
Millets are a group of highly variable small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets also belong to various other taxa.

Eleusine coracana, or finger millet, also known as ragi in India, kodo in Nepal, is an annual herbaceous plant widely grown as a cereal crop in the arid and semiarid areas in Africa and Asia. It is a tetraploid and self-pollinating species probably evolved from its wild relative Eleusine africana.

Pearl millet is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and suggested area of domestication, for the crop is in the Sahel zone of West Africa. Recent archaeobotanical research has confirmed the presence of domesticated pearl millet on the Sahel zone of northern Mali between 2500 and 2000 BC.
Common millet is a common name for several plants and may refer to:

Foxtail millet, scientific name Setaria italica, is an annual grass grown for human food. It is the second-most widely planted species of millet, and the most grown millet species in Asia. The oldest evidence of foxtail millet cultivation was found along the ancient course of the Yellow River in Cishan, China, carbon dated to be from around 8,000 years before present. Foxtail millet has also been grown in India since antiquity.

Echinochloa is a very widespread genus of plants in the grass family and tribe Paniceae. Some of the species are known by the common names barnyard grass or cockspur grass.

Peronosporaceae are a family of water moulds that contains 21 genera, comprising more than 600 species. Most of them are called downy mildews.
Glomerella graminicola is an economically important crop parasite affecting both wheat and maize where it causes the plant disease Anthracnose Leaf Blight.

Setaria is a widespread genus of plants in the grass family. The name is derived from the Latin word seta, meaning "bristle" or "hair", which refers to the bristly spikelets.
Panicum mosaic virus (PMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA viral pathogen that infects plant species in the panicoid tribe of the grass family, Poaceae. The pathogen was first identified in Kansas in 1953 and most commonly causes disease on select cultivars of turf grass, switchgrass, and millet. The disease most commonly associated with the panicum mosaic virus pathogen is St. Augustine Decline Syndrome, which infects species of turf grass and causes chlorotic mottling. In addition to St. Augustine Decline, panicum mosaic virus is responsible for chlorotic streaking and mild green mosaicking in select cultivars of switchgrass and millet.

Panicum antidotale Retz. is a tall, coarse, woody perennial grass throughout the Himalaya and the Upper Gangetic Plain and specifically in various regions of the Indian state of Punjab and the Pakistan province of Punjab and the neighbouring areas of these regions. The plant has strong spreading rhizomes.
Hallur is an archaeological site located in the Haveri district, in the Indian state of Karnataka. Hallur, South India's earliest Iron Age site, lies in a semi-arid region with scrub vegetation, located on the banks of the river Tungabhadra. The site is a low mound about 6.4 m high. The site was first discovered by Nagaraja Rao in 1962, and excavated in 1965. Further sampling was carried out in the late 1990s for the recovery of archaeobotanical evidence and new high precision radiocarbon dates

Setaria viridis is a species of grass known by many common names, including green foxtail, green bristlegrass, and wild foxtail millet. It is sometimes considered a subspecies of Setaria italica. It is native to Eurasia, but it is known on most continents as an introduced species and is closely related to Setaria faberi, a noxious weed. It is a hardy grass which grows in many types of urban, cultivated, and disturbed habitat, including vacant lots, sidewalks, railroads, lawns, and at the margins of fields. It is the wild antecedent of the crop foxtail millet.
Commonly known as Philippine downy mildew, this disease is caused by the species Peronosclerospora philippinensis of the fungal-like protist class Oomycetes, which also has members such as water molds and Phytophthora infestans, which caused the potato blight that led to the Great Irish famine.
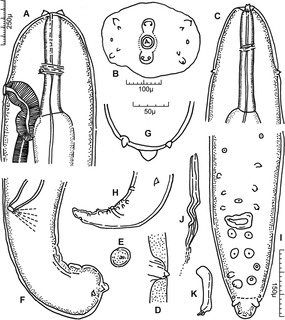
Setaria is a genus of parasitic roundworms that infect domesticated mammals such as pigs, camels, cattle and horses. Some species also infect wild mammals such as deer and antelope. The genus consists of about 43 species. Members of the genus are uniquely parasites in the abdominal cavity of the body. They are mostly large-sized roundworms, possessing an elaborate head (cephalic) region that is characterised by spines, presence of four lips, and well-guarded mouth. Little is known about their pathogenic effects, but some are known to affect nervous system and eye. The larval infective forms are transmitted from one animal to another by the bite of mosquitoes and flies. In addition Setaria marshalli can be transmitted from the womb to new-born calf.
Setaria cervi is a species of parasitic roundworms belonging to the genus Setaria. It infects cattle, bison, yak, reindeer, buffalo, moose, and sheep all over the world. It is most prevalent in Europe and Asia. Different species of Aedes mosquito can transmit the filarial worm. Stable fly Haematobia stimulans is the major vector. The mature roundworms are primarily present in the abdominal (peritoneal) cavity, but are capable of migrating to central nervous system causing serious neurological disease.

Atherigona is a genus of flies in the family Muscidae.
Atherigona pulla, the proso millet shoot fly, is a species of fly in the family Muscidae. The larvae feed on the central growing shoots of crops such as proso millet and little millet. It is found in South Asia.
Atherigona atripalpis, the foxtail millet shoot fly, is a species of fly in the family Muscidae. It is found in East Asia and South Asia. Its host range includes the Setaria species Setaria italica, Setaria glauca, and Setaria plicata.









