Chad is one of the 47 landlocked countries in the world and is located in North Central Africa, measuring 1,284,000 square kilometers (495,755 sq mi), nearly twice the size of France and slightly more than three times the size of California. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square kilometer in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. (Borkou-Ennedi-Tibesti) desert region, which itself is larger than France. The capital city of N'Djaména, situated at the confluence of the Chari and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 people.

Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and overexploitation of soil as a result of human activity.

Niger is a landlocked nation in West Africa located along the border between the Sahara and Sub-Saharan regions. Its geographic coordinates are longitude 16°N and latitude 8°E. Its area is 1.267 million square kilometers, of which 1 266 700 km2 is land and 300 km2 water, making Niger slightly less than twice the size of France.

Nigeria is a country in West Africa, it shares land borders with the Republic of Benin to the west, Chad and Cameroon to the east, and Niger to the north. Its coast lies on the Gulf of Guinea in the south and it borders Lake Chad to the northeast. Notable geographical features in Nigeria include the Adamawa Plateau, Mambilla Plateau, Jos Plateau, Obudu Plateau, the Niger River, Benue River, and Niger Delta.

Senegal is a coastal West African nation located 14 degrees north of the equator and 14 degrees west of the Prime Meridian. The country's total area is 196,190 km2 of which 192,000 km2 is land and 4,190 km2 is water.

A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions. This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season". A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought often exerts substantial impacts on the ecosystems and agriculture of affected regions, and causes harm to the local economy. Annual dry seasons in the tropics significantly increase the chances of a drought developing and subsequent wildfires. Periods of heat can significantly worsen drought conditions by hastening evaporation of water vapour.

Mauritania, a country in the western region of the continent of Africa, is generally flat, its 1,030,700 square kilometres forming vast, arid plains broken by occasional ridges and clifflike outcroppings. Mauritania is the world’s largest country lying entirely below an altitude of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft). It borders the North Atlantic Ocean, between Senegal and Western Sahara, Mali and Algeria. It is considered part of both the Sahel and the Maghreb. A series of scarps face southwest, longitudinally bisecting these plains in the center of the country. The scarps also separate a series of sandstone plateaus, the highest of which is the Adrar Plateau, reaching an elevation of 500 metres or 1,640 feet. Spring-fed oases lie at the foot of some of the scarps. Isolated peaks, often rich in minerals, rise above the plateaus; the smaller peaks are called Guelbs and the larger ones Kedias. The concentric Guelb er Richat is a prominent feature of the north-central region. Kediet ej Jill, near the city of Zouîrât, has an elevation of 915 metres or 3,002 feet and is the highest peak.

Mali is a landlocked nation in West Africa, located southwest of Algeria, extending south-west from the southern Sahara Desert through the Sahel to the Sudanian savanna zone. Mali's size is 1,240,192 square kilometers.

West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. The population of West Africa is estimated at 419 million people as of 2021, and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 were female and 192,309,000 male. The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent.

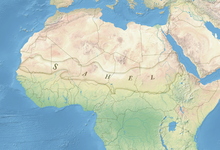
The Sahel is a region in Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid climate, it stretches across the south-central latitudes of Northern Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea.

Sudan is the geographical region to the south of the Sahara, stretching from Western Africa to Central and Eastern Africa. The name derives from the Arabic bilād as-sūdān, or "the lands of the Blacks", referring to West Africa and northern Central Africa.

The Permanent Interstate Committee for Drought Control in the Sahel is an international organization consisting of countries in the Sahel region of Africa.

The Ferlo Desert, also known as the Ferio Desert, is a desert in northern-central Senegal. It is inhabited by the Serer and the Fulani.
Farmer-managed natural regeneration (FMNR) is a low-cost, sustainable land restoration technique used to combat poverty and hunger amongst poor subsistence farmers in developing countries by increasing food and timber production, and resilience to climate extremes. It involves the systematic regeneration and management of trees and shrubs from tree stumps, roots and seeds. FMNR was developed by the Australian agricultural economist Tony Rinaudo in the 1980s in West Africa. The background and development are described in Rinaudo's book The Forest Underground.
A large-scale, drought-induced famine occurred in Africa's Sahel region and many parts of the neighbouring Sénégal River Area from February to August 2010. It is one of many famines to have hit the region in recent times.
Michael Mortimore was a British geographer and a prolific researcher of issues in the African drylands. He was an academic in Nigerian universities for over 25 years. He ran a British research consultancy, Drylands Research. He is best known for an anti-Malthusian account of population-environment relationships, More People, Less Erosion, and field-based studies of adaptation to drought.

Climate change in Africa is an increasingly serious threat in Africa which is among the most vulnerable continents to the effects of climate change. Some sources even classify Africa as "the most vulnerable continent on Earth". This vulnerability is driven by a range of factors that include weak adaptive capacity, high dependence on ecosystem goods for livelihoods, and less developed agricultural production systems. The risks of climate change on agricultural production, food security, water resources and ecosystem services will likely have increasingly severe consequences on lives and sustainable development prospects in Africa. With high confidence, it was projected by the IPCC in 2007 that in many African countries and regions, agricultural production and food security would probably be severely compromised by climate change and climate variability. Managing this risk requires an integration of mitigation and adaptation strategies in the management of ecosystem goods and services, and the agriculture production systems in Africa.
2012 had a very severe drought in the Sahel, the semiarid region of Africa that lies between the Sahara and the savannas. Countries included in this region are Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Sudan, and Eritrea. Droughts in the Sahel occur quite often and tend to reduce the already meager water supply and stress the economies of developing countries in that region.

Climate change in Senegal will have wide reaching impacts on many aspects of life in Senegal. Climate change will cause an increase in average temperatures over west Africa by between 1.5 and 4 °C by mid-century, relative to 1986–2005. Projections of rainfall indicate an overall decrease in rainfall and an increase in intense mega-storm events over the Sahel. The sea level is expected to rise faster in West Africa than the global average. Although Senegal is currently not a major contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions, it is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change.

The prehistory of West Africa spans from the earliest human presence in the region until the emergence of the Iron Age in West Africa. West African populations were considerably mobile and interacted with one another throughout the population history of West Africa. Acheulean tool-using archaic humans may have dwelled throughout West Africa since at least between 780,000 BP and 126,000 BP. During the Pleistocene, Middle Stone Age peoples, who dwelled throughout West Africa between MIS 4 and MIS 2, were gradually replaced by incoming Late Stone Age peoples, who migrated into West Africa as an increase in humid conditions resulted in the subsequent expansion of the West African forest. West African hunter-gatherers occupied western Central Africa earlier than 32,000 BP, dwelled throughout coastal West Africa by 12,000 BP, and migrated northward between 12,000 BP and 8000 BP as far as Mali, Burkina Faso, and Mauritania.