Related Research Articles

Benue–Congo is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa.
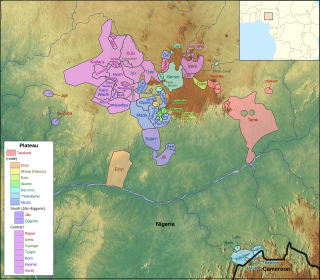
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau, Southern Kaduna, Nasarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language and most widely spoken lingua franca is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. Nigerian Pidgin – an English-based creole – is spoken by 30 million people in Nigeria.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.
Pan is an Afro-Asiatic dialect cluster spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria.

Ron is an Afro-Asiatic language cluster spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. Dialects include Bokkos, Daffo-Mbar-Butura, Monguna. Blench (2006) considers these to be separate languages.
Daza or Dazawa is listed by Blench (2006) as a Chadic language within the Bole group, spoken in a few villages of Darazo LGA, Bauchi State, Nigeria. It was confirmed to exist in 2021.
The Nupoid languages are a branch of Volta–Niger spoken in west-central Nigeria, particularly in southeastern Niger State and northern Kogi State. They include the Nupe and Ebira languages, each with about 4 million speakers. Most Nupoid languages have 3 level tones.
The five Tarokoid languages are a branch of the Plateau family spoken in central Nigeria, just north of the middle reaches of the Benue River. Tarok itself has 300,000 speakers, with Pe and Sur about 5,000 each. Yangkam is severely endangered, being spoken by around fifty elderly men.
Alumu is a Plateau language spoken by approximately 7,000 people in Nassarawa State, Nigeria. It has lost the nominal affix system characteristic of the Niger–Congo family.
The East Kainji languages are spoken in a compact area of the Jos Plateau in Nigeria, near Jos. There are more than 20 of them, most of which are poorly studied.
Ahwai, also called the Ndunic languages, is a Plateau language cluster spoken to the southwest of Fadan Karshi in Sanga LGA, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Most villages are located at the foot of the Ahwai Mountains in Kaduna State.
Kwanka, or Kwang (Kwaŋ), is a dialect cluster of Plateau languages in Nigeria.
Bauchi is a cluster of Kainji languages spoken in Rafi, Nigeria LGA, Niger State, Nigeria.
Lamang (Laamang) is an Afro-Asiatic language cluster of Nigeria. Blench (2006) classifies the Woga variety as a separate language.
kuSur–Myet, also known as Sur (Nsur), Tapshin, or Myet, is a minor Plateau language of Bauchi and Plateau states, Nigeria. There are two closely related dialects, Súr and Myet.
Pe, also spelled Pai or Pye, is a minor Plateau language of southeastern Plateau State, Nigeria. It is classified as a Tarokoid language by Roger Blench (2023).
Yangkam (Yankam), or Bashar (Basherawa), is a moribund Plateau language of Nigeria. It is located to the west of Bashar town in Plateau State.
Firan or Fəràn is a Plateau language closely related to Izere. Most Firan speakers are multilingual in Firan, Hausa, English, Iten and sometimes Berom.
The Nka language is a Plateau language of Nigeria. Mutual intelligibility with the related Gbantu language is low.
References
- ↑ Shall-Zwall at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Blench, Roger. 2023. The Pe language of Central Nigeria and its affinities . Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.