
Wolf spiders are members of the family Lycosidae, from the Ancient Greek word "λύκος" meaning "wolf". They are robust and agile hunters with excellent eyesight. They live mostly in solitude and hunt alone, and do not spin webs. Some are opportunistic hunters pouncing upon prey as they find it or even chasing it over short distances. Some wait for passing prey in or near the mouth of a burrow.

Selenocosmia crassipes, synonym Phlogius crassipes, also known as the "Queensland whistling tarantula" is a species of tarantula native to the east coast of Queensland, Australia. The name "whistling tarantula" comes from its ability to produce a hissing noise when provoked, a trait it shares with other Australian theraphosids. This hissing is produced by the spider stridulating a patch of setae associated with its chelicerae. It has also been called the "eastern tarantula". The species name crassipes is Latin for "fat leg" referring to the relatively fat front legs.

Pancorius is a genus of Asian jumping spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1902. They are similar to Hyllus.
Hysterocrates crassipes is a species of spiders in the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas) found in Cameroon, Africa.

Sexual selection in spiders shows how sexual selection explains the evolution of phenotypic traits in spiders. Male spiders have many complex courtship rituals and have to avoid being eaten by the females, with the males of most species survive a few matings, and having short life spans.

Schizocosa is a genus wolf spider containing around 60 species, distributed in North and South America, Africa, and East and Southeast Asia.
Schizocosa saltatrix is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae. It is found in North America.
Metepeira crassipes is a species of orb weaver in the spider family Araneidae. It is found in the United States and Mexico.
Schizocosa retrorsa is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae. It is found in the United States and Mexico.

Xestoleptura crassipes is a species of flower longhorn in the beetle family Cerambycidae. It is found in North America.
Schizocosa bilineata is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae. It is found in the United States and Canada.
Eisonyx crassipes is a species of flower weevil in the beetle family Curculionidae. It is found in North America.
Eisonyx is a genus of flower weevils in the beetle family Curculionidae. There are at least three described species in Eisonyx.
Pilophorus crassipes is a species of plant bug in the family Miridae. It is found in Central America and North America.
Schizocosa avida is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae. It is found in North America.
Schizocosa minnesotensis is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae. It is found in the United States and Canada.
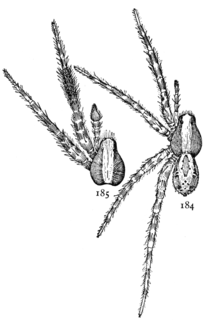
Schizocosa ocreata is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae that is found in North America. The Schizocosa ocreata is a spider that is most commonly known as the “brush-legged wolf spider” because of their distinct dark-colored fur-like coverings around their legs. The S. ocreata are commonly found in North American states, usually in the middle and eastern United States.

Schizocosa mccooki is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae. It is found in North America.
Schizocosa crassipalpata is a species of wolf spider in the family Lycosidae. It is found in the United States and Canada.
Schizocosa stridulans is a sibling species of S. ocreata and S. rovneri and is part of the wolf spider family. The name of the genus comes from the epigynum structure being lycosid and having a split T excavation. This spider is well-known for its specific leg ornamentation and courtship rituals and that is how it has been differentiated from its related species. The S. stridulans take systematic steps during its courtship ritual, which involves two independent signals. More specifically, female spiders will leave silk and pheromones to communicate that they are ready to mate.








