SBus is a computer bus system that was used in most SPARC-based computers from Sun Microsystems and others during the 1990s. It was introduced by Sun in 1989 to be a high-speed bus counterpart to their high-speed SPARC processors, replacing the earlier VMEbus used in their Motorola 68020- and 68030-based systems and early SPARC boxes. When Sun moved to open the SPARC definition in the early 1990s, SBus was likewise standardized and became IEEE-1496. In 1997 Sun started to migrate away from SBus to the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus, and today SBus is no longer used.

The DECstation was a brand of computers used by DEC, and refers to three distinct lines of computer systems—the first released in 1978 as a word processing system, and the latter two both released in 1989. These comprised a range of computer workstations based on the MIPS architecture and a range of PC compatibles. The MIPS-based workstations ran ULTRIX, a DEC-proprietary version of UNIX, and early releases of OSF/1.

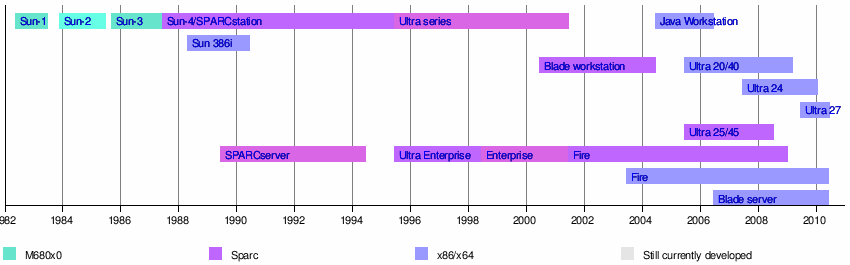
The SPARCstation 1 is the first of the SPARCstation series of SPARC-based computer workstations sold by Sun Microsystems. The design originated in 1987 by a Sun spin-off company, Unisun, which was soon re-acquired. The SPARCstation 1 has a distinctive slim enclosure and was first sold in April 1989, with Sun's support ending in 1995.

The SPARCstation, SPARCserver and SPARCcenter product lines are a series of SPARC-based computer workstations and servers in desktop, desk side (pedestal) and rack-based form factor configurations, that were developed and sold by Sun Microsystems.

MBus is a computer bus designed and implemented by Sun Microsystems for communication between high speed computer system components, such as the central processing unit, motherboard and main memory. SBus is used in the same machines to connect add-on cards to the motherboard.

The SPARCstation 20 or SS20 is a discontinued Sun Microsystems workstation introduced in March 1994 based on the SuperSPARC or hyperSPARC CPU. It is one of the last models in the SPARCstation family of Sun "pizza box" computers, which was superseded by the UltraSPARC design in 1995.

SPARCstation 5 or SS5 is a workstation introduced by Sun Microsystems in March 1994. It is based on the sun4m architecture, and is enclosed in a pizza-box chassis. Sun also offered a SPARCserver 5 without a framebuffer. A simplified, cheaper version of the SS5 was released in February 1995 as the SPARCstation 4. Sun also marketed these same machines under the "Netra" brand, without framebuffers or keyboards and preconfigured with all the requisite software to be used as web servers. An estimated 400,000+ SPARCstation 5s were sold.
Sun-4 is a series of Unix workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in 1987. The original Sun-4 series were VMEbus-based systems similar to the earlier Sun-3 series, but employing microprocessors based on Sun's own SPARC V7 RISC architecture in place of the 68k family processors of previous Sun models.

The SPARCstation 2, or SS2 is a SPARC workstation computer sold by Sun Microsystems. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is implemented in a pizza box form factor.

The Ultra 1 is a family of Sun Microsystems workstations based on the 64-bit UltraSPARC microprocessor. It was the first model in the Ultra series of Sun computers, which succeeded the SPARCstation series. It launched in November 1995 alongside the MP-capable Ultra 2 and shipped with Solaris 2.5. It is capable of running other operating systems such as Linux and BSD.

The Sun Microsystems Ultra 80 is a computer workstation that shipped from November 1999 to 2002.

Sun4d is a computer architecture introduced by Sun Microsystems in 1992. It is a development of the earlier Sun-4 architecture, using the XDBus system bus, SuperSPARC processors, and SBus I/O cards. The XDBus was the result of a collaboration between Sun and Xerox; its name comes from an earlier Xerox project, the Xerox Dragon. These were Sun's largest machines to date, and their first attempt at making a mainframe-class server.
The ICL DRS was a range of departmental computers from International Computers Limited (ICL). Standing originally for Distributed Resource System, the full name was later dropped in favour of the abbreviation.

The SPARCclassic is a workstation introduced by Sun Microsystems in November 1992. It is based on the sun4m architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis. It shares the code name Sunergy with the SPARCclassic X, SPARCstation LX, and SPARCstation ZX. It was replaced by the SPARCstation 4 in February 1994.
The SPARCstation LX is a workstation that was designed, manufactured, and sold by Sun Microsystems. Introduced in November 1992, it is based on the sun4m architecture and enclosed in a lunchbox chassis. It shares the code name Sunergy with the low-end range of SPARCclassic, SPARCclassic X, and SPARCstation ZX.

The SPARCstation IPC is a workstation sold by Sun Microsystems, introduced July 1990. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis.

The SPARCstation IPX is a workstation that was sold by Sun Microsystems, introduced July 1991. It is based on the sun4c architecture, and is enclosed in a lunchbox chassis.
The Ultra 60 is a fairly large and heavy computer workstation in a tower enclosure from Sun Microsystems. The Ultra 60 was launched in November 1997 and shipped with Solaris 7. It was available in several specifications.

The Ultra 30 is a family of Sun Microsystems workstations based on the UltraSPARC II microprocessor. It was the first Sun workstation to use the industry-standard PCI bus instead of Sun's proprietary SBus, and is a member of the Sun Ultra series. It launched in July 1997 and shipped with Solaris 2.6. The Ultra 30 reached its end-of-life in May 1999.