Related Research Articles

Messier 87 is a supergiant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo that contains several trillion stars. One of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local universe, it has a large population of globular clusters—about 15,000 compared with the 150–200 orbiting the Milky Way—and a jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends at least 1,500 parsecs, traveling at a relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky and a popular target for both amateur and professional astronomers.

Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. The distance between the radio telescopes is then calculated using the time difference between the arrivals of the radio signal at different telescopes. This allows observations of an object that are made simultaneously by many radio telescopes to be combined, emulating a telescope with a size equal to the maximum separation between the telescopes.

A supermassive black hole is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of hundreds of thousands, or millions to billions, of times the mass of the Sun (M☉). Black holes are a class of astronomical objects that have undergone gravitational collapse, leaving behind spheroidal regions of space from which nothing can escape, including light. Observational evidence indicates that almost every large galaxy has a supermassive black hole at its center. For example, the Milky Way galaxy has a supermassive black hole at its center, corresponding to the radio source Sagittarius A*. Accretion of interstellar gas onto supermassive black holes is the process responsible for powering active galactic nuclei (AGNs) and quasars.

The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately 8 kiloparsecs (26,000 ly) away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula.

3C 279 is an optically violent variable quasar (OVV), which is known in the astronomical community for its variations in the visible, radio and X-ray bands. The quasar was observed to have undergone a period of extreme activity from 1987 until 1991. The Rosemary Hill Observatory (RHO) started observing 3C 279 in 1971, the object was further observed by the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory in 1991, when it was unexpectedly discovered to be one of the brightest gamma ray objects in the sky. It is also one of the brightest and most variable sources in the gamma ray sky monitored by the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. It was used as a calibrator source for Event Horizon Telescope observations of M87* that resulted in the first image of a black hole.

Andrea Mia Ghez is an American astrophysicist, Nobel laureate, and professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy and the Lauren B. Leichtman & Arthur E. Levine chair in Astrophysics, at the University of California, Los Angeles. Her research focuses on the center of the Milky Way galaxy.

Sagittarius A*, abbreviated as Sgr A*, is the supermassive black hole at the Galactic Center of the Milky Way. Viewed from Earth, it is located near the border of the constellations Sagittarius and Scorpius, about 5.6° south of the ecliptic, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) and Lambda Scorpii.

OJ 287 is a BL Lac object 4 billion light-years from Earth that has produced quasi-periodic optical outbursts going back approximately 120 years, as first apparent on photographic plates from 1891. Seen on photographic plates since at least 1887, it was first detected at radio wavelengths during the course of the Ohio Sky Survey. It is a supermassive black hole binary (SMBHB). The intrinsic brightness of the flashes corresponds to over a trillion times the Sun's luminosity, greater than the entire Milky Way galaxy's light output.

Fulvio Melia is an Italian-American astrophysicist, cosmologist and author. He is professor of physics, astronomy and the applied math program at the University of Arizona and was a scientific editor of The Astrophysical Journal and an associate editor of The Astrophysical Journal Letters. A former Presidential Young Investigator and Sloan Research Fellow, he is the author of six English books and 230 refereed articles on theoretical astrophysics and cosmology.
Feryal Özel is a Turkish-American astrophysicist born in Istanbul, Turkey, specializing in the physics of compact objects and high energy astrophysical phenomena. As of 2022, Özel is the department chair and a professor at the Georgia Institute of Technology School of Physics in Atlanta. She was previously a professor at the University of Arizona in Tucson, in the Astronomy Department and Steward Observatory.

Priyamvada (Priya) Natarajan is a theoretical astrophysicist and professor in the departments of astronomy and physics at Yale University. She is noted for her work in mapping dark matter and dark energy, particularly in gravitational lensing and in models describing the assembly and accretion histories of supermassive black holes. She authored the book Mapping the Heavens: The Radical Scientific Ideas That Reveal the Cosmos.
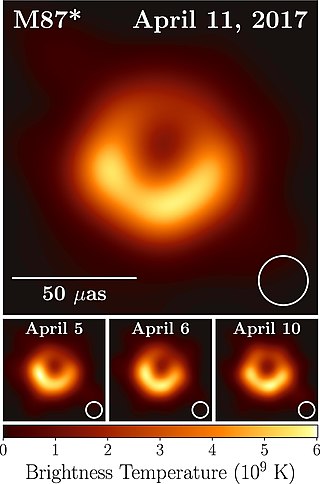
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is a telescope array consisting of a global network of radio telescopes. The EHT project combines data from several very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) stations around Earth, which form a combined array with an angular resolution sufficient to observe objects the size of a supermassive black hole's event horizon. The project's observational targets include the two black holes with the largest angular diameter as observed from Earth: the black hole at the center of the supergiant elliptical galaxy Messier 87, and Sagittarius A*, at the center of the Milky Way.
Heino Falcke is a German professor of radio astronomy and astroparticle physics at the Radboud University Nijmegen (Netherlands). His main field of study is black holes, and he is the originator of the concept of the 'black hole shadow'. In 2019, Falcke announced the first Event Horizon Telescope results at the EHT Press Conference in Brussels.

Violette Impellizzeri is an Italian astronomer and astrophysicist specializing in active galactic nuclei and molecular clouds surrounding supermassive black holes. She is currently a professor at Leiden University, where she conducts research on these phenomena using radio interferometry.

Luciano Rezzolla is an Italian professor of relativistic astrophysics and numerical relativity at the Goethe University Frankfurt. His main field of study is the physics and astrophysics of compact objects such as black holes and neutron stars. It was announced in 2019 that he had been appointed honorary Andrews Professor of Astronomy at Trinity College Dublin (TCD).

CHIRP is a Bayesian algorithm used to perform a deconvolution on images created in radio astronomy. The acronym was coined by lead author Katherine L. Bouman in 2016.

Johann Anton Zensus is a German radio astronomer. He is director at the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (MPIfR) and honorary professor at the University of Cologne. He is chairman of the collaboration board of the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). The collaboration announced the first image of a black hole in April 2019.

Ramesh Narayan is an Indian-American theoretical astrophysicist, currently the Thomas Dudley Cabot Professor of the Natural Sciences in the Department of Astronomy at Harvard University. Full member of the National Academy of Sciences, Ramesh Narayan is widely known for his contributions on the theory of black hole accretion processes. He is involved in the Event Horizon Telescope project, which led in 2019 to the first image of the event horizon of a black hole.

James Moran is an American radio astronomer living in Massachusetts, USA. He was a professor of Astronomy at Harvard University from 1989 through 2016, a senior radio astronomer at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory from 1981 through 2020 and the director of the Submillimeter Array during its construction and early operational phases from 1995 through 2005. In 1998 he was elected to the National Academy of Sciences, in 2010 to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, and in 2020 to the American Philosophical Society. He is currently the Donald H. Menzel Professor of Astrophysics, Emeritus, at Harvard University.

Frank Eisenhauer is a German astronomer and astrophysicist, a director of the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE), and a professor at Technical University of Munich. He is best known for his contributions to interferometry and spectroscopy and the study of the black hole at the centre of the Milky Way.
References
- ↑ "Sheperd Doeleman Awarded the 2023 Georges Lemaître International Prize". News, Center for Astrophysics, Harvard University. April 18, 2023.
- ↑ "organization". eventhorizontelescope.org.
- ↑ "Sheperd Doeleman". bhi.fas.harvard.edu.
- ↑ "Harvard scientists shed light on importance of black hole image". 10 April 2019.
- 1 2 Ghosh, Pallab (10 April 2019). "First ever black hole image released". BBC.
- ↑ "Shep Doeleman: The 100 Most Influential People of 2019". TIME. Retrieved 2020-09-22.
- ↑ Seth Fletcher: Einstein's Shadow: A Black Hole, a Band of Astronomers, and the Quest to See the Unseeable (part 1, chapter 3). HarperCollins, 2018, ISBN 978-0-06-231202-0
- 1 2 "Sheperd S. Doeleman". John Simon Guggenheim Foundation.
- ↑ "Sheperd S. Doeleman".
- ↑ "Lancelot M. Berkley Prize". American Astronomical Society.