
A municipality is usually a single urban administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. It is to be distinguished (usually) from the county, which may encompass rural territory or numerous small communities such as towns, villages and hamlets.

A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town, with a population ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement.
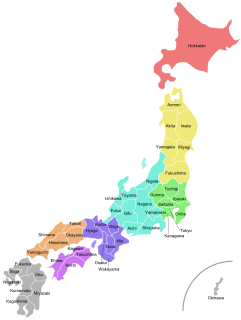
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures , forming the first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They consist of 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures , one "circuit" or "territory" and one "metropolis" .
The Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures from 1868 to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions of municipalities, school district, or political district.

Tambon is a local governmental unit in Thailand. Below district (amphoe) and province (changwat), they form the third administrative subdivision level. As of 2016 there were 7,255 tambons, not including the 180 khwaeng of Bangkok, which are set at the same administrative level, thus every district contains eight to ten tambon. Tambon is usually translated as "township" or "subdistrict" in English — the latter is the recommended translation, though also often used for king amphoe, the designation for a subdistrict acting as a branch of the parent district. Tambon are further subdivided into 69,307 villages (muban), about ten per tambon. Tambon within cities or towns are not subdivided into villages, but may have less formal communities called chumchon (ชุมชน) that may be formed into community associations.

According to the Moldovan law on territorial administrative organisation, Moldova is divided administratively into the following administrative territorial units: districts, cities/towns and villages. The administrative territorial organization of Moldova is made on 2 levels:
- villages (communes), sectors and cities/towns (municipalities) constitute the first level,
- districts, Chișinău municipality, Bălți municipality and Bender municipality constitute the second level.

Syria is a unitary state, but for administrative purposes, it is divided into fourteen governorates, also called provinces in English. The governorates are divided into sixty districts, which are further divided into subdistricts. The nawāḥī contain villages, which are the smallest administrative units.

Ukraine is divided into several levels of territorial entities. On the first level there are 27 regions: 24 oblasts, one autonomous republic, and two "cities with special status". Following the 2014 Crimean crisis, Crimea and Sevastopol became de facto administrated by the Russian Federation, which claims them as the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol. The international community recognises them as being Ukrainian territory.
A kaza is an administrative division historically used in the Ottoman Empire and currently used in several of its successor states. The term is from Ottoman Turkish and means "jurisdiction"; it is often translated "district", "sub-district", or "juridical district".

The administrative divisions of Nepal are subnational administrative units of Nepal. The first level of country subdivisions of Nepal are the Provinces. Each province is further subdivided into districts, and each district into municipalities and rural municipalities. Before 2015, instead of provinces, Nepal was divided into developmental regions and administrative zones.
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they compose a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision.

Since the Declaration of Independence in 1912, Albania has undergone administrative territorial reforms a total of 21 times. Its administrative boundaries have been divided and/or merged into regions (krahina), prefectures, sub-prefectures, counties (qarqe), districts (rrethe), municipalities (bashki), cities, communes (komuna), neighborhoods (lagje), villages (fshatra) and localities. The country is presently divided into 61 municipalities and 373 units of local governance.

Muban is the lowest administrative sub-division of Thailand. Usually translated as village and sometimes as hamlet, they are a subdivision of a tambon. As of 2008, there were 74,944 administrative muban in Thailand. As of the 1990 census, the average village consisted of 144 households or 746 persons.
A bakhsh is a type of administrative division of Iran. While sometimes translated as county, it should be more accurately translated as district, similar to a township in the United States or a district of England.

Raions of Ukraine are the second level of administrative division of Ukraine, below the oblast, and are the most common division of regions of Ukraine. Equivalent type of regional subdivision are also raions in city, and cities of regional significance.
A sołectwo (listen) is an administrative unit in Poland, an optional subdivision of a gmina. In many cases it consists of one village, but sometimes large villages may be divided into several sołectwos, while in other cases one sołectwo may consist of several villages or hamlets. Like the dzielnica and osiedle, a sołectwo is an auxiliary unit of a gmina. Only rural locations are assigned to sołectwos, while the comparable administrative unit in town is either dzielnica or osiedle.

Municipalities are the first-level administrative divisions of Albania. Prior to 2015, there were two types of municipalities in Albania: municipalities with an urban character called bashki, and municipalities with a rural character called komunë (commune). Municipalities are all divided into at least two "administrative units", which are sometimes referred to as "municipal units" or "mini-municipalities". Administrative units are composed of one or more cities, villages, or neighbourhoods and constitute the third- and final-level administrative divisions of Albania.

palakot wodapalika
A tehsil is an administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is an area of land with a city or town that serves as its administrative centre, with possible additional towns, and usually a number of villages. The terms in India have replaced earlier geographical terms, such as pargana, pergunnah and thannah, used under Delhi Sultanate and the British Raj.
















