
Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It makes up the majority of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe.
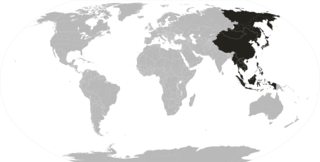
The Far East is a geographical region that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons. The term "Far East" came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 12th century, denoting the Far East as the "farthest" of the three "easts", beyond the Near East and the Middle East. Likewise, in Qing Dynasty of the 19th and early 20th centuries the term "Tàixī (泰西)" – i.e., anything further west than the Arab world – was used to refer to the Western countries.

The Levant is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, it is equivalent to the historical region of Syria, which included present-day Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine and most of Turkey south-east of the middle Euphrates. In its widest historical sense, the Levant included all of the Eastern Mediterranean with its islands; that is, it included all of the countries along the Eastern Mediterranean shores, extending from Greece to Cyrenaica in eastern Libya.

The Middle East is a region spanning the vast majority of Western Asia and all of Egypt. The term has come into wider usage as a replacement of the term Near East beginning in the early 20th century. The broader concept of the "Greater Middle East" also includes the Maghreb, Sudan, Djibouti, Somalia, the Comoros, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and sometimes Transcaucasia and Central Asia into the region. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions.

West Berlin was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although no specific date on which the sectors of Berlin occupied by the Western Allies became "West Berlin", 1949 is widely accepted as when the name was adopted. Although not a part of the Federal Republic of Germany, West Berlin aligned itself politically with that state and was directly or indirectly represented in its federal institutions.

Western Europe is the region of Europe farthest from Asia, with the countries and territories included varying depending on context.

Eastern Europe is the region of the European continent between Western Europe and Asia. There is no consistent definition of the precise area it covers, partly because the term has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socioeconomic connotations. Russia, located in Eastern Europe, is both the largest and most populous country of Europe, spanning roughly 40% of the continent's total landmass, with over 15% of its total population.

Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in Western Asia, Egypt, Northeast Africa, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, Asia Minor, the Malabar coast of southern India, and parts of the Far East. The term does not describe a single communion or religious denomination. Major Eastern Christian bodies include the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Oriental Orthodox Churches, the Eastern Catholic Churches, Protestant Eastern Christian churches who are Protestant in theology but Eastern Christian in cultural practice, and the denominations descended from the historic Church of the East. The various Eastern churches do not normally refer to themselves as "Eastern", with the exception of the Assyrian Church of the East and the Ancient Church of the East.

The east coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. Regionally, the term refers to the coastal states and area east of the Appalachian Mountains that have shoreline on the Atlantic Ocean, from north to south, Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia and Florida.

The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc, the Socialist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, and Southeast Asia under the influence of the Soviet Union and its ideology (communism) that existed during the Cold War 1947–1991 in opposition to the capitalist Western Bloc. The Eastern Bloc was often called the Second World, whereas the term "First World" referred to the Western Bloc and "Third World" referred to the non-aligned countries that were mainly in Asia, Africa, and Latin America. In Western Europe, the term Eastern Bloc generally referred to the USSR and its satellite states in the Comecon ; in Asia, the Soviet Bloc comprised the Mongolian People's Republic, the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, the Lao People's Democratic Republic and the People's Republic of Kampuchea, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea and the People's Republic of China. In the Americas the countries aligned with the Soviet Union included Cuba since 1961 and for limited periods Nicaragua and Grenada.

The Russian Far East is a region in North Asia which is coextensive with Russia’s easternmost territory, the Far Eastern Federal District, which is between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean.

The Near East is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region comprising Western Asia, Turkey, and Egypt. Despite having varying definitions within different academic circles, the term was originally applied to the maximum extent of the Ottoman Empire. The term has fallen into disuse in the English language and has been replaced by the terms Middle East, which includes Egypt, and Western Asia, which includes the South Caucasus.

The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches and in some historical cases referred to as Uniates, are twenty-three Eastern Christian sui iuris (autonomous) particular churches of the Catholic Church, in full communion with the pope in Rome. Although they are distinct from the Latin Church, they are all in full communion with it and with each other.

The Eastern Cape is one of the provinces of South Africa. Its capital is Bhisho, but its two largest cities are East London and Gqeberha.

The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama and Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small portion of westernmost Brazil in South America, along with certain Caribbean and Atlantic islands.

Northeast India is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Sikkim.

UTC−05:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −05:00. In North America, it is observed in the Eastern Time Zone during standard time, and in the Central Time Zone during the other eight months. The western Caribbean uses it year round.

The Eastern Hemisphere is a geographical term for the half of Earth which is east of the prime meridian and west of the antimeridian. It is also used to refer to Afro-Eurasia and Australia, in contrast with the Western Hemisphere, which includes mainly North and South America. The Eastern Hemisphere may also be called the "Oriental Hemisphere." In addition, it may be used in a cultural or geopolitical sense as a synonym for the "Old World."
Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical region of Europe, consisting primarily of the Balkans. Sovereign states and territories that are included in the region are, in alphabetical order: Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Greece, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, and Turkey. Sometimes, Moldova and Slovenia are also included. The largest city of the region is Istanbul, followed by Bucharest, Sofia, Belgrade, and Athens.

The Asia-Pacific (APAC) is the part of the world in or near the Western Pacific Ocean. Asia-Pacific varies in area depending on context, but it generally includes East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Oceania.





















