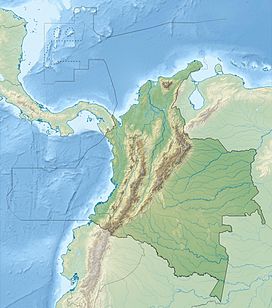
The Republic of Colombia is situated largely in the north-west of South America, with some territories falling within the boundaries of Central America. It is bordered to the north-west by Panama; to the east by Brazil and Venezuela; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; and it shares maritime limits with Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, Jamaica, the Dominican Republic, and Haiti.

Panama is a country located in Caribbean, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica. Panama is located on the narrow and low Isthmus of Panama.
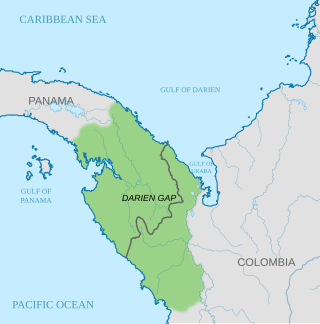
The Darién Gap is a geographic region that connects the American continents, stretching across southern Panama's Darién Province and the northern portion of Colombia's Chocó Department. Consisting of a large watershed, dense rainforest, and mountains, it is known for its remoteness, difficult terrain, and extreme environment, with a reputation as one of the most inhospitable regions in the world. Nevertheless, as the only land bridge between North and South America, the Darién Gap has historically served as a major route for both humans and wildlife.

Cauca Department is a department of Southwestern Colombia. Located in the southwestern part of the country, facing the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Valle del Cauca Department to the north, Tolima Department to the northeast, Huila Department to the east, and Nariño Department to the south. Putumayo and Caqueta Departments border the southeast portion of Cauca Department as well. It covers a total area of 29,308 km2 (11,316 sq mi), the 13th largest in Colombia. Its capital is the city of Popayán. The offshore island of Malpelo belongs to the department. It is located in the southwest of the country, mainly in the Andean and Pacific regions plus a tiny part (Piamonte) in the Amazonian region. The area makes up 2.56% of the country.

Chocó Department is a department of the Pacific region of Colombia known for hosting the largest Afro-Colombian population in the nation, and a large population of Amerindian and mixed African-Amerindian Colombians. It is in the west of the country, and is the only Colombian department to have coastlines on both the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean. It contains all of Colombia's border with Panama. Its capital is Quibdó.

Darién National Park is a World Heritage Site in Panama. It is about 325 kilometers (202 mi) from Panama City, is the most extensive of all national parks of Panama, and is one of the most important World Heritage Sites in Central America.

The Cordillera Occidental is the lowest in elevation of the three branches of the Colombian Andes. The average altitude is 2,000 m (6,600 ft) and the highest peak is Cerro Tatamá at 4,100 m (13,500 ft). The range extends from south to north dividing from the Colombian Massif in Nariño Department, passes north through Cauca, Valle del Cauca, Risaralda, Chocó, and Caldas Departments to the Paramillo Massif in Antioquia and Córdoba Departments. The cordillera is paralleled on the east by the Cauca river. From this massif the range divides further to form the Serranías de Ayapel, San Jerónimo and Abibe. Only to recede into the Caribbean plain and the Sinú River valley.

The Pacific/Chocó region is one of the five major natural regions of Colombia. Ecologically, this region belongs entirely to the Chocó Biogeographic Region and is considered a biodiversity hotspot. It also has areas with the highest rainfall in the world, with areas near Quibdo, Chocó reaching up to 13,000 mm (510 in) annually.

Andinobates altobueyensis is a species of frog in the family Dendrobatidae. It is endemic to Alto del Buey mountain in the Serranía del Baudó range, in the Chocó Department of western Colombia. Its common names include Alto de Buey poison frog, golden poison-arrow frog, and golden poison frog.

Because of its natural structure, Colombia can be divided into six distinct natural regions. These consist of the Andean Region, covering the three branches of the Andes mountains found in Colombia; the Caribbean Region, covering the area adjacent to the Caribbean Sea; the Pacific Region adjacent to the Pacific Ocean; the Orinoquía Region, part of the Llanos plains mainly in the Orinoco river basin along the border with Venezuela; the Amazon Region, part of the Amazon rainforest; and finally the Insular Region, comprising the islands in both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Colombia is located in South America.

Geology of Colombia refers to the geological composition of the Republic of Colombia that determines its geography. Most of the emerged territory of Colombia covers vast areas within the South American Plate, whereas much submerged territory lies within the Caribbean Plate and the Nazca Plate.

Farallones de Cali is a cluster of mountains in the West Andes of Colombia. It is located west of the city of Cali and gives rise to many of the rivers that provide water and electricity to Cali. The PNN Farallones de Cali encompasses 150,000 ha (580 sq mi) in the mountains as well as much of the Pacific slope and is an area of very high biodiversity. The average temperature ranges from 25 °C (77 °F) in the tropical foothills to 5 °C (41 °F) in the páramo. In this territory are located the district of Pichinde, Andes and Leonera, and two villages Penas Blancas and Lomas de la Cajita.
Frederick M. Kelley (1822–1905) was a Wall Street banker, who sponsored 7 expeditions to discover the purported "Sea Level Interoceanic Canal" of the Isthmus of Darien.

The Colombia–Panama border is the 339-kilometer-long (211 mi) international boundary between Colombia and Panama. It also splits the Darién Gap, a break across the North American and South American continents. This large watershed, forest, and mountainous area is in the north-western portion of Colombia's Chocó Department and south-eastern portion of Panama's Darién Province.

The Chocó–Darién moist forests (NT0115) is a largely forested, tropical ecoregion of northwestern South America and southern Central America. The ecoregion extends from the eastern Panamanian province of Darién and the indigenous region of Guna Yala to almost the entirety of Colombia's Pacific coast, including the departments of Cauca, Chocó, Nariño and Valle del Cauca.

The Eastern Panamanian montane forests (NT0122) is an ecoregion in the east of Panama and the extreme northwest of Colombia. It contains diverse flora and fauna, with considerable endemism. The ecoregion is largely intact due to its inaccessibility, although the opening of an extension of the Pan-American Highway has introduced threats from human activity.

The Malpelo plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located off the coasts west of Ecuador and Colombia. It is the 57th plate to be identified. It is named after Malpelo Island, the only emerged part of the plate. It is bounded on the west by the Cocos plate, on the south by the Nazca plate, on the east by the North Andes Plate, and on the north by the Coiba plate, separated by the Coiba transform fault (CTF). This microplate was previously assumed to be part of the Nazca plate. The Malpelo plate borders three major faults of Pacific Colombia, the north to south striking Bahía Solano Fault in the north and the Naya-Micay and Remolino-El Charco Faults in the south.

The Bahía Solano Fault, Utría Fault or Utría-Bahía Solano Fault is a westward dipping thrust fault in the department of Chocó on the Pacific Coast of Colombia. The fault has a total length of 290.6 kilometres (180.6 mi) and runs along an average north–south strike of 347 ± 13 from the Panama-Colombia border to Bajo Baudó. The fault is partly offshore in the bays of Solano and Utría and crosses the Chocó Basin and the coastal Serranía del Baudó. Movement of the fault produced the Mw 6.5 1970 Bahía Solano earthquake.
The Unguía Fault is an oblique dextral thrust fault in the department of Chocó in northwestern Colombia and continuing offshore Panama in the Caribbean Sea. The fault has a total length of 139.9 kilometres (86.9 mi) and is arcuate, running along a strike of 356.3 ± 30.

The Coiba plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located off the coasts south of Panama and northwestern Colombia. It is named after Coiba, the largest island of Central America, just north of the plate offshore southern Panama. It is bounded on the west by the Cocos plate, on the south by the Malpelo plate, on the east by the North Andes plate, and on the north by the Panama plate. This microplate was previously assumed to be part of the Nazca Plate, forming the northeastern tongue of the Nazca plate together with the Malpelo plate. Bordering the Coiba plate on the east are the north–south striking Bahía Solano Fault and east of that, the Serranía de Baudó, an isolated mountain chain in northwestern Chocó, Colombia.