
Sphaerites is a genus of beetles, the only genus in the family Sphaeritidae, sometimes called the false clown beetles. It is closely related to the clown beetles but with distinct characteristics. There are four known species, widespread in temperate area but not commonly seen.

Fistulina hepatica is an unusual bracket fungus classified in the Agaricales, that is commonly seen in Britain, but can be found in North America, Australia, North Africa, Southern Africa and the rest of Europe. As its name suggests, it looks remarkably similar to a slab of raw meat. It has been used as a meat substitute in the past, and can still be found in some French markets. It has a sour, slightly acidic taste. For eating it must be collected young and it may be tough and need long cooking.
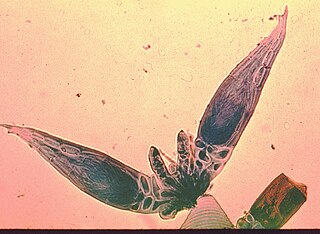
The Laboulbeniomycetes are a unique group of fungi that are apparent external parasites of insects and other arthropods, both terrestrial and aquatic. These fungi are minute; their fruiting bodies commonly measure less than one millimeter. They live on the antennae, the mouthparts or other body regions of their arthropod hosts. Although several species of Laboulbeniomycetes have more or less extensive, root-like hyphal systems (haustoria) inside their hosts, as a group these fungi are apparently harmless to the animals they live on. These fungi are usually apparent only on adult hosts; apparently immature arthropods eliminate them during ecdysis. Some fungi in the Laboulbeniomycetes have separate female and male individuals, like Herpomyces.

Schizophyllum commune is a species of fungus in the genus Schizophyllum. The mushroom resembles undulating waves of tightly packed corals or loose chinese fan. ”Gillies” or Split Gills vary from creamy yellow to pale white in colour. The cap is small, 1-4.5 cm wide with a dense yet spongey body texture. It is known as the split-gill mushroom because of the unique longitudinally divided nature of the gill producing basidospores, which often splits when they dry out and moistened into gills as they shed into spores. It is the only known fungi capable of retracting by movement. This mushroom is found predominantly in Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Madagascar, Nigeria and Northeastern India. It is found in the wild on decaying trees after rainy seasons followed by dry spells where the mushrooms are naturally collected. It is known for its high medicinal value and aromatic taste profile. It has recently attracted the medicinal industry for its immunomodulatory, antifungal, antineoplastic and antiviral activities that are higher than those of any other glucan complex carbohydrate.
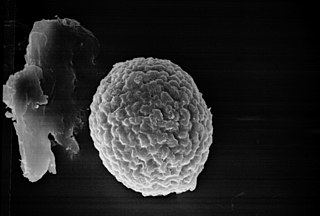
Tilletia is a genus of smut fungi in the Tilletiaceae family. Species in this genus are plant pathogens that affect various grasses. Tilletia indica, which causes Karnal bunt of wheat, and Tilletia horrida, responsible for rice kernel smut, are examples of species that affect economically important crops.
Verpa is a genus of ascomycete fungi related to the morels. Resembling the latter genus, they are called false or early morels. There are five species in the widespread genus.

The Helotiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Helotiales. The distribution of species in the family are widespread, and typically found in tropical areas. There are 117 genera and 826 species in the family.

The Sphaerophoraceae are a family of lichenized fungi in the order Lecanorales. Species of this family have a widespread distribution, especially in southern temperate regions. The genus contains 5 genera and 32 species.

Sowerbyella is a genus of fungi in the family Pyronemataceae. The genus has a widespread distribution, and contains 16 species found mostly in Europe and China.
Acaulospora is a genus of fungi in the family Acaulosporaceae. Species in this genus are widespread in distribution, and form arbuscular mycorrhiza and vesicles in roots.

Gymnopus is a genus of fungus in the family Marasmiaceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains about 300 species.
M. communis may refer to:

Gilled fungi with laterally-attached fruiting bodies are said to be pleurotoid. Pleurotoid fungi are typically wood-decay fungi and are found on dead and dying trees and coarse woody debris. The pleurotoid form is polyphyletic, having evolved a number of times within the Basidiomycota. Many species of pleurotoid fungi are commonly referred to as "oyster" mushrooms. Laterally-attached fungi with pores rather than gills are referred to as bracket fungi.

Tuber is a genus in the Tuberaceae family of fungi. It includes several species of truffles that are highly valued as delicacies. According to a standard reference text, the widespread genus contains 86 species.
Stenella is a genus of anamorphic fungi in the family Mycosphaerellaceae. The widespread genus contains about 155 species.
John "Red" Raper was a mycologist who studied genetic control of sexuality in fungi, mating type compatibility, fungal genetics, and taught at Harvard University among other places.
Louis Charles Christopher Krieger was an American mycologist and botanical illustrator who was considered the finest painter of North American fungi.

David Hunt Linder (1899–1946) was an American mycologist known for his work on the Helicosporous fungi and his dedications for the advancement of mycological knowledge. He curated the Farlow Herbarium of Cryptogamic Botany at Harvard University and founded a highly respected journal Farlowia.

Clambidae is a family of beetles. They are known commonly as the minute beetles or the fringe-winged beetles. They are found worldwide on every continent except Antarctica.














