The Bayern class was a class of four super-dreadnought battleships built by the German Kaiserliche Marine. The class comprised Bayern, Baden, Sachsen, and Württemberg. Construction started on the ships shortly before World War I; Baden was laid down in 1913, Bayern and Sachsen followed in 1914, and Württemberg, the final ship, was laid down in 1915. Only Baden and Bayern were completed, due to shipbuilding priorities changing as the war dragged on. It was determined that U-boats were more valuable to the war effort, and so work on new battleships was slowed and ultimately stopped altogether. As a result, Bayern and Baden were the last German battleships completed by the Kaiserliche Marine.

SMSBaden was a Bayern-class dreadnought battleship of the German Imperial Navy built during World War I. Launched in October 1915 and completed in March 1917, she was the last battleship completed for use in the war; two of her sisters—Sachsen and Württemberg—were incomplete when the war ended. The ship mounted eight 38-centimeter (15 in) guns in four twin turrets, displaced 32,200 metric tons at full combat load, and had a top speed of 21 knots. Along with her sister Bayern, Baden was the largest and most powerfully armed battleship built by the Imperial Navy.

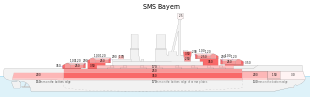
SMS Bayern was the lead ship of the Bayern class of dreadnought battleships in the German Kaiserliche Marine. The vessel was launched in February 1915 and entered service in July 1916, too late to take part in the Battle of Jutland. Her main armament consisted of eight 38 cm (15 in) guns in four turrets, which was a significant improvement over the preceding König's ten 30.5 cm (12 inch) guns. The ship was to have formed the nucleus for a fourth battle squadron in the High Seas Fleet, along with three of her sister ships. Of the other ships only one—Baden—was completed; the other two were canceled later in the war when production requirements shifted to U-boat construction.

The Mackensen class was the last class of battlecruisers to be built by Germany in World War I. The design initially called for seven ships, but three of them were redesigned as the Ersatz Yorck class. Of the four ships of the Mackensen class, Mackensen, Graf Spee, and Prinz Eitel Friedrich were launched, and Fürst Bismarck was not—but none were completed, after wartime shipbuilding priorities were redirected towards U-boats—and the ships were broken up in the early 1920s. The lead ship of the class was named for August von Mackensen, a prominent military commander during the war. In response to the Mackensen-class ships, the British Royal Navy laid down the Admiral-class battlecruisers, all but one of which would eventually be cancelled; the sole survivor, HMS Hood, was completed after the end of the war.

SMS König was the first of four König-class dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy during World War I. König was named in honor of King William II of Württemberg. The battleship was armed with ten 30.5-centimeter (12 in) guns in five twin turrets and could steam at a top speed of 21 knots. Laid down in October 1911, the ship was launched on 1 March 1913. The construction of König was completed shortly after the outbreak of World War I; she was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 9 August 1914.

The König class was a group of four dreadnought battleships built for the German Kaiserliche Marine in the early 1910s. The class comprised König, the lead ship, Grosser Kurfürst, Markgraf, and Kronprinz. The design for the ships was derived from the preceding Kaiser class, using the same basic hull but with a rearranged main battery of ten 30.5 cm (12 in) guns in five twin-gun turrets to improve the guns' firing arcs. Instead of the staggered wing turrets used in the Kaisers, the Königs placed their main guns all on the centerline using superfiring pairs fore and aft. Budgetary constraints and the need to begin construction quickly to compete with Britain in the Anglo-German naval arms race prevented any more radical changes. Diesel engines were planned for the ships, but they could not be readied in time, so all four vessels reverted to steam turbines for their propulsion system.

The Kaiser class was a class of five dreadnought battleships that were built in Germany prior to World War I and served in the Kaiserliche Marine during the war. They were the third class of German dreadnoughts, and the first to feature turbine engines and superfiring turrets. The five ships were Kaiser, Friedrich der Grosse, Kaiserin, Prinzregent Luitpold, and König Albert. As was usual for German battleships of the period, the Kaiser class mounted main guns that were smaller than those of their British rivals: 30.5 cm (12 in), compared to the 34.3 cm (13.5 in) guns of the British Orion class.

SMS Westfalen was one of the Nassau-class battleships, the first four dreadnoughts built for the German Imperial Navy. Westfalen was laid down at AG Weser in Bremen on 12 August 1907, launched nearly a year later on 1 July 1908, and commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 16 November 1909. The ship was equipped with a main battery of twelve 28 cm (11 in) guns in six twin turrets in an unusual hexagonal arrangement.

The Nassau class was a group of four dreadnought battleships built for the German Kaiserliche Marine in the early 1900s. The class comprised Nassau, the lead ship, Rheinland, Posen, and Westfalen. All four ships were laid down in mid-1907, and completed by late 1910. Though commonly perceived as having been built in response to the British Dreadnought, their design traces its origin to 1903; they were in fact a response to Dreadnought's predecessors of the Lord Nelson class. The Nassaus adopted a main battery of twelve 28 cm (11 in) guns in six twin-gun turrets in an unusual hexagonal arrangement. Unlike many other dreadnoughts, the Nassau-class ships retained triple-expansion steam engines instead of more powerful steam turbines.

The Brandenburg class consisted of four pre-dreadnought battleships built for the German Kaiserliche Marine, the first modern battleships of the fleet. The four ships of the class—Brandenburg, Wörth, Weissenburg, and Kurfürst Friedrich Wilhelm—were the first ocean-going capital ships built for the German fleet in nearly two decades, owing to reluctance in the Reichstag to fund large projects. They followed a series of small coastal defense ships, and though in retrospect they anticipated the buildup that created the High Seas Fleet, they were ordered as part of a construction program that reflected the strategic and tactical confusion that affected many navies in the 1880s. The design process that resulted in the Brandenburg class was very lengthy, with proposals that ranged from outdated casemate ships to versions with two twin-gun turrets placed side by side. The designers ultimately settled on ships that were armed with an unusual main battery of six 28 cm (11 in) guns at a time when all foreign battleships were built with four or fewer heavy guns.

The Kaiser Friedrich III class consisted of five pre-dreadnought battleships of the Imperial German Navy; all ships of the class were named for German emperors. The ships were Kaiser Friedrich III, Kaiser Wilhelm II, Kaiser Wilhelm der Grosse, Kaiser Barbarossa, and Kaiser Karl der Grosse, all built between 1895 and 1901. The class saw the introduction of the traditional armament layout for German battleships prior to the advent of the dreadnought type of battleship in the early 1900s: four large-caliber guns, but of comparatively smaller size compared to their contemporaries, in two gun turrets. The German adoption of smaller guns was a result of a preference for higher volumes of fire over weight of shell. The Kaiser Friedrich III class also standardized the use of three screws for battleships and introduced water-tube boilers and Krupp cemented armor.

The Moltke class was a class of two "all-big-gun" battlecruisers of the German Imperial Navy built between 1909–1911. Named SMS Moltke and SMS Goeben, they were similar to the previous battlecruiser Von der Tann, but the newer design featured several incremental improvements. The Moltkes were slightly larger, faster, and better armored, and had an additional pair of 28 cm (11 in) guns.

The Victoria Louise class of protected cruisers was the last class of ships of that type built for the German Imperial Navy. The class design introduced the combined clipper and ram bow and the blocky sides that typified later German armored cruisers. The class comprised five vessels, Victoria Louise, the lead ship, Hertha, Freya, Vineta, and Hansa. The ships were laid down in 1895–1896, and were launched in 1897–1898 and commissioned into the fleet over the following year.

The Sachsen class of armored corvettes was a class of four ships built by the Imperial German Navy in the late 1870s to early 1880s. The ships—Sachsen, Bayern, Württemberg, and Baden—were designed to operate as part of an integrated coastal defense network. The ships were intended to sortie from fortified bases to break up an enemy blockade or landing attempt. Armed with six 26 cm (10.2 in) guns, they were also intended to fight hostile ironclads on relatively equal terms.
The Ersatz Yorck class was a group of three battlecruisers ordered but not completed for the German Kaiserliche Marine in 1916. The three ships had originally been ordered as additions to the Mackensen class, but developments abroad, particularly the British Renown-class battlecruisers, led to the navy re-designing the ships. The primary change was an increase of the main battery from eight 35-centimeter (14 in) guns to eight 38 cm (15 in) weapons. Work on the first ship had already begun by the time the navy decided to re-design the ships, so the design staff was constrained by the need to use the material already assembled.

L 20e α was a design for a class of battleships to be built in 1918 for the German Kaiserliche Marine during World War I. Design work on the class of battleship to succeed the Bayern-class battleships began in 1914, but the outbreak of World War I in July 1914 led to these plans being shelved. Work resumed in early 1916 and lessons from the Battle of Jutland, fought later that year, were incorporated into the design. Reinhard Scheer, the commander of the fleet, wanted larger main guns and a higher top speed than earlier vessels, to combat the latest ships in the British Royal Navy. A variety of proposals were submitted, with armament ranging from the same eight 38 cm (15 in) guns of the Bayern class to eight 42 cm (16.5 in) guns.

SMS Württemberg was the fourth and final member of the Bayern-class dreadnought battleships ordered but never finished for the German Kaiserliche Marine in the 1910s, sometimes considered to be part of a sub-class with her sister Sachsen. She was to be armed with the same main battery of eight 38 cm (15 in) guns in four gun turrets. Originally intended to serve as a fleet flagship, the start of World War I in July 1914 forced the Navy to simplify her design in the hopes that she could be completed in time to see service during the conflict. She was laid down in January 1915 at the AG Vulcan shipyard, but as resources were diverted to more pressing projects, including U-boat construction, work on the ship slowed; she was launched in June 1917, but only to clear the slipway for other work. By the time construction stopped, she was about twelve months from completion. The Treaty of Versailles that ended the war in June 1919 specified that all warships under construction in Germany were to be destroyed, and Württemberg was accordingly sold for scrap in 1921 and dismantled the following year.