Related Research Articles

In electrical engineering,a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit,or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core,which induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction,discovered in 1831,describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil.

Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material,component or system without causing damage. The terms nondestructive examination (NDE),nondestructive inspection (NDI),and nondestructive evaluation (NDE) are also commonly used to describe this technology. Because NDT does not permanently alter the article being inspected,it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation,troubleshooting,and research. The six most frequently used NDT methods are eddy-current,magnetic-particle,liquid penetrant,radiographic,ultrasonic,and visual testing. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering,mechanical engineering,petroleum engineering,electrical engineering,civil engineering,systems engineering,aeronautical engineering,medicine,and art. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical imaging,including on echocardiography,medical ultrasonography,and digital radiography.

Magnetic particle inspection (MPI) is a nondestructive testing process where a magnetic field is used for detecting surface,and shallow subsurface,discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials. Examples of ferromagnetic materials include iron,nickel,cobalt,and some of their alloys. The process puts a magnetic field into the part. The piece can be magnetized by direct or indirect magnetization. Direct magnetization occurs when the electric current is passed through the test object and a magnetic field is formed in the material. The magnetic lines of force are perpendicular to the direction of the electric current,which may be either alternating current (AC) or some form of direct current (DC). Indirect magnetization occurs when no electric current is passed through the test object,but a magnetic field is applied from an outside source.

In pipeline transportation,pigging is the practice of using pipeline inspection gauges or gadgets,devices generally referred to as pigs or scrapers,to perform various maintenance operations. This is done without stopping the flow of the product in the pipeline.
Eddy-current testing is one of many electromagnetic testing methods used in nondestructive testing (NDT) making use of electromagnetic induction to detect and characterize surface and sub-surface flaws in conductive materials.
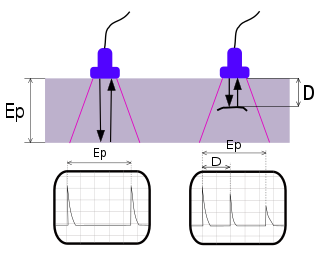
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications,very short ultrasonic pulse waves with centre frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz and occasionally up to 50 MHz,are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement,which tests the thickness of the test object,for example,to monitor pipework corrosion and erosion. Ultrasonic testing is extensively used to detect flaws in welds.
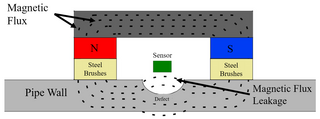
Magnetic flux leakage is a magnetic method of nondestructive testing to detect corrosion and pitting in steel structures,for instance:pipelines and storage tanks. The basic principle is that the magnetic field "leaks" from the steel at areas where there is corrosion or missing metal. To magnetize the steel,a powerful magnet is used. In an MFL tool,a magnetic detector is placed between the poles of the magnet to detect the leakage field. Analysts interpret the chart recording of the leakage field to identify damaged areas and to estimate the depth of metal loss.
Electromagnetic testing (ET),as a form of nondestructive testing,is the process of inducing electric currents or magnetic fields or both inside a test object and observing the electromagnetic response. If the test is set up properly,a defect inside the test object creates a measurable response.
Geophysical survey is the systematic collection of geophysical data for spatial studies. Detection and analysis of the geophysical signals forms the core of Geophysical signal processing. The magnetic and gravitational fields emanating from the Earth's interior hold essential information concerning seismic activities and the internal structure. Hence,detection and analysis of the electric and Magnetic fields is very crucial. As the Electromagnetic and gravitational waves are multi-dimensional signals,all the 1-D transformation techniques can be extended for the analysis of these signals as well. Hence this article also discusses multi-dimensional signal processing techniques.

Rail inspection is the practice of examining rail tracks for flaws that could lead to catastrophic failures. According to the United States Federal Railroad Administration Office of Safety Analysis,track defects are the second leading cause of accidents on railways in the United States. The leading cause of railway accidents is attributed to human error. The contribution of poor management decisions to rail accidents caused by infrequent or inadequate rail inspection is significant but not reported by the FRA,only the NTSB. Every year,North American railroads spend millions of dollars to inspect the rails for internal and external flaws. Nondestructive testing (NDT) methods are used as preventive measures against track failures and possible derailment.
An electromagnetic acoustic transducer (EMAT) is a transducer for non-contact acoustic wave generation and reception in conducting materials. Its effect is based on electromagnetic mechanisms,which do not need direct coupling with the surface of the material. Due to this couplant-free feature,EMATs are particularly useful in harsh,i.e.,hot,cold,clean,or dry environments. EMATs are suitable to generate all kinds of waves in metallic and/or magnetostrictive materials. Depending on the design and orientation of coils and magnets,shear horizontal (SH) bulk wave mode,surface wave,plate waves such as SH and Lamb waves,and all sorts of other bulk and guided-wave modes can be excited. After decades of research and development,EMAT has found its applications in many industries such as primary metal manufacturing and processing,automotive,railroad,pipeline,boiler and pressure vessel industries,in which they are typically used for nondestructive testing (NDT) of metallic structures.
Robotic non-destructive testing (NDT) is a method of inspection used to assess the structural integrity of petroleum,natural gas,and water installations. Crawler-based robotic tools are commonly used for in-line inspection (ILI) applications in pipelines that cannot be inspected using traditional intelligent pigging tools.
Electromagnetically induced acoustic noise,electromagnetically excited acoustic noise,or more commonly known as coil whine,is audible sound directly produced by materials vibrating under the excitation of electromagnetic forces. Some examples of this noise include the mains hum,hum of transformers,the whine of some rotating electric machines,or the buzz of fluorescent lamps. The hissing of high voltage transmission lines is due to corona discharge,not magnetism.

Radovan Stojanović is the Professor of Electrical Engineering at the University of Montenegro,Montenegro and Founder and President of the Montenegrin Association for New Technologies (MANT). He is a member of the Board of the Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts for Natural and Technical Sciences.
Massood Tabib-Azar is an Iranian-American electrical engineer,researcher and academic. He is a USTAR Professor of Electrical Engineering in the University of Utah and an Editor of IEEE Electron Device Letters.
Mahta Moghaddam is an Iranian-American electrical and computer engineer and William M. Hogue Professor of Electrical Engineering in the Ming Hsieh Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering. Moghaddam is also the president of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society and is known for developing sensor systems and algorithms for high-resolution characterization of the environment to quantify the effects of climate change. She also has developed innovative tools using microwave technology to visualize biological structures and target them in real-time with high-power focused microwave ablation.

Mohamad Sawan is a Canadian-Lebanese electrical engineer,academic and researcher. He is a Chair Professor at Westlake University,China,and an Emeritus Professor of Electrical Engineering at Polytechnique Montréal,Canada.
Lalita Udpa is University Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Michigan State University. She was educated in India and the US,and focuses her research on nondestructive testing,including the inspection of aircraft and pipelines.
References
- ↑ "Reunion of 1971-1975 Alumni". Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad. December 2024. Retrieved 2025-01-30.
- 1 2 "Satish S. Udpa–Michigan State University".
- 1 2 "Satish Udpa–Michigan State University".
- 1 2 "Honorifics".
- 1 2 "Satish S. Udpa–Who's Who Top Educators".
- ↑ "College of Fellows-The Engineering Society of Detroit".
- 1 2 "Fellows List–National Academy of Inventors".
- ↑ "ASNT Board of Directors".
- ↑ "Satish Udpa–IEEE Xplore".
- ↑ "Thomas M. Whitney Professorship in Electrical and Computer Engineering".
- ↑ "Invariance transformations for magnetic flux leakage signals".
- ↑ "Adaptive Wavelets for Characterizing Magnetic Flux Leakage Signals from Pipeline inspection".
- ↑ "Apparatus and method for driving an ultrasonic transducer".
- ↑ "Rotating field transceiver nondestructive inspection probe".
- ↑ "Apparatus for detecting surface flaws in cylindrical articles".
- ↑ "Rotating Current Excitation with Array Magnetic Sensors Nondestructive Testing Probe For Tube Inspection".