Sectarianism is a debated concept. Some scholars and journalists define it as pre-existing fixed communal categories in society, and use it to explain political, cultural, or religious conflicts between groups. Others conceive of sectarianism as a set of social practices where daily life is organized on the basis of communal norms and rules that individuals strategically use and transcend. This definition highlights the co-constitutive aspect of sectarianism and people's agency, as opposed to understanding sectarianism as being fixed and incompatible communal boundaries.

The dynamic between the League of Arab States and the Islamic Republic of Iran has been ambivalent, owing to the latter's varying bilateral conduct with each country of the former. Iran is located on the easternmost frontier of the Arab League, which consists of 22 Arab countries and spans the bulk of the Middle East and North Africa, of which Iran is also a part. The Arab League's population is dominated by ethnic Arabs, whereas Iran's population is dominated by ethnic Persians; and while both sides have Islam as a common religion, their sects differ, with Sunnis constituting the majority in the Arab League and Shias constituting the majority in Iran. Since Iran's Islamic Revolution in 1979, the country's Shia theocracy has attempted to assert itself as the legitimate religious and political leadership of all Muslims, contesting a status that has generally been understood as belonging to Sunni-majority Saudi Arabia, where the cities of Mecca and Medina are located. This animosity, manifested in the Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, has greatly exacerbated the Shia–Sunni divide throughout the Muslim world.

Several different denominations and sects of Islam are practised within Syria, who collectively constitute approximately 87% of the population and form a majority in most of the districts of the country.

Hezbollah Al-Hejaz, or Hizbollah in the Hijaz, is a militant Shia organization operating in Saudi Arabia. It was founded in May 1987 in Saudi Arabia's Eastern Province. In the years 1987–89 the party launched attacks against official Saudi targets inside and outside Saudi Arabia. After being implicated in the Khobar Towers Bombing in 1996, the party was outlawed in Saudi Arabia. The party was part of the Iranian government's "exporting the Islamic revolution" policy. Most of its members were arrested and the party practically ceased to exist. In 2014 it was designated a terrorist organization by the kingdom's government.
Islam is divided into two major sects, Sunni and Shia Islam, each with its own sub-sects. Large numbers of Shia Arab Muslims live in some Arab countries including Lebanon, Yemen, Bahrain, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman, the UAE, and Qatar.

After the death of Muhammad in 632, the Muslim world split into two camps, the Sunnis, who believed that the caliphs of the Islamic community should be chosen by consensus, and a second group, the Shia who believed that Mohammed's successors should be members of his own family, beginning with Ali ibn Abi Talib, his cousin and son-in-law.
For approximately a millennium, the Abrahamic religions have been predominant throughout all of the Middle East. The Abrahamic tradition itself and the three best-known Abrahamic religions originate from the Middle East: Judaism and Christianity emerged in the Levant in the 6th century BCE and the 1st century CE, respectively, while Islam emerged in Arabia in the 7th century CE.

Religion in Syria refers to the range of religions practiced by the citizens of Syria. Historically, the region has been a mosaic of diverse faiths with a range of different sects within each of these religious communities.
The Saudi government does not conduct a census on religion or ethnicity, but some sources estimate the Shia population in Saudi Arabia to make up around 10-15% of the approximately 34 million natives of Saudi Arabia.

Lebanese Shiite Muslims, communally and historically known as matāwila, are Lebanese people who are adherents of Shia Islam in Lebanon, which plays a major role alongside Lebanon's main Sunni, Maronite and Druze sects. The vast majority of Shiite Muslims in Lebanon adhere to Twelver Shi'ism.

Asa'ib Ahl al-Haq, also known as the Khazali Network, is a radical Iraqi Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary organization previously active in the Iraqi insurgency and Syrian Civil War. During the Iraq War it was known as Iraq's largest "Special Group", and it is part of the Popular Mobilization Forces (PMF) in the 41st, 42nd, and 43rd Brigades, cooperating with the Iraqi government in its fight against ISIS.
Content from the United States diplomatic cables leak has depicted Saudi Arabia and related subjects extensively. The leak, which began on 28 November 2010, occurred when the website of WikiLeaks — an international new media non-profit organization that publishes submissions of otherwise unavailable documents from anonymous news sources and news leaks — started to publish classified documents of detailed correspondence — diplomatic cables — between the United States Department of State and its diplomatic missions around the world. Since the initial release date, WikiLeaks is releasing further documents every day.

Sayyidah Zaynab, commonly known as Sitt Zaynab, is a town in the Rif Dimashq Governorate of Syria, 10 km (6 mi) south of Damascus, the national capital. With a population of 136,427, it is the 10th most populous city in Syria and the most populous satellite city of Damascus. Administratively, the town is located in Markaz Rif Dimashq district and belongs to the nahiyah ("subdistrict") of Babbila. The municipality of Sayyidah Zaynab is still considered as a rural community by the governorate of Rif Dimashq. The city contains the Qabr Essit Palestinian refugee camp.
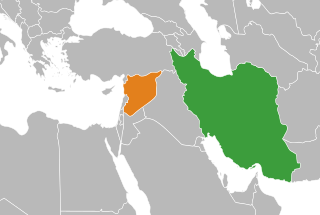
Syria established diplomatic relations with Pahlavi Iran after independence, but it was not until the Iranian revolution that Alawite-led Syria established close ties with Iran. Under the Ba'athist rule, Syria was usually called Iran's "closest ally". Iran and Syria had a strategic alliance ever since the Iran–Iraq War, when Syria sided with non-Arab Iran against neighbouring Ba'ath-ruled Iraq. The two countries shared a common animosity towards then-Iraqi president Saddam Hussein and coordination against the United States and Israel until the fall of the Assad regime after the 2024 Syrian opposition offensives were completed on December 8th, 2024.

Anti-Shi'ism is hatred of, prejudice against, discrimination against, persecution of, and violence against Shia Muslims because of their religious beliefs, traditions, and cultural heritage. The term was first used by Shia Rights Watch in 2011, but it has been used in informal research and written in scholarly articles for decades.

The Axis of Resistance is an informal coalition of Iranian-supported militias and political organizations across the Middle East. Formed by Iran, it unites actors committed to countering the influence of the United States and Israel in the region.

Hezbollah involvement in the Syrian civil war has been substantial since the beginning of armed insurgency phase of the Syrian civil war in 2011, and evolved into active support for Syrian government forces and troop deployment from 2012 onwards. By 2014, Hezbollah was deployed across Syria. Hezbollah has also been very active in preventing Al-Nusra Front and Islamic State penetration into Lebanon, being one of the most active forces in the Syrian civil war spillover in Lebanon.

Iran and Saudi Arabia are engaged in a proxy conflict over influence in the Middle East and other regions of the Muslim world. The two countries have provided varying degrees of support to opposing sides in nearby conflicts, including the civil wars in Syria and Yemen; and disputes in Bahrain, Lebanon, Qatar, and Iraq. The struggle also extends to disputes or broader competition in other countries globally including in West, North and East Africa, South, Central, Southeast Asia, the Balkans, and the Caucasus.
The demographics of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region show a highly populated, culturally diverse region spanning three continents. As of 2023, the population was around 501 million. The class, cultural, ethnic, governmental, linguistic and religious make-up of the region is highly variable.

Sectarianism in Saudi Arabia refers to the Saudi government's "top-down push towards sectarian polarization" between the Sunni majority, and Shi'ite minority. This encompasses anti-Shi'ite policies by the Saudi regime, as well as tensions between the Sunni majority and the Shi'ite minority. The Saudi government is often viewed to be oppressing the Shi'ite community, who constitute up to 15% of the Saudi population. This occurs against the backdrop of the broader Iran-Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, since Iran is a Shi'ite republic.














