, engineering students would, theoretically, be better prepared to enter the engineering workforce. As a result, the United States would gain a competitive advantage over other countries. There have been three generations of Engineering Research Centers. Each of these generations has been specifically designed to meet the dynamic engineering demands of the United States. Due to the limited amount of funding available for ERCs, the program is competitive; out of 143 proposals submitted in 2008, only 5 were awarded centers. Commercialization of academic research is one of the primary goals of NSF ERCs.

The University of Massachusetts Amherst College of Engineering is one of the schools and colleges at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. It was established on September 1, 1947 as the School of Engineering and now considered as the best public engineering school in New England, enrolling 2250 undergraduate students and 610 graduate students including 300 M.S. students and 310 Ph.D. students for the 2018–2019 school year. The College of Engineering at UMass Amherst has eight buildings, including the Elab II, research facilities, computer labs, and graduate offices. It has more than 16,000 living alumni around the world.

Susan K. Avery is an American atmospheric physicist and President Emerita of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) in Massachusetts, where she led the marine science and engineering research organization from 2008–2015. She was the ninth president and director and the first woman to hold the leadership role at WHOI. She is Professor Emerita at the University of Colorado, Boulder (UCB), where she served on the faculty from 1982–2008. While at UCB she also served in various administrative positions, including director of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES), a 550-member collaborative institute between UCB and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (1994-2004); and interim positions (2004-2007) as vice chancellor for research and dean of the graduate school, and provost and executive vice chancellor for academic affairs. Currently she is a senior fellow at the Consortium for Ocean Leadership in Washington, D.C.
Yehia Massoud has had significant progressive academic leadership and has been involved in forging and building effective partnerships with numerous academic and industrial institutions, and international organizations, and governmental funding agencies.

Kelvin Kay Droegemeier is an American research meteorologist, most recently having served as Director of The White House Office of Science and Technology Policy. Droegemeier is known for his research in predicting the development of extreme weather events, and previously served as Oklahoma Secretary of Science and Technology and the Vice President for Research at the University of Oklahoma. He currently is serving as a Professor and Special Advisor to the Chancellor for Science and Policy at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.












