Related Research Articles

The Tivoid languages are a branch of the Southern Bantoid languages spoken in parts of Nigeria and Cameroon. The subfamily takes its name after Tiv, the most spoken language in the group.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.
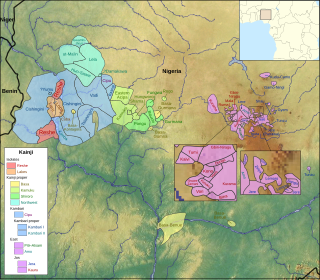
The Kainji languages are a group of about 60 related languages spoken in west-central Nigeria. They form part of the Central Nigerian (Platoid) branch of Benue–Congo.
The Nupoid languages are a branch of Volta–Niger spoken in west-central Nigeria, particularly in southeastern Niger State and northern Kogi State. They include the Nupe and Ebira languages, each with about 4 million speakers. Most Nupoid languages have 3 level tones.
The five Tarokoid languages are a branch of the Plateau family spoken in central Nigeria, just north of the middle reaches of the Benue River. Tarok itself has 300,000 speakers, with Pe and Sur about 5,000 each. Yangkam is severely endangered, being spoken by around fifty elderly men.
Zeem, or Chaari, is an endangered Chadic dialect cluster of Nigeria, whose speakers are shifting to Hausa. Dyarim is closely related.
Alumu is a Plateau language spoken by approximately 7,000 people in Nassarawa State, Nigeria. It has lost the nominal affix system characteristic of the Niger–Congo family.
Kwah (Kwa), also known as Baa (Bàː), is a Niger–Congo language of uncertain affiliation; the more it has been studied, the more divergent it appears. Joseph Greenberg counted it as one of the Bambukic languages of the Adamawa family. Boyd (1989) assigned it its own branch within Waja–Jen. Kleinewillinghöfer (1996) removed it from Waja–Jen as an independent branch of Adamawa. When Blench (2008) broke up Adamawa, Kwah became a provisional independent branch of his larger Savannas family.
Buru and Angwe constitute a potentially rather divergent Southern Bantoid language spoken in Sardauna LGA, Taraba State of Nigeria.
The East Kainji languages are spoken in a compact area of the Jos Plateau in Nigeria, near Jos. There are more than 20 of them, most of which are poorly studied.
Daka is one of two languages spoken by the Chamba people in Nigeria, the other being Chamba Leko.
Ahwai, also called the Ndunic languages, is a Plateau language cluster spoken to the southwest of Fadan Karshi in Sanga LGA, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Most villages are located at the foot of the Ahwai Mountains in Kaduna State.
Cara, also called Teriya after the village it is spoken in, is a small Plateau language of central Nigeria. Cara is spoken by about 3,000 people in Teriya village, Bassa, Plateau State, Nigeria.
Hyam is a regionally important linguistic cluster of Plateau languages in Nigeria. Hyam of Nok is the prestige dialect. Writing the sociolinguistics of Hyam, Blench treats Sait, and Dzar as distinct varieties, and notes that Yat and Ankung may be viewed as separate languages, however, Hayab (2016) presents a differing opinion arguing that it is Ankung, a language called Iduya, that is not mutually intelligible to Hyam. Meanwhile, Hyam, which is spoken by the Ham people of Nigeria, popularly known as 'Jaba' in a recent study by Philip Hayab, a native of the area and a linguist who carried out in-depth research into the language, reveals that 'Jaba' has a Hausa etymology and is derogatory and should be discarded.
Bauchi is a cluster of Kainji languages spoken in Rafi, Nigeria LGA, Niger State, Nigeria.
Ju is a language from the West Chadian branch of the Chadic language family. The language is spoken solely in Nigeria, and had approximately 900 native speakers in 1993. The language is unwritten.
Tala is a language from the West Chadian branch of the Chadic language family. The language is spoken in the central regions of Nigeria, and had approximately 1000 native speakers in 1993. The language is unwritten.
Pe, also spelled Pai or Pye, is a minor Plateau language of southeastern Plateau State, Nigeria. It is classified as a Tarokoid language by Roger Blench (2023).
Ziriya (Jiriya) and Sheni (Shaini) constitute a Kainji language of Nigeria. They are geographically but perhaps not linguistically distinct.
Zora (Izora), or Cokoba (Cokobanci) in Hausa, is a Kainji language of Nigeria.
References
- ↑ Vori at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.
- ↑ Blench, Roger. 2016. Weeping over the disappearance of Nigeria’s minority languages: how to get more reliable information and what to do about it. Presentation, Jos Linguistic Circle.