
Brewing is the production of beer by steeping a starch source in water and fermenting the resulting sweet liquid with yeast. It may be done in a brewery by a commercial brewer, at home by a homebrewer, or communally. Brewing has taken place since around the 6th millennium BC, and archaeological evidence suggests that emerging civilizations, including ancient Egypt, China, and Mesopotamia, brewed beer. Since the nineteenth century the brewing industry has been part of most western economies.

Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.

An amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of starch but little sugar, such as rice and potatoes, may acquire a slightly sweet taste as they are chewed because amylase degrades some of their starch into sugar. The pancreas and salivary gland make amylase to hydrolyse dietary starch into disaccharides and trisaccharides which are converted by other enzymes to glucose to supply the body with energy. Plants and some bacteria also produce amylase. Specific amylase proteins are designated by different Greek letters. All amylases are glycoside hydrolases and act on α-1,4-glycosidic bonds.

Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by the fermentation of dough using wild lactobacillaceae and yeast. Lactic acid from fermentation imparts a sour taste and improves keeping qualities.

Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like Escherichia coli as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. S. cerevisiae cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding.

In brewing and distilling, mashing is the process of combining a mix of ground grains – typically malted barley with supplementary grains such as corn, sorghum, rye, or wheat – known as the "grain bill" with water and then heating the mixture. Mashing allows the enzymes in the malt to break down the starch in the grain into sugars, typically maltose to create a malty liquid called wort.
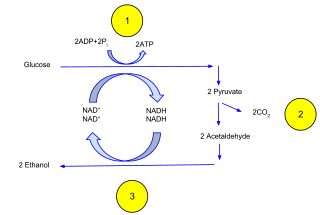
Ethanol fermentation, also called alcoholic fermentation, is a biological process which converts sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose into cellular energy, producing ethanol and carbon dioxide as by-products. Because yeasts perform this conversion in the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation is considered an anaerobic process. It also takes place in some species of fish where it provides energy when oxygen is scarce.

Komagataella is a methylotrophic yeast within the order Saccharomycetales. It was found in the 1960s as Pichia pastoris, with its feature of using methanol as a source of carbon and energy. In 1995, P. pastoris was reassigned into the sole representative of genus Komagataella, becoming Komagataella pastoris. Later studies have further distinguished new species in this genus, resulting in a total of 7 recognized species. It is not uncommon to see the old name still in use, as of 2023; in less formal use, the yeast may confusingly be referred to as pichia.
petite (ρ–) is a mutant first discovered in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Due to the defect in the respiratory chain, 'petite' yeast are unable to grow on media containing only non-fermentable carbon sources and form small colonies when grown in the presence of fermentable carbon sources. The petite phenotype can be caused by the absence of, or mutations in, mitochondrial DNA, or by mutations in nuclear-encoded genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation. A neutral petite produces all wild type progeny when crossed with wild type.

Amylolytic process or amylolysis is the conversion of starch into sugar by the action of acids or enzymes such as amylase.
Saccharomyces pastorianus is a yeast used industrially for the production of lager beer, and was named in honour of Louis Pasteur by the German Max Reess in 1870. This yeast's complicated genome appears to be the result of hybridisation between two pure species in the Saccharomyces species complex, a factor that led to difficulty in establishing a proper taxonomy of the species.
A yeast expression platform is a strain of yeast used to produce large amounts of proteins, sugars or other compounds for research or industrial uses. While yeast are often more resource-intensive to maintain than bacteria, certain products can only be produced by eukaryotic cells like yeast, necessitating use of a yeast expression platform. Yeasts differ in productivity and with respect to their capabilities to secrete, process and modify proteins. As such, different types of yeast are better suited for different research and industrial applications.
Scheffersomyces stipitis is a species of yeast, belonging to the "CUG Clade" of ascomycetous yeasts. This is a group of fungi that substitute serine for leucine when the CUG codon is encountered. S. stipitis is distantly related to brewer's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which uses the conventional codon system. Found, among other places, in the guts of passalid beetles, S. stipitis is capable of both aerobic and oxygen limited fermentation, and has the highest known natural ability of any yeast to directly ferment xylose, converting it to ethanol, a potentially economically valuable trait. Xylose is a hemicellulosic sugar found in all angiosperm plants. As such xylose constitutes the second most abundant carbohydrate moiety in nature. Xylose can be produced from wood or agricultural residues through auto- or acid hydrolysis. Ethanol production from such lignocellulosic residues does not compete with food production through the consumption of grain.

The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugars of the fruit into alcohol and carbon dioxide through the process of fermentation. The more sugars in the grapes, the higher the potential alcohol level of the wine if the yeast are allowed to carry out fermentation to dryness. Sometimes winemakers will stop fermentation early in order to leave some residual sugars and sweetness in the wine such as with dessert wines. This can be achieved by dropping fermentation temperatures to the point where the yeast are inactive, sterile filtering the wine to remove the yeast or fortification with brandy or neutral spirits to kill off the yeast cells. If fermentation is unintentionally stopped, such as when the yeasts become exhausted of available nutrients and the wine has not yet reached dryness, this is considered a stuck fermentation.
The α-mannan degradation Mannan which can be found in the cell wall of yeast has a particular chemical structure, and constitutes a food source since humans begun eating fermented foods several thousands of years ago. To determine whether the intake of yeast mannans through fermented foods has promoted specific adaptations of the human gut microbiota, an international team of researchers studied the ability of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron to specifically degrade yeast mannans.
Aerobic fermentation or aerobic glycolysis is a metabolic process by which cells metabolize sugars via fermentation in the presence of oxygen and occurs through the repression of normal respiratory metabolism. Preference of aerobic fermentation over aerobic respiration is referred to as the Crabtree effect in yeast, and is part of the Warburg effect in tumor cells. While aerobic fermentation does not produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in high yield, it allows proliferating cells to convert nutrients such as glucose and glutamine more efficiently into biomass by avoiding unnecessary catabolic oxidation of such nutrients into carbon dioxide, preserving carbon-carbon bonds and promoting anabolism.
Naganishia antarctica is a yeast species that has been isolated from soil in Antarctica.
Naganishia adeliensis is a species of fungus in the family Filobasidiaceae. It is currently only known from its yeast state, isolated from decaying algae in Antarctica.
Naganishia albidosimilis is a species of fungus in the family Filobasidiaceae. It is currently only known from its yeast state, isolated from soil in Antarctica.
Hanseniaspora osmophila is a species of yeast in the family Saccharomycetaceae. It is found in soil and among the bark, leaves, and fruits of plants, as well as fermented foods and beverages made from fruit.









