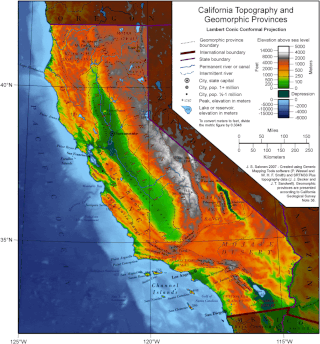
California is a U.S. state on the western coast of North America. Covering an area of 163,696 sq mi (423,970 km2), California is among the most geographically diverse states. The Sierra Nevada, the fertile farmlands of the Central Valley, and the arid Mojave Desert of the south are some of the geographic features of this U.S. state. It is home to some of the world's most exceptional trees: the tallest, most massive, and oldest. It is also home to both the highest and lowest points in the 48 contiguous states.

The Pacific Coast Ranges are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Although they are commonly thought to be the westernmost mountain range of the continental United States and Canada, the geologically distinct Insular Mountains of Vancouver Island lie farther west.
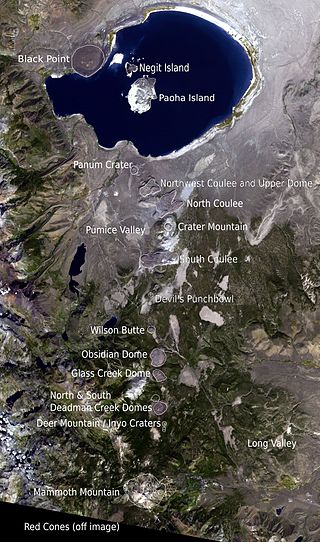
The Mono–Inyo Craters are a volcanic chain of craters, domes and lava flows in Mono County, Eastern California. The chain stretches 25 miles (40 km) from the northwest shore of Mono Lake to the south of Mammoth Mountain. The Mono Lake Volcanic Field forms the northernmost part of the chain and consists of two volcanic islands in the lake and one cinder cone volcano on its northwest shore. Most of the Mono Craters, which make up the bulk of the northern part of the Mono–Inyo chain, are phreatic volcanoes that have since been either plugged or over-topped by rhyolite domes and lava flows. The Inyo volcanic chain form much of the southern part of the chain and consist of phreatic explosion pits, and rhyolitic lava flows and domes. The southernmost part of the chain consists of fumaroles and explosion pits on Mammoth Mountain and a set of cinder cones south of the mountain; the latter are called the Red Cones.

The Santa Ana Mountains are a short peninsular mountain range along the coast of Southern California in the United States. They extend for approximately 61 miles (98 km) southeast of the Los Angeles Basin largely along the border between Orange and Riverside counties.

The Chino Hills are a mountain range on the border of Orange, Los Angeles, and San Bernardino counties, California, with a small portion in Riverside County. The Chino Hills State Park preserves open space and habitat in them.

The Laguna Mountains are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges System in eastern San Diego County, southern California. The mountains run in a northwest/southeast alignment for approximately 35 miles (56 km).

Palomar Mountain is a mountain ridge in the Peninsular Ranges in northern San Diego County. It is famous as the location of the Palomar Observatory and Hale Telescope, and known for the Palomar Mountain State Park.

The Jacumba Mountains are a mountain range of the Peninsular Ranges system, located in eastern San Diego County, Southern California, near the U.S. border with Mexico.

The Vallecito Mountains are located in the Colorado Desert, in eastern San Diego County, Southern California. They are about 28 miles (45 km) north of the U.S. border with Mexico.

The Coast Ranges of California span 400 miles (644 km) from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains.
The Estrella River is a 28.5-mile-long (45.9 km) tributary river in eastern San Luis Obispo County, California. The river forms at the confluence of Cholame Creek, from the north, and San Juan Creek, from the south, near the town of Shandon. From there it flows west-northwest to its confluence with the Salinas River, of which it is a tributary, 8 miles north of Paso Robles. Cholame Creek has its headwaters on the southwest side of Middle Mountain and its tributary, Little Cholame Creek, begins on the northeast side. The creek drains the Cholame Valley, which is bordered by Diablo Range on the east and Cholame Hills, a northern extension of the Temblor Range, on the west. The average precipitation in the area ranges from 11 to 17 inches, increasing northward.

Yamsay Mountain is a large shield volcano in the Cascade Range of south-central Oregon, located about 35 miles (56 km) east of Crater Lake on the border between Klamath County and Lake County. It is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc but is located in a mountain range 30 to 50 miles behind the main Cascade volcanic front. The best known members of this enigmatic arc are the massive shields of Newberry Volcano, about 55 miles (89 km) farther north in Oregon, and Medicine Lake Volcano, about 80 miles (130 km) south in Northern California. Yamsay is the second highest volcano in the eastern arc, almost 300 feet (90 m) higher than Newberry and Medicine Lake.

Cuyamaca Peak is a mountain peak of the Cuyamaca Mountains range, in San Diego County, Southern California.

The Coyote Mountains are a small mountain range in San Diego and Imperial Counties in southern California. The Coyotes form a narrow ESE trending 2 mi (3.2 km) wide range with a length of about 12 mi (19 km). The southeast end turns and forms a 2 mi (3.2 km) north trending "hook". The highest point is Carrizo Mountain on the northeast end with an elevation of 2,408 feet (734 m). Mine Peak at the northwest end of the range has an elevation of 1,850 ft (560 m). Coyote Wash along I-8 along the southeast margin of the range is 100 to 300 feet in elevation. Plaster City lies in the Yuha Desert about 5.5 mi (8.9 km) east of the east end of the range.
The San Felipe Hills are a low mountain range in eastern San Diego County, southern California.

The Vaca Mountains are a mountain range in Napa and Solano Counties, California that is one of the California Coast Ranges. They represent the easternmost of the Inner Coast Ranges in north−central California, and divide the Suisun Valley on their west, from the Sacramento Valley on their east.
There are 34 routes assigned to the "S" zone of the California Route Marker Program, which designates county routes in California. The "S" zone includes county highways in Imperial, Orange, Riverside, San Diego, and Santa Barbara counties.

San Felipe Valley is an inland valley of the Peninsular Ranges, located in eastern San Diego County, California. Most of the valley is protected within the San Felipe Valley Wildlife Area.
The Carrizo Creek and Carrizo Wash in California are a stream and an arroyo that the stream flows into, in San Diego County, California, and Imperial County, California.