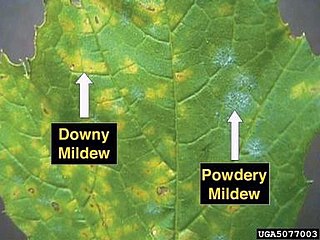
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spores are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant.

A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions often have a centre of necrosis. Symptoms can overlap across causal agents, however differing signs and symptoms of certain pathogens can lead to the diagnosis of the type of leaf spot disease. Prolonged wet and humid conditions promote leaf spot disease and most pathogens are spread by wind, splashing rain or irrigation that carry the disease to other leaves.

The soybean cyst nematode (SCN), Heterodera glycines, is the most devastating pest to soybean crop yields in the U.S., targeting the roots of soybean and other legume plants. When infection is severe SCNs cause stunting, yellowing, impaired canopy development, and yield loss. The symptoms caused by SCNs can go easily unrecognized by farmers—in some cases there are no warning symptoms before a loss of 40% of the yield. Due to the slight stunting and yellowing, many farmers may mistake these symptoms as environmental problems when in fact they are SCNs. Another symptom of SCNs that may affect farmers' yields is stunted roots with fewer nitrogen-fixing nodules. Due to the fact that soybean cyst nematodes can only move a few centimeters in the soil by themselves, they mostly are spread via tillage or plant transplants. This area of infection will look patchy and nonuniform making diagnosis more difficult for farmers. They can be seen in the roots of summer soybean plants if the roots are taken out very carefully and gently washed with water. The egg masses should be seen as bright white or yellow "pearls" on the roots. The later the roots are pulled the harder it will be to diagnose due to the SCNs female dying and turning a much darker color, forming a "cyst". The best way to know if a field is infected by soybean cyst nematodes is to take a soil sample to a nematologist.

Pyrenophora tritici-repentis (teleomorph) and Drechslera tritici-repentis (anamorph) is a necrotrophic plant pathogen of fungal origin, phylum Ascomycota. The pathogen causes a disease originally named yellow spot but now commonly called tan spot, yellow leaf spot, yellow leaf blotch or helminthosporiosis. At least eight races of the pathogen are known to occur based on their virulence on a wheat differential set.
Mycoleptodiscus terrestris is a fungal plant pathogen.

Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a plant pathogenic fungus and can cause a disease called white mold if conditions are conducive. S. sclerotiorum can also be known as cottony rot, watery soft rot, stem rot, drop, crown rot and blossom blight. A key characteristic of this pathogen is its ability to produce black resting structures known as sclerotia and white fuzzy growths of mycelium on the plant it infects. These sclerotia give rise to a fruiting body in the spring that produces spores in a sac which is why fungi in this class are called sac fungi (Ascomycota). This pathogen can occur on many continents and has a wide host range of plants. When S. sclerotiorum is onset in the field by favorable environmental conditions, losses can be great and control measures should be considered.

Corynespora cassiicola is a species of fungus well known as a plant pathogen. It is a sac fungus in the family Corynesporascaceae. It is the type species of the genus Corynespora.
Calonectria ilicicola is a fungal plant pathogen in the family Nectriaceae. It has been found to cause leaf spot in holly, root rot in blueberry, red crown rot in soybean, a root and crown rot of anthurium, and a soft rot of ginger.
Colletotrichum truncatum is a fungal species and plant pathogen on soybeans.

Fusarium solani is a species complex of at least 26 closely related filamentous fungi in the division Ascomycota, family Nectriaceae. It is the anamorph of Nectria haematococca. It is a common soil fungus and colonist of plant materials. Fusarium solani is implicated in plant disease as well as human disease notably infection of the cornea of the eye.

Cercospora sojina is a fungal plant pathogen which causes frogeye leaf spot of soybeans. Frog eye leaf spot is a major disease on soybeans in the southern U.S. and has recently started to expand into the northern U.S. where soybeans are grown. The disease is also found in other soybean production areas of the world.
Diaporthe phaseolorum var. caulivora is a fungal plant pathogen which infects soybean, causing soybean stem canker.
Cercospora kikuchii is a fungal plant pathogen that affects soybeans. It results in both the Cercospora leaf blight and purple seed stain diseases on soybean and is found almost worldwide. C. kikuchii produces the toxin cercosporin, as do a number of other Cercospora species.
Microsphaera diffusa is a plant pathogen. M. diffusa infections on soybeans are referred to as powdery mildew.

Diaporthe phaseolorum var. sojae is a plant pathogen infecting soybean and peanut.
Phyllosticta sojaecola is a plant pathogen infecting soybean.
Phialophora gregata is a Deuteromycete fungus that is a plant pathogen which causes the disease commonly known as brown stem rot of soybean. P. gregata does not produce survival structures, but has the ability to overwinter as mycelium in decaying soybean residue.
Bean pod mottle virus, or BPMV, is a species of plant pathogenic virus in the family Secoviridae. It is known to infect soybean crops.
This article summarizes different crops, what common fungal problems they have, and how fungicide should be used in order to mitigate damage and crop loss. This page also covers how specific fungal infections affect crops present in the United States.
Sudden death syndrome (SDS), a disease in soybean plants, quickly spread across the southern United States in the 1970s, eventually reaching most agricultural areas of the US. SDS is caused by multiple Fusarium fungi in the Fusariumsolani complex. Fusarium virguliforme is the sole causal agent in North America. In South America, Fusarium brasiliense, F. cuneirostrum, F. tucumaniae, and F. virguliforme are all causal agents. Losses could exceed hundreds of millions of dollars in US soybean markets alone making it one of the most important diseases found in Soybeans across the US.








