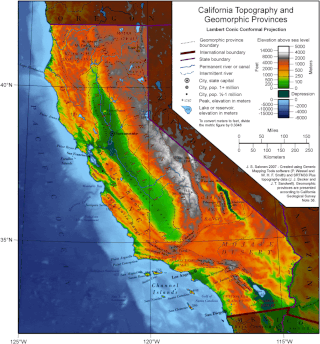
California is a U.S. state on the western coast of North America. Covering an area of 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2), California is among the most geographically diverse states. The Sierra Nevada, the fertile farmlands of the Central Valley, and the arid Mojave Desert of the south are some of the major geographic features of this U.S. state. It is home to some of the world's most exceptional trees: the tallest, most massive, and oldest. It is also home to both the highest and lowest points in the 48 contiguous states. The state is generally divided into Northern and Southern California, although the boundary between the two is not well defined. San Francisco is decidedly a Northern California city and Los Angeles likewise a Southern California one, but areas in between do not often share their confidence in geographic identity. The US Geological Survey defines the geographic center of the state at a point near North Fork, California.

Southern California is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. It includes the South Coast region which contains the Los Angeles metropolitan area, the second most populous urban agglomeration in the United States. The region generally contains ten of California's 58 counties: Imperial, Kern, Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside, San Bernardino, San Diego, Santa Barbara, San Luis Obispo and Ventura counties.

Anza-Borrego Desert State Park is a California State Park located within the Colorado Desert of southern California, United States. The park takes its name from 18th century Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza and borrego, a Spanish word for sheep. With 585,930 acres (237,120 ha) that includes one-fifth of San Diego County, it is the largest state park in California.

The Transverse Ranges are a group of mountain ranges of southern California, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region in North America. The Transverse Ranges begin at the southern end of the California Coast Ranges and lie within Santa Barbara, Ventura, Los Angeles, San Bernardino, Riverside and Kern counties. The Peninsular Ranges lie to the south. The name Transverse Ranges is due to their east–west orientation, making them transverse to the general northwest–southeast orientation of most of California's coastal mountains.

The Peninsular Ranges are a group of mountain ranges that stretch 1,500 km (930 mi) from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula; they are part of the North American Coast Ranges, which run along the Pacific Coast from Alaska to Mexico. Elevations range from 150 to 3,300 m.

The Tehachapi Mountains are a mountain range in the Transverse Ranges system of California in the Western United States. The range extends for approximately 40 miles (64 km) in southern Kern County and northwestern Los Angeles County and form part of the boundary between the San Joaquin Valley and the Mojave Desert.
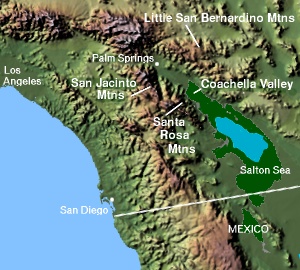
The Santa Rosa Mountains are a short mountain range in the Peninsular Ranges system, located east of the Los Angeles Basin and northeast of the San Diego metropolitan area of southern California, in the southwestern United States.

The Little San Bernardino Mountains are a short mountain range of the Transverse Ranges, located in southern California in the United States. They extend for approximately 40 mi (64 km) southeast from the San Bernardino Mountains through San Bernardino and Riverside Counties to near the northeast edge of the Salton Sink and Salton Sea.

California's Colorado Desert is a part of the larger Sonoran Desert. It encompasses approximately 7 million acres, including the heavily irrigated Coachella and Imperial valleys. It is home to many unique flora and fauna.

The Sierra Madre is a mountain range primarily in northern Santa Barbara County and extending into northwestern Ventura County in Southern California, western United States. It is a range of the Inner South Coast Ranges group, and is the southernmost reach of the California Coast Ranges, which are themselves part of the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America.

The Laguna Mountains are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges System in eastern San Diego County, southern California. The mountains run in a northwest/southeast alignment for approximately 35 miles (56 km).

The Santa Rosa and San Jacinto Mountains National Monument is a National Monument in southern California. It includes portions of the Santa Rosa and San Jacinto mountain ranges, the northernmost ones of the Peninsular Ranges system. The national monument covers portions of Riverside County, west of the Coachella Valley, approximately 100 miles (160 km) southeast of downtown Los Angeles.

The Morongo Basin is an endorheic basin and valley region located in eastern San Bernardino County, in Southern California.

The Lower Colorado River Valley (LCRV) is the river region of the lower Colorado River of the southwestern United States in North America that rises in the Rocky Mountains and has its outlet at the Colorado River Delta in the northern Gulf of California in northwestern Mexico, between the states of Baja California and Sonora. This north–south stretch of the Colorado River forms the border between the U.S. states of California/Arizona and Nevada/Arizona, and between the Mexican states of Baja California/Sonora.
The Cuyamaca Mountains, locally the Cuyamacas, are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges System, in San Diego County, southern California. The mountain range runs roughly northwest to southeast. The Laguna Mountains are directly adjacent to the east, with Palomar Mountain and Hot Springs Mountain more distant to the north.
The Deadman Hills are a low mountain range in the central Mojave Desert, in San Bernardino County, southern California.
The Volcan Mountains are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges System, located in the East County region of San Diego County, California.
There are 34 routes assigned to the "S" zone of the California Route Marker Program, which designates county routes in California. The "S" zone includes county highways in Imperial, Orange, Riverside, San Diego, and Santa Barbara counties.

San Felipe Valley is an inland valley of the Peninsular Ranges, located in eastern San Diego County, California. Most of the valley is protected within the San Felipe Valley Wildlife Area.