
The Lamiaceae or Labiatae are a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mint or deadnettle or sage family. Many of the plants are aromatic in all parts and include widely used culinary herbs, such as basil, mint, rosemary, sage, savory, marjoram, oregano, hyssop, thyme, lavender, and perilla. Some species are shrubs, trees, or, rarely, vines. Many members of the family are widely cultivated, not only for their aromatic qualities, but also their ease of cultivation, since they are readily propagated by stem cuttings. Besides those grown for their edible leaves, some are grown for decorative foliage, such as Coleus. Others are grown for seed, such as Salvia hispanica (chia), or for their edible tubers, such as Plectranthus edulis, Plectranthus esculentus, Plectranthus rotundifolius, and Stachys affinis.

Salvia rosmarinus, commonly known as rosemary, is a woody, perennial herb with fragrant, evergreen, needle-like leaves and white, pink, purple, or blue flowers, native to the Mediterranean region.
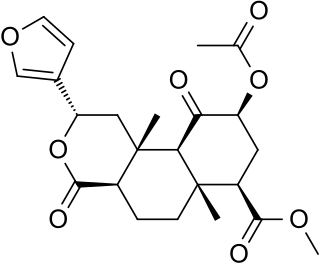
Salvinorin A is the main active psychotropic molecule in Salvia divinorum, a Mexican plant which has a long history of use as an entheogen by indigenous Mazatec shamans. Salvinorin A is considered a dissociative hallucinogen.

Salvia officinalis is a perennial, evergreen subshrub, with woody stems, grayish leaves, and blue to purplish flowers. It is a member of the mint family Lamiaceae and native to the Mediterranean region, though it has naturalized in many places throughout the world. It has a long history of medicinal and culinary use, and in modern times as an ornamental garden plant. The common name "sage" is also used for a number of related and unrelated species.
Jacqueline Isobel "Jacqui" Dean is a New Zealand politician and the current Member of Parliament for the Waitaki electorate, where she represents the National Party.
Brett's law is a name commonly given to a Delaware statute generally prohibiting use of the psychoactive herb Salvia divinorum. The law was named after Brett Chidester, a 17 year old who committed suicide by carbon monoxide poisoning.
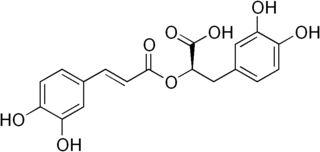
Rosmarinic acid is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants.
Salvia divinorum, a psychoactive plant, is legal in most countries. Exceptions, countries where there is some form of control, include Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Poland, Ukraine, Spain, Sweden, Armenia and the United States.

Salvia coccinea, the blood sage, scarlet sage, Texas sage, or tropical sage, is a herbaceous perennial in the family Lamiaceae that is widespread throughout the Southeastern United States, Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and northern South America. At one time Brazil was considered to be where it originated, but its diploid chromosome count now points to Mexico as its place of origin.

Officinalis, or officinale, is a Medieval Latin epithet denoting substances or organisms – mainly plants – with uses in medicine and herbalism. It commonly occurs as a specific epithet - the second term of a two-part botanical name. Officinalis is used to modify masculine and feminine nouns, while officinale is used for neuter nouns.

Salvia divinorum is a plant species with transient psychoactive properties when its leaves are consumed by chewing, smoking or as a tea. The leaves contain opioid-like compounds that induce hallucinations. Because the plant has not been well-studied in high-quality clinical research, little is known about its toxicology, adverse effects, or safety over long-term consumption. Its native habitat is cloud forest in the isolated Sierra Mazateca of Oaxaca, Mexico, where it grows in shady, moist locations. The plant grows to over a meter high, has hollow square stems like others in the mint family Lamiaceae, large leaves, and occasional white flowers with violet calyxes. Botanists have not determined whether Salvia divinorum is a cultigen or a hybrid because native plants reproduce vegetatively and rarely produce viable seed.

Chrysolina americana, common name rosemary beetle, is a species of beetle belonging to the family Chrysomelidae.

Taxodone is a naturally occurring diterpenoid found in Taxodium distichum, Rosmarinus officinalis (Rosemary), several Salvia species and other plants, along with its oxidized rearrangement product, taxodione. Taxodone and taxodione exhibit anticancer, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal, insecticide, and antifeedant activities.
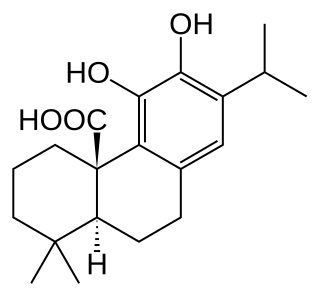
Carnosic acid is a natural benzenediol abietane diterpene found in rosemary and common sage. Dried leaves of rosemary or sage contain 1.5 to 2.5% carnosic acid.

Osmia latreillei is a species of mason bee belonging to the family Megachilidae subfamily Megachilinae.

Carnosol is a phenolic diterpene found in the herbs rosemary and Mountain desert sage.

Mentheae is the largest tribe of plants in the family Lamiaceae. It includes herbs such as sage, hyssop, mint, bee balm and thyme.

Salvia granatensis is a species of Salvia from southern Spain.
















