
The Jungfrau Railway is a mountain rack railway in the Bernese Alps, Switzerland, connecting Kleine Scheidegg in the Bernese Oberland to the Jungfraujoch, across the Valais border. It is the highest railway in Switzerland and Europe, running 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) from the station of Kleine Scheidegg to the Jungfraujoch, well above the perennial snow line. As a consequence, the railway runs essentially within the Jungfrau Tunnel, built into the neighbouring Eiger and Mönch, to protect the line from snow and extreme weather.

The Wengernalp Railway is a 19.11 kilometres (11.87 mi) long rack railway line in Switzerland. It runs from Lauterbrunnen to Grindelwald via Wengen and Kleine Scheidegg, making it the world's longest continuous rack and pinion railway. The name refers to the alpine meadow of Wengernalp, above Wengen.

The Jungfrau, at 4,158 meters (13,642 ft) is one of the main summits of the Bernese Alps, located between the northern canton of Bern and the southern canton of Valais, halfway between Interlaken and Fiesch. Together with the Eiger and Mönch, the Jungfrau forms a massive wall of mountains overlooking the Bernese Oberland and the Swiss Plateau, one of the most distinctive sights of the Swiss Alps.

The Harderbahn (HB) is one of two funiculars that operate from the town of Interlaken. The Harderbahn leads to the western end of the Harder in the north of Interlaken across the river Aare, in Switzerland.

Grindelwald is a village and municipality in the Interlaken-Oberhasli administrative district in the canton of Berne. In addition to the village of Grindelwald, the municipality also includes the settlements of Alpiglen, Burglauenen, Grund, Itramen, Mühlebach, Schwendi, Tschingelberg and Wargistal.

The Bernese Oberland Railway is a narrow-gauge mountain railway in the Bernese Oberland region of Switzerland. It runs, via a "Y" junction at Zweilütschinen to serve Lauterbrunnen and Grindelwald from Interlaken. The railway is rack assisted.

The Lauterbrunnen–Mürren Mountain Railway is a hybrid transport system in the Bernese Oberland area of Switzerland, which connects the villages of Lauterbrunnen and Mürren. The system consists of a connected aerial cableway, also known as the Grütschalpbahn, and an adhesion worked mountain railway. The cableway replaced a funicular, on the same route, in 2010.

The Jungfraujoch is a saddle connecting two major 4000ers of the Bernese Alps: the Jungfrau and the Mönch. It lies at an elevation of 3,463 metres (11,362 ft) above sea level and is directly overlooked by the rocky prominence of the Sphinx. The Jungfraujoch is a glacier saddle, on the upper snows of the Aletsch Glacier, and part of the Jungfrau-Aletsch area, situated on the boundary between the cantons of Bern and Valais, halfway between Interlaken and Fiesch.

The Bernese Oberland, sometimes also known as the Bernese Highlands, is the highest and southernmost part of the canton of Bern. It is one of the canton's five administrative regions. It constitutes the Alpine region of the canton and the northern side of the Bernese Alps, including many of its highest peaks, among which the Finsteraarhorn, the highest in both range and canton.

Wilderswil railway station is a railway station in the village and municipality of Wilderswil in the Swiss canton of Bern. The station is on the Berner Oberland Bahn, whose trains operate services to Interlaken Ost, Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen. It is also the valley terminus of the Schynige Platte Railway, whose trains operate to the Schynige Platte and are stabled at a depot bordering the station.

The Schynige Platte is a small mountain ridge and a viewpoint in the Bernese Highlands and belongs to the Schwarzhorn group. The mountain range consists of three peaks: Gumihorn, Tuba, and the closest summit next to the viewpoint, Geiss. The viewpoint lies at an altitude of about 2,000 metres (7,000 ft), at the western end of a prominent ridge of the Schwarzhorn group, which separates the valley of the Schwarze Lütschine from Lake Brienz.

Lauterbrunnen is a railway station in the village and municipality of Lauterbrunnen in the Swiss canton of Bern. The station is on the Berner Oberland Bahn (BOB), whose trains operate services to Interlaken Ost. It is also the valley terminus of the Wengernalpbahn (WAB), whose trains operate to Kleine Scheidegg via Wengen, and of the Bergbahn Lauterbrunnen-Mürren (BLM), whose hybrid cable car and rail link runs to Mürren. Before 2006, this was a funicular.

Lütschental railway station is a railway station in the village and municipality of Lutschental in the Swiss canton of Bern. The station is on the Berner Oberland Bahn, whose trains operate services to Interlaken Ost and Grindelwald.

Kleine Scheidegg is a railway station and hub that is situated on the summit of Kleine Scheidegg, a mountain pass in the Bernese Oberland region of Switzerland. The pass, located between the Lauberhorn and the Eiger's ridge, houses a complex of hotels and railway buildings. Administratively, the station is in the municipality of Lauterbrunnen in the canton of Bern, a few metres from the border with the municipality of Grindelwald.

Grindelwald Grund is a railway station in the village and municipality of Grindelwald in the Swiss canton of Bern. The station is served by the Wengernalpbahn (WAB), whose trains operate from Grindelwald to Kleine Scheidegg. It takes its name from the Grund area of the village, in which it is located.

Eigergletscher is a railway station in the municipality of Lauterbrunnen in the canton of Bern. The station is served by trains of the Jungfrau railway, which run to the Jungfraujoch from Kleine Scheidegg, where they connect with services from Interlaken, Lauterbrunnen, Wengen and Grindelwald via the Bernese Oberland railway and the Wengernalp railway.

Jungfraujoch is an underground railway station situated near the Jungfraujoch, in the canton of Valais, a few metres from the border with the canton of Bern. At 3,454 metres (11,332 ft) above sea level, it is the terminus of the Jungfrau Railway and the highest railway station in Switzerland and Europe. The Jungfrau Railway runs from Kleine Scheidegg in the Bernese Oberland, through the Jungfrau Tunnel and crosses the border between the two cantons shortly before the terminus.

Schynige Platte is a railway station that is the upper terminus of the Schynige Platte railway, a rack railway that connects Wilderswil with the Schynige Platte mountain in the Bernese Oberland region of Switzerland. The Schynige Platte alpine botanical garden is accessed from the station, whilst a mountain hotel and restaurant is nearby.

The Schynige Platte Alpine Garden is a botanical garden located at an altitude of about 2,000 metres (7,000 ft), near the summit of the Schynige Platte mountain in the Bernese Oberland region of Switzerland. It specialises in research into the high altitude flora of Switzerland, and has a display of over 600 species of plants native to the Swiss Alps. The garden is run by the Schynige Platte Alpine Garden Society, working closely with the Botanical Garden of Bern and the Institute for Plant Sciences at the University of Bern.
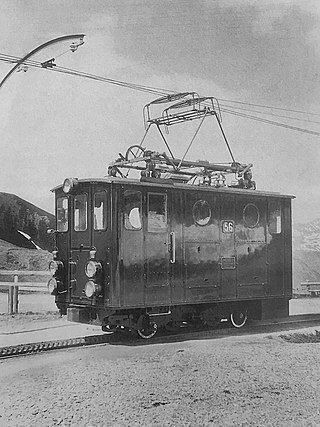
The He 2/2 51 to 58 of the Wengernalp Railway, abbreviated WAB, are electric rack railway locomotive for 1500 volt direct current and a track gauge of 800 mm. They were built in 1909 and 1910 on the occasion of the electrification of the railway lines Lauterbrunnen–Wengernalp–Kleine Scheidegg as well as Grindelwald–Grindelwald Grund–Kleine Scheidegg and served as a model for the largely identical locomotives that were subsequently procured He 2/2 59 to 63.







































