
Lee Oscar Lawrie was an American architectural sculptor and an important figure in the American sculpture scene preceding World War II. Over his long career of more than 300 commissions Lawrie's style evolved through Modern Gothic, to Beaux-Arts, Classicism, and, finally, into Moderne or Art Deco.

The Frank B. Kellogg House is a historic house at 633 Fairmount Avenue in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. It is listed as a National Historic Landmark for its association with Nobel Peace Prize-winner Frank B. Kellogg, co-author of the Kellogg–Briand Pact. Kellogg Boulevard in downtown Saint Paul is also named for him. The house was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1976. It is also a contributing property to the Historic Hill District.

The Rice County Courthouse, located at 218 3rd Street NW in Faribault, Rice County, in the U.S. state of Minnesota, is an Art Deco building constructed of natural-face Faribault stone horizontally banded at intervals with sawed-faced stone. Nairne W. Fisher of St. Cloud was the architect for the courthouse, and is also credited with designing the Pope County Courthouse. The main rotunda has metal fixtures and Art Deco glass. Polished black and gray Tennessee marble is used extensively in the walls, floors, and stairs, with a terrazzo map of Rice County centered on the floor. The 16-foot-high (4.9 m) courtroom on the third floor was finished with fine-grained walnut walls with matching custom-built furnishings. The building was built in 1934 at a cost of $200,000.

The Wilkin County Courthouse is the primary government building of Wilkin County, Minnesota, United States, located in the city of Breckenridge. Built from 1928 to 1929, the courthouse was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980 for having local significance in the themes of architecture and politics/government. It was nominated for being Wilkin County's seat of government and for its well-preserved architecture.

The Burbank–Livingston–Griggs House is the second-oldest house on Summit Avenue in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. It was designed in Italianate style by architect Otis L. Wheelock of Chicago and built from 1862 to 1863. The work was commissioned by James C. Burbank, a wealthy owner of the Minnesota Stage Company. Later, four significant local architects left their mark on the landmark structure.
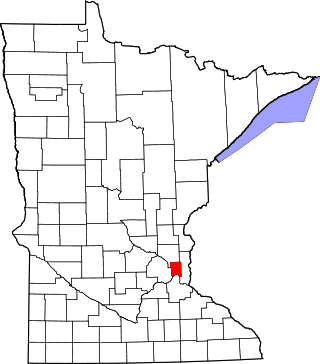
This is a complete list of National Register of Historic Places listings in Ramsey County, Minnesota. It is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Ramsey County, Minnesota, United States. The locations of National Register properties and districts for which the latitude and longitude coordinates are included below, may be seen in an online map.

Downtown Saint Paul is the central business district of Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. Its boundaries are the Mississippi River to the south, University Avenue to the north, US 52 to the east, and Kellogg Boulevard to the west. It is bounded by the Dayton's Bluff, Summit-University, West Seventh, Frogtown, West Side, and Payne-Phalen neighborhoods. The West Side neighborhood is on the other side of the river, and can be accessed via the Robert Street Bridge or the Wabasha Street Bridge. Interstate 35E and Interstate 94 run through the north side of the neighborhood, providing a separation between the Minnesota State Capitol and other state government buildings with the rest of downtown.

The Vision of Peace is a statue in the three-story memorial concourse lobby along the Fourth Street entrance of the Saint Paul City Hall and Ramsey County Courthouse in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. The memorial to the Minnesota 20th-century war dead was created by Swedish sculptor Carl Milles, who named it Indian God of Peace. He drew on memories of a Native American ceremony he witnessed in Ponca City, Oklahoma. Although there is no connection between Native American spirituality and his own vision, Milles depicted five Native Americans seated around a fire holding sacred pipes. Emerging from the smoke of those pipes is a "god of peace" which Milles imagined speaking to "all the world.”

The E. Ross Adair Federal Building and U.S. Courthouse is a historic post office, courthouse, and federal office building located at Fort Wayne in Allen County, Indiana. The building is a courthouse of the United States District Court for the Northern District of Indiana. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2006 as U.S. Post Office and Courthouse.

The William J. Nealon Federal Building and United States Courthouse is a courthouse of the United States District Court for the Middle District of Pennsylvania, located in Scranton, Pennsylvania. It was completed in 1931, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2018.

The United States Post Office and Courthouse in Meridian, Mississippi was built in 1933. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984. It is a three-story limestone building built in a classical Art Deco style which was home to Meridian's main post office and a federal courthouse from its construction in 1933 until 2012 when the federal courthouse was closed due to budget cuts. The building itself is still open and still houses the post office.

The Salvation Army Headquarters, later known as the Seton Center, was a historic structure in St. Paul, Minnesota. Deemed eligible for listing on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in February 1983, owner opposition prevented it from being officially listed. Despite protests by preservationists, the building was demolished by its owner in January 1998.

The Minnesota Building is a historic office building in Saint Paul, Minnesota, United States. The structure was placed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) on June 10, 2009. The building was noted for its design, which was a harbinger for the transition from Classical architecture to the Art Deco/Moderne among commercial buildings in downtown Saint Paul; originally designed in a conservative style, the building became more Moderne as it was being built.

The Des Moines County Court House located in Burlington, Iowa, United States, was built in 1940. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2003 as a part of the PWA-Era County Courthouses of Iowa Multiple Properties Submission. The courthouse is the fourth structure to house court functions and county administration.

Buechner & Orth was a St. Paul, Minnesota-based architectural firm that designed buildings in Minnesota and surrounding states, including 13 courthouses in North Dakota. It was the subject of a 1979 historic resources study.

The United States Post Office and Courthouse, commonly called the Knoxville Post Office, is a state building located at 501 Main Street in Knoxville, Tennessee, United States. Constructed in 1934 for use as a post office and federal courthouse, the building contains numerous Art Deco and Moderne elements, and is clad in Tennessee marble. While the building is still used as a branch post office, the court section is now used by the state courts. The building is listed on the National Register of Historic Places for its architecture and political significance.

Toltz, King & Day was an architectural and engineering firm in Minnesota, which is now TKDA.

The Sebastian County Courthouse/Fort Smith City Hall is a historic civic building at 100 South 6th Street in Fort Smith, Arkansas. It is a large four-story stone and concrete structure with modest Art Deco styling, designed by Fort Smith architects E. Chester Nelson, T. E. Bassham, and Carnall Wheeler and built in 1937 with funding from the Public Works Administration. Its interior lobby and courthouse spaces are richly decorated, with marble walls, terrazzo marble flooring, and ornamental moldings around doorways. The building continues to house county facilities; the city offices are now located on Garrison Avenue.

The Art Deco style, which originated in France just before World War I, had an important impact on architecture and design in the United States in the 1920s and 1930s. The most notable examples are the skyscrapers of New York City, including the Empire State Building, Chrysler Building, and Rockefeller Center. It combined modern aesthetics, fine craftsmanship, and expensive materials, and became the symbol of luxury and modernity. While rarely used in residences, it was frequently used for office buildings, government buildings, train stations, movie theaters, diners and department stores. It also was frequently used in furniture, and in the design of automobiles, ocean liners, and everyday objects such as toasters and radio sets.

























