| Small Cajal body specific RNA 13 | |
|---|---|
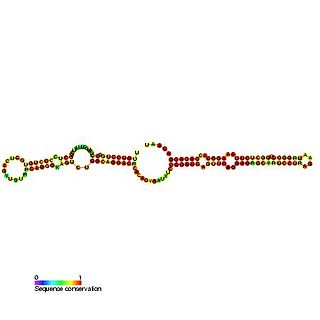
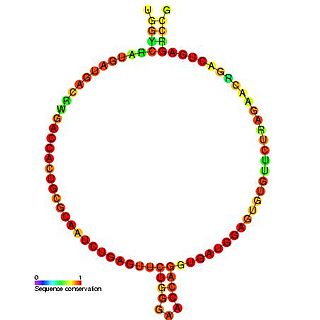
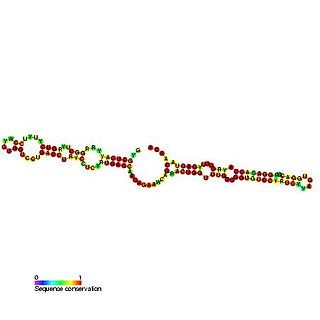
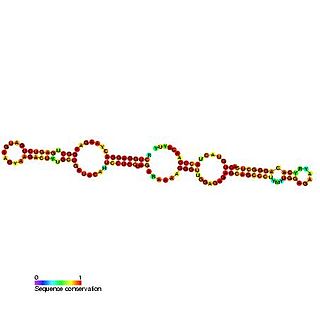
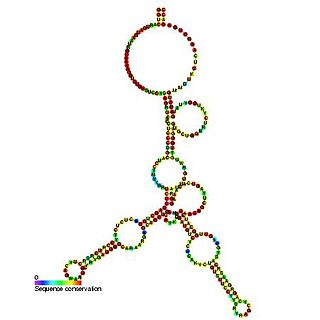
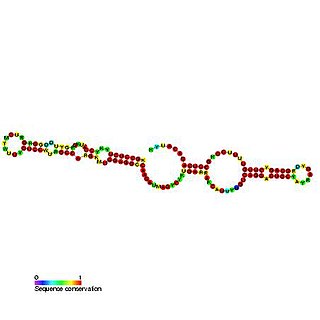
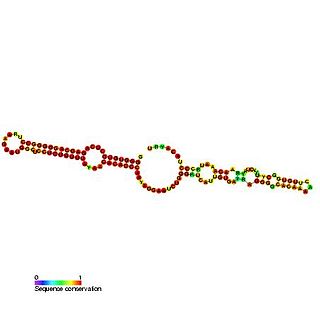
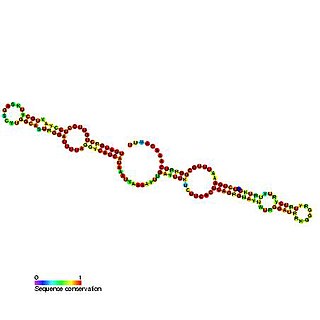
Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of SCARNA13 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SCARNA13 |
| Alt. Symbols | U93 |
| Rfam | RF00231 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; snRNA; snoRNA; scaRNA |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| GO | 0006396 0015030 0005730 |
| SO | 0000275 |
In molecular biology, Small Cajal body specific RNA 13 (also known as scaRNA13 or U93) is a small nucleolar RNA found in Cajal bodies and believed to be involved in the pseudouridylation of U2 and U5 spliceosomal RNA.

Molecular biology is a branch of biology that concerns the molecular basis of biological activity between biomolecules in the various systems of a cell, including the interactions between DNA, RNA, proteins and their biosynthesis, as well as the regulation of these interactions. Writing in Nature in 1961, William Astbury described molecular biology as:
...not so much a technique as an approach, an approach from the viewpoint of the so-called basic sciences with the leading idea of searching below the large-scale manifestations of classical biology for the corresponding molecular plan. It is concerned particularly with the forms of biological molecules and [...] is predominantly three-dimensional and structural – which does not mean, however, that it is merely a refinement of morphology. It must at the same time inquire into genesis and function.
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes.

Cajal bodies (CBs) also coiled bodies, are spherical sub-organelles of 0.3–1.0 µm in diameter found in the nucleus of proliferative cells like embryonic cells and tumor cells, or metabolically active cells like neurons. In contrast to cytoplasmic organelles, CBs lack any phospholipid membrane which would separate their content, largely consisting of proteins and RNA, from the surrounding nucleoplasm. They were first reported by Santiago Ramón y Cajal in 1903, who called them nucleolar accessory bodies due to their association with the nucleoli in neuronal cells. They were rediscovered with the use of the electron microscope (EM) and named coiled bodies, according to their appearance as coiled threads on EM images, and later renamed after their discoverer. Research on CBs was accelerated after discovery and cloning of the marker protein p80/Coilin. CBs have been implicated in RNA-related metabolic processes such as the biogenesis, maturation and recycling of snRNPs, histone mRNA processing and telomere maintenance. CBs assemble RNA which is used by telomerase to add nucleotides to the ends of telomeres.
scaRNAs are a specific class of small nucleolar RNAs that localise to the Cajal bodies and guide the modification of RNA polymerase II transcribed spliceosomal RNAs U1, U2, U4, U5 and U12. [1]

RNA polymerase II is a multiprotein complex. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mRNA and most snRNA and microRNA. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription.

A spliceosome is a large and complex molecular machine found primarily within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The spliceosome is assembled from snRNAs and approximately 80 proteins. The spliceosome removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA, a type of primary transcript. This process is generally referred to as splicing. An analogy is a film editor, who selectively cuts out irrelevant or incorrect material from the initial film and sends the cleaned-up version to the director for the final cut.
U1 spliceosomal RNA is the small nuclear RNA (snRNA) component of U1 snRNP, an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs. Splicing, or the removal of introns, is a major aspect of post-transcriptional modification, and takes place only in the nucleus of eukaryotes.
U93 is composed of two tandemly arranged box H/ACA box sequence motifs and belongs to the H/ACA box class of guide RNAs. [2] U93 is predicted to guide pseudouridylation of U2 spliceosomal snRNA residue U54 and residue U53 of snRNA U5. [2] [3] [4]