
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.

Holocentridae is a family of ray-finned fish, the only family of the order Holocentriformes. The members of the subfamily Holocentrinae are typically known as squirrelfish, while the members of Myripristinae typically are known as soldierfish. In Hawaii, they are known by the Japanese name mempachi/menpachi (メンパチ) or the Hawaiian ʻūʻū.

Sargocentron is a genus of squirrelfish found in tropical parts of the Indian, Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, with the greatest species diversity near reefs in the Indo-Pacific. Being largely or entirely nocturnal, they have relatively large eyes. Red and silvery colours dominate. The preopercle spines are venomous and can give painful wounds. Most have a maximum length of 15–25 cm (6–10 in), but S. iota barely reaches 8 cm (3 in), and S. spiniferum can reach more than 50 cm (20 in).

Hippocampus guttulatus, commonly known as the long-snouted seahorse and in Great Britain as the spiny seahorse, is a marine fish belonging to the family Syngnathidae, native from the northeast Atlantic, including the Mediterranean.

The round scad is a species of fish in the Carangidae. It was described in 1829 by the French naturalist and zoologist, Georges Cuvier. Although the round scad is considered a good food fish, it is mostly caught for use as bait.

The grey gurnard is a species of ray-finned fish from the family Triglidae, the gurnards and sea robins. It is native to the eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Black Sea. It is caught as a food fish and is known for producing sounds. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Eutrigla.

Sargocentron spiniferum, common name sabre squirrelfish, giant squirrelfish and spiny squirrelfish, is a large Indo-Pacific species of squirrelfish belonging to the family Holocentridae.

Holocentrinae is a subfamily of Holocentridae containing 40 recognized species and one proposed species. Its members are typically known as squirrelfish and all are nocturnal. All three genera in the subfamily are found in the Atlantic and Holocentrus is restricted to this ocean. Most species in genera Neoniphon and Sargocentron are from the Indo-Pacific region and several of these occur in the Indian Ocean west of the southern tip of India.

Holocentrus adscensionis is a squirrelfish of the family Holocentridae found in the Atlantic Ocean. Its range extends from North Carolina, USA to Brazil and throughout the Caribbean Sea in the Western Atlantic and from Gabon to Ascension Island in the Eastern Atlantic. A single record was reported in 2016 from the central Mediterranean Sea off Malta.
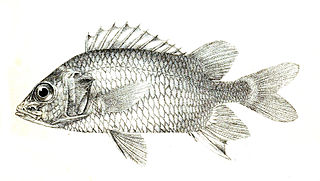
Sargocentron caudimaculatum, the silverspot squirrelfish or whitetail squirrelfish, is a reef-associated member of the family Holocentridae. It is native to the Indian and Pacific Oceans from East Africa to Japan and northern Australia and as far east as the Marshall Islands. It lives near reefs, but can also be found in lagoons and drop-offs at depths between 2 and 40 metres. It is a nocturnal predator, feeding primarily on crabs and shrimps. It can reach sizes of up to 25.0 centimetres (9.8 in) TL. Although it is caught commercially and can be found in the aquarium trade, there are no known major threats to this species.

Sargocentron coruscum, more commonly known as the reef squirrelfish, is a member of the family Holocentridae native to the western Atlantic Ocean from Florida, USA to northern South America. It lives over sandy and rocky substrates, as well as coral reefs, generally between 1 and 30 metres deep. It is a nocturnal predator, feeding primarily on shrimps, but will also eat crabs. It searches for food alone or in small schools. It can reach sizes of up to 15.0 centimetres (5.9 in) TL. When alarmed, it will hide in crevices between corals.

Sargocentron ensifer, or the yellow-striped squirrelfish, is a member of the family Holocentridae. It is native to the Pacific Ocean from southern Japan to New Caledonia, Hawaii and the Pitcairn Islands. It lives in deep reefs at depths between 0 and 64 metres, hiding in crevices by day and foraging for food by night. It feeds on small fishes and crustaceans and can reach sizes of up to 23.0 centimetres (9.1 in) SL, though a length of 15.0 centimetres (5.9 in) TL is more common.
Sargocentron bullisi, more commonly known as the deepwater squirrelfish, is a nocturnal, reef-associated predator of the family Holocentridae. It is native to the West Atlantic from North Carolina, USA to southern Brazil and throughout the Caribbean Sea. It lives 33 to 110 metres below the surface. It can reach sizes of up to 13.0 centimetres (5.1 in) SL.

Sargocentron cornutum, the threespot squirrelfish, is a member of the family Holocentridae native to the western Pacific Ocean from Indonesia to the Great Barrier Reef. It lives in coral reefs and drop-offs between depths of 6–40 m (20–131 ft). It is a nocturnal predator, feeding on crabs and shrimps by night and hiding under ledges or in caves by day. It can reach sizes of up to 27.0 cm (10.6 in) TL and has a venomous preopercle.
The banded seabream is a species of marine fish of the family Sparidae. The species was first described as Sargus fasciatus by Achille Valenciennes in 1830.
The São Tomé clingfish is a species of marine fish of the family Gobiesocidae (clingfish). It grows to 1.4 cm maximal length. It occurs in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, around the islands of São Tomé and Príncipe between 0 and 3 metres depth. The species was first described in 2007 by Ronald Fricke, its specific name honouring the collector of the type, marine biologist Peter Wirtz of Madeira.
Chromis lubbocki is a species of marine fish of the family Pomacentridae. This fish grows to 12.5 cm maximal length. It occurs in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Cape Verde. The specific name honours the marine biologist Hugh Roger Lubbock (1951-1981) who led the Cambridge Expedition to Saint Paul's Rocks, part of the Cape Verde Islands, who collected the type specimen and realised it was a new species.

Pseudupeneus prayensis, the West African goatfish, is a species of goatfish, a marine ray-finned fish from the family Mullidae. This fish grows to 55 cm maximal length. The species name "prayensis" refers to the city Praia, the capital of Cape Verde, the species was described with a type locality of "Port Praya, Cape Verde Islands".

The lesser amberjack, also known as the false amberjack or little amberjack, is a species of ray-finned fish from the family Carangidae, the jacks and pompanos.
Sargocentron poco, the saddle squirrelfish, is a species of squirrelfish belonging to the genus of Sargocentron. It is found in the Western Central Atlantic Ocean from the United States to the Cayman Islands, and in the Bahamas. It may also possibly be found in Cuba. It is likely to be more commonly found inhabiting shelf-edge reefs.
















