Siberia is an extensive geographical region spanning much of Eurasia and North Asia. Siberia has historically been a part of modern Russia since the 16th and 17th centuries.

The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean. With a mean annual discharge of 588 cubic kilometers per year, it is the second largest of the Arctic rivers. It is the largest river whose catchment is entirely within the Russian territorial boundaries. Permafrost underlies most of the catchment, with 77% of the catchment containing continuous permafrost.

The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy Cape. The Kara Sea lies to the west, the East Siberian Sea to the east.

The Argun or Ergune is a 1,621 kilometres (1,007 mi) river that forms part of the eastern China–Russia border, together with the Amur River. Its upper reaches are known as Hailar River in China. The Ergune marks the border between Russia and China for about 944 kilometres (587 mi), until it meets the Amur River.

The Indigirka River is a river in the Sakha Republic in Russia between the Yana River and the Kolyma River. It is 1,726 kilometres (1,072 mi) long. The area of its basin is 360,000 square kilometres (140,000 sq mi). The river flows into the Kolyma Bay, East Siberian Sea. It freezes up in October and stays under the ice until May–June.

The Yana River, is a river in Sakha in Russia, located between the Lena to the west and the Indigirka to the east.
The Poles of Cold are the places in the southern and northern hemispheres where the lowest air temperatures have been recorded.

The Chersky Range is a chain of mountains in northeastern Siberia between the Yana River and the Indigirka River. It generally runs from northwest to southeast through the Sakha Republic and Magadan Oblast. The highest peak in the range is Peak Pobeda, which is 3,003 meters tall. The range lies on the boundary between the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates. The Chersky mountains, along with the neighboring Verkhoyansk Range, have a moderate effect on the climate of Siberia. The ridges obstruct west-moving air flows, decreasing the amount of snowfall in the plains to the west.
The Kuma is an 802-kilometre (498 mi) long river on the Black Sea-Caspian Steppe of southern Russia. It flows northeast into the Caspian Sea. Its drainage basin covers 33,500 square kilometres (12,900 sq mi). Its source is in the Greater Caucasus, in the republic Karachay-Cherkessia, west of Kislovodsk. It flows in northeastern direction, through Stavropol Krai and further east through the Caspian Depression as the natural border between Kalmykia and Dagestan. That part of the Kuma's valley forms the eastern part of the Kuma–Manych Depression, separating the East European Plain from the Caucasus region. The Kuma flows into the Kizlyar Gulf of the Caspian Sea near the border between Dagestan and Kalmykia.

Uvs Lake Basin is an endorheic basin located on the territorial border of Mongolia and Tuva, a republic of the Russian Federation. The basin is part of the Central Asian Internal Drainage Basin and is named after Uvs Lake, a large saline lake situated in the western part of its drainage basin. Uvs Lake is a shallow lake with an area of 3,350 km2 (1,290 sq mi). Its entire basin, which includes several smaller lakes, is 70,000 km2 (27,000 sq mi).
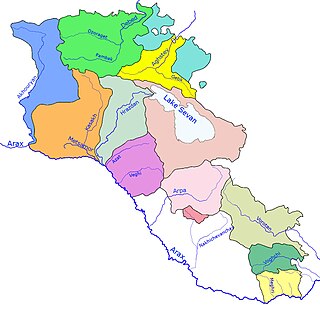
Aghstev River is a river in Armenia and Azerbaijan, and is a right tributary of the Kura River.

The Arsenyevka River is a left tributary of the Ussuri River in Anuchinsky and Yakovlevsky Districts of Primorsky Krai, Russia.

Dwórzno is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Górowo Iławeckie, within Bartoszyce County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, close to the border with the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. It lies approximately 3 kilometres (2 mi) south-west of Górowo Iławeckie, 22 km (14 mi) west of Bartoszyce, and 52 km (32 mi) north of the regional capital Olsztyn.

Wilczyny is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Srokowo, within Kętrzyn County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland, close to the border with the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia. It lies approximately 6 kilometres (4 mi) north-west of Srokowo, 20 km (12 mi) north of Kętrzyn, and 82 km (51 mi) north-east of the regional capital Olsztyn.
The Kanhar River is a tributary of the Son River and flows through the India states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh.
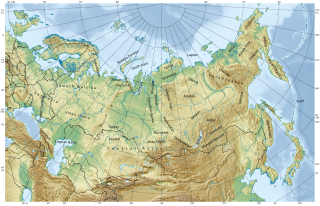
The geology of Russia, the world's largest country, which extends over much of northern Eurasia, consists of several stable cratons and sedimentary platforms bounded by orogenic (mountain) belts.
The Allakh-Yun is a river in Sakha Republic and Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It is a right tributary of the Aldan River.

Dulgalakh is a river in Yakutia, a left tributary of the Yana River. Its length is 507 km (315 mi) and its basin size 27,300 square kilometres (10,541 sq mi).