
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with, and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex. These two forms of selection mean that some individuals have greater reproductive success than others within a population, for example because they are more attractive or prefer more attractive partners to produce offspring. For instance, in the breeding season, sexual selection in frogs occurs with the males first gathering at the water's edge and making their mating calls: croaking. The females then arrive and choose the males with the deepest croaks and best territories. In general, males benefit from frequent mating and monopolizing access to a group of fertile females. Females can have a limited number of offspring and maximize the return on the energy they invest in reproduction.

Vertebrates comprise all species of animals within the subphylum Vertebrata. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates include such groups as the following:

Peafowl is a common name for three bird species in the genera Pavo and Afropavo of the family Phasianidae, the pheasants and their allies. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are referred to as peahens, even though peafowl of either sex are often referred to colloquially as "peacocks".

Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the two sexes of the same species exhibit different characteristics beyond the differences in their sexual organs. The condition occurs in many animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristics, size, weight, colour, markings, and may also include behavioral and cognitive differences. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated, and may be subjected to sexual selection and natural selection. The opposite of dimorphism is monomorphism.

In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms, usually for the purposes of sexual reproduction. Some definitions limit the term to pairing between animals, while other definitions extend the term to mating in plants and fungi. Fertilization is the fusion of two gametes. Copulation is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproducing animals for insemination and subsequent internal fertilization. Mating may also lead to external fertilization, as seen in amphibians, fishes and plants. For the majority of species, mating is between two individuals of opposite sexes. However, for some hermaphroditic species, copulation is not required because the parent organism is capable of self-fertilization (autogamy); for example, banana slugs.

Courtship is the period of development towards an intimate relationship wherein a couple get to know each other and decide if there will be an engagement, followed by a marriage. A courtship may be an informal and private matter between two people or may be a public affair, or a formal arrangement with family approval. Traditionally, in the case of a formal engagement, it is the role of a male to actively "court" or "woo" a female, thus encouraging her to understand him and her receptiveness to a marriage proposal.

Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a shorter, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller ears and eyes; and differently formed molars. They are sometimes known as meadow mice or field mice in North America and Australia.

Ursus is a genus in the family Ursidae (bears) that includes the widely distributed brown bear, the polar bear, the American black bear, and the Asian black bear. The name is derived from the Latin ursus, meaning bear.

In biology, a clasper is a male anatomical structure found in some groups of animals, used in mating.

The common tsessebe or sassaby is one of six subspecies of African antelope Damaliscus lunatus of the genus Damaliscus and subfamily Alcelaphinae in the family Bovidae. It is most closely related to the topi, korrigum, coastal topi and tiang, and the bangweulu tsessebe and bontebok in the same genus. Tsessebe are found primarily in Angola, Zambia, Namibia, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Eswatini (Swaziland), and South Africa. Tsessebe are one of the fastest antelopes in Africa and can run at speeds up to 90 km/h.
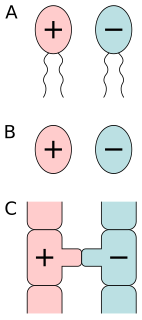
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves gametes of similar morphology, found in most unicellular organisms. Because both gametes look alike, they generally cannot be classified as male or female. Instead, organisms undergoing isogamy are said to have different mating types, most commonly noted as "+" and "−" strains. Some isogamous species have more than two mating types, but the number is usually lower than ten, though in some extremely rare cases a species can have thousands of mating types. In all cases, fertilization occurs when gametes of two different mating types fuse to form a zygote.

Animal sexual behaviour takes many different forms, including within the same species. Common mating or reproductively motivated systems include monogamy, polygyny, polyandry, polygamy and promiscuity. Other sexual behaviour may be reproductively motivated or non-reproductively motivated.

A hemipenis is one of a pair of intromittent organs of male squamates. Hemipenes are usually held inverted within the body, and are everted for reproduction via erectile tissue, much like that in the human penis. They come in a variety of shapes, depending on species, with ornamentation, such as spines or hooks.
Monogamous pairing in animals refers to the natural history of mating systems in which species pair bond to raise offspring. This is associated, usually implicitly, with sexual monogamy.

Cervus is a genus of deer that primarily are native to Eurasia, although one species occurs in northern Africa and another in North America. In addition to the species presently placed in this genus, it has included a whole range of other species now commonly placed in other genera. Additionally, the species-level taxonomy is in a state of flux.

Serromyia is a genus of biting midges in the subfamily Ceratopogoninae.

A queen ant is an adult, reproducing female ant in an ant colony; generally she will be the mother of all the other ants in that colony. Some female ants, such as the Cataglyphis, do not need to mate to produce offspring, reproducing through asexual parthenogenesis or cloning, and all of those offspring will be female. Others, like those in the genus Crematogaster, mate in a nuptial flight. Queen offspring ants develop from larvae specially fed in order to become sexually mature among most species. Depending on the species, there can be either a single mother queen, or potentially hundreds of fertile queens in some species. A queen of Lasius niger was held in captivity by German entomologist Hermann Appel for 283⁄4 years; also a Pogonomyrmex owyheei has a maximum estimated longevity of 30 years in the field.

A courtship display is a set of display behaviors in which an animal, usually a male, attempts to attract a mate; the mate exercises choice, so sexual selection acts on the display. These behaviors often include ritualized movement ("dances"), vocalizations, mechanical sound production, or displays of beauty, strength, or agonistic ability.
Frogs and toads produce a rich variety of sounds, calls, and songs during their courtship and mating rituals. The callers, usually males, make stereotyped sounds in order to advertise their location, their mating readiness and their willingness to defend their territory; listeners respond to the calls by return calling, by approach, and by going silent. These responses have been shown to be important for species recognition, mate assessment, and localization. Beginning with the pioneering experiments of Robert Capranica in the 1930s using playback techniques with normal and synthetic calls, behavioral biologists and neurobiologists have teamed up to use frogs and toads as a model system for understanding the auditory function and evolution. It is now considered an important example of the neural basis of animal behavior, because of the simplicity of the sounds, the relative ease with which neurophysiological recordings can be made from the auditory nerve, and the reliability of localization behavior. Acoustic communication is essential for the frog's survival in both territorial defense and in localization and attraction of mates. Sounds from frogs travel through the air, through water, and through the substrate. The neural basis of communication and audition gives insights into the science of sound applied to human communication.
Seasonal breeders are animal species that successfully mate only during certain times of the year. These times of year allow for the optimization of survival of young due to factors such as ambient temperature, food and water availability, and changes in the predation behaviors of other species. Related sexual interest and behaviors are expressed and accepted only during this period. Female seasonal breeders will have one or more estrus cycles only when she is "in season" or fertile and receptive to mating. At other times of the year, they will be anestrus, or have a dearth of their sexual cycle. Unlike reproductive cyclicity, seasonality is described in both males and females. Male seasonal breeders may exhibit changes in testosterone levels, testes weight, and fertility depending on the time of year.

















