| small Cajal body-specific RNA 17 | |
|---|---|
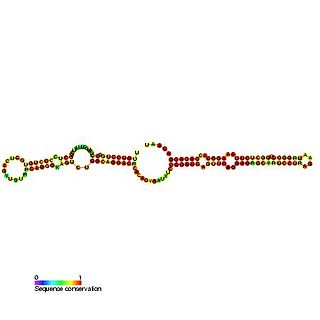
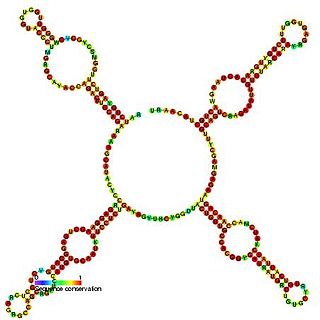
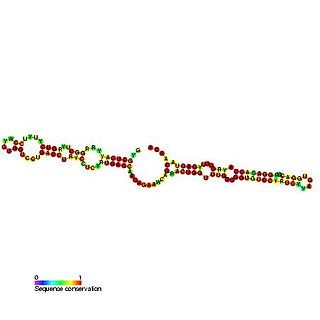
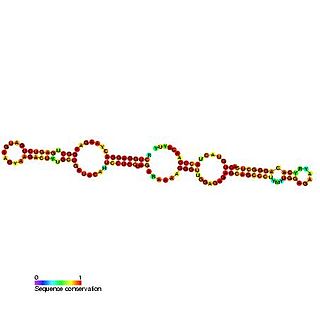
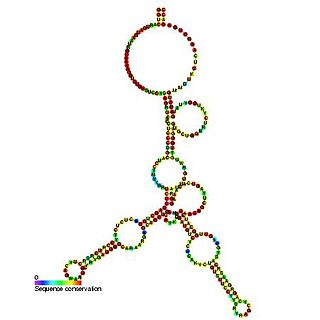
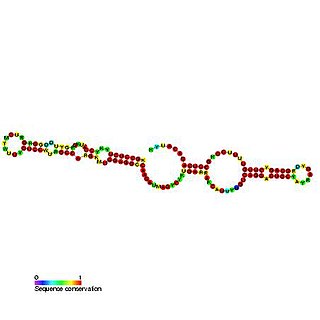
Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of SCARNA17 | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | SCARNA17 |
| Alt. Symbols | snoU12-22 |
| Rfam | RF00492 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; snRNA; snoRNA; scaRNA |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| GO | 0006396 0015030 0005730 |
| SO | 0000275 |
Small Cajal body-specific RNA 17 (also known as U12-22 scaRNA) is a type of small nuclear RNA which localises to the cajal bodies and proposed to guide the modification of RNA polymerase II transcribed spliceosomal RNAs U1, U2, U4, U5 and U12. [1] [2]
Small nuclear ribonucleic acid (snRNA) is a class of small RNA molecules that are found within the splicing speckles and Cajal bodies of the cell nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The length of an average snRNA is approximately 150 nucleotides. They are transcribed by either RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. Their primary function is in the processing of pre-messenger RNA (hnRNA) in the nucleus. They have also been shown to aid in the regulation of transcription factors or RNA polymerase II, and maintaining the telomeres.

Cajal bodies (CBs) also coiled bodies, are spherical sub-organelles of 0.3–1.0 µm in diameter found in the nucleus of proliferative cells like embryonic cells and tumor cells, or metabolically active cells like neurons. In contrast to cytoplasmic organelles, CBs lack any phospholipid membrane which would separate their content, largely consisting of proteins and RNA, from the surrounding nucleoplasm. They were first reported by Santiago Ramón y Cajal in 1903, who called them nucleolar accessory bodies due to their association with the nucleoli in neuronal cells. They were rediscovered with the use of the electron microscope (EM) and named coiled bodies, according to their appearance as coiled threads on EM images, and later renamed after their discoverer. Research on CBs was accelerated after discovery and cloning of the marker protein p80/Coilin. CBs have been implicated in RNA-related metabolic processes such as the biogenesis, maturation and recycling of snRNPs, histone mRNA processing and telomere maintenance. CBs assemble RNA which is used by telomerase to add nucleotides to the ends of telomeres.

RNA polymerase II is a multiprotein complex. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mRNA and most snRNA and microRNA. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription.
The complete human U12-22/U4-8 scaRNA is composed of two tandem C/D box domains (termed U12-22 and U4-8). The 5' and 3' C/D domains are predicted to guide the 2'O-ribose methylation of residue U22 in U12 and residue C8 in U4 snRNAs respectively. [1] This family includes only the 5' C/D box domain (U12-22) as the 3' C/D box is represented by Small Cajal body specific RNA 18. The 3' C/D domain (U4-8) was also cloned previously by Darzacq and called U91. [3] Both the doublet (U12-22/U4-8) and singlet (U4-8) forms of this snRNA have been purified from HeLa cells. [1] The doublet form U12-22/U4-8 has been shown to localise to the nucleoplasm and is proposed to reside in the Cajal bodies whereas the U4-8 single domain appears to accumulate in the nucleolus. [1] In humans the genomic location of U12-88/U4-8 is intergenic and the purified transcript has been shown to possess a methylated guanosine cap suggesting it is independently transcribed by RNA polymerase II. [1]

Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide sugar-ring means that there will be a 5′-end, which frequently contains a phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose ring, and a 3′-end, which typically is unmodified from the ribose -OH substituent. In a DNA double helix, the strands run in opposite directions to permit base pairing between them, which is essential for replication or transcription of the encoded information.
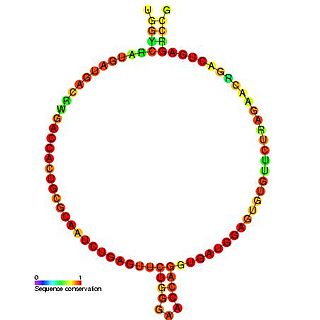
small Cajal body-specific RNA 18 is a type of small nuclear RNA which localises to the cajal bodies and proposed to guide the modification of RNA polymerase II transcribed spliceosomal RNAs U1, U2, U4, U5 and U12.
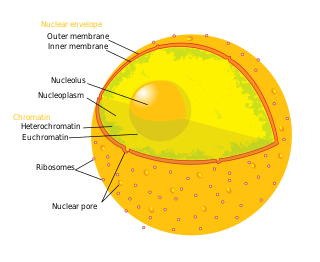
Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains nucleoplasm, karyoplasm, or nucleus sap. The nucleoplasm is one of the types of protoplasm, and it is enveloped by the nuclear membrane. The nucleoplasm includes the chromosomes and nucleolus. Many substances such as nucleotides and enzymes are dissolved in the nucleoplasm. The soluble, liquid portion of the nucleoplasm is called the nucleosol or nuclear hyaloplasm.