
The SETI Institute is a not-for-profit research organization incorporated in 1984 whose mission is to explore, understand, and explain the origin and nature of life in the universe, and to use this knowledge to inspire and guide present and future generations, sharing knowledge with the public, the press, and the government. SETI stands for the "search for extraterrestrial intelligence".
James Herbert Zumberge was a professor of geology and president of Grand Valley State University from 1962 to 1969, of Southern Methodist University from 1975 to 1980, and of the University of Southern California from 1980 to 1991.

The EarthScope project (2003-2018) was an National Science Foundation (NSF) funded Earth science program using geological and geophysical techniques to explore the structure and evolution of the North American continent and to understand the processes controlling earthquakes and volcanoes. The project had three components: USArray, the Plate Boundary Observatory, and the San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth. Organizations associated with the project included UNAVCO, the Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS), Stanford University, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Several international organizations also contributed to the initiative. EarthScope data are publicly accessible.

The China Geological Survey (CGS) (Chinese: 中国地质调查局) is a government-owned, not-for-profit, Chinese organization researching China's mineral resources. It is a public institution managed by the State Council's ministries and commissions responsible for geological and mineral exploration under the State Council of the People's Republic of China. According to the national land and resources survey plan, it is now managed by the Ministry of Natural Resources. It is the largest Geoscience agency in China since being reinstated in 1999, and the headquarter is in Beijing, the capital of China.
The US National Virtual Observatory'-NVO- was conceived to allow scientists to access data from multiple astronomical observatories, including ground and space-based facilities, through a single portal. Originally, the National Science Foundation (NSF) funded the information technology research that created the basic NVO infrastructure through a multi-organization collaborative effort. The NVO was more than a “digital library”; it was a vibrant, growing online research facility akin to a bricks-and-mortar observatory for professional astronomers.

The University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science is the undergraduate and graduate engineering school of the University of Virginia. Established in 1836, the school is the oldest university-affiliated engineering school in United States, and oldest engineering school in the Southern United States.
The Jackson School of Geosciences at The University of Texas at Austin unites the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences with two research units, the Institute for Geophysics and the Bureau of Economic Geology.
The National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis (NCEAS) is a research center at the University of California, Santa Barbara, in Santa Barbara, California. Better known by its acronym, NCEAS (pronounced “n-seas”) opened in May 1995. Funding for NCEAS is diverse and includes supporters such as the U.S. National Science Foundation, the State of California, and the University of California, Santa Barbara.
The University of California, Irvine has over fourteen academic divisions.

The College of Engineering (CoE) is one of the three undergraduate colleges at the University of California, Santa Barbara. The College offers a mid-sized, interdisciplinary environment where innovation drives the development of both fundamental science and applied technology solutions.
The Center for Microbial Oceanography (C-MORE) is a research and education organization established in 2006 as a National Science Foundation funded Science and Technology Center.
UNAVCO was a non-profit university-governed consortium that facilitated geology research and education using geodesy.
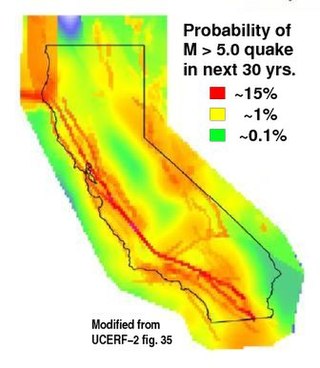
The 2008 Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast, Version 2, or UCERF2, is one of a series of earthquake forecasts prepared for the state California by the Working Group on California Earthquake Probabilities (WGCEP), collaboration of the U.S. Geological Survey, the California Geological Survey, and the Southern California Earthquake Center, with funding from the California Earthquake Authority. UCERF2 was superseded by UCERF3 in 2015.

The 2015 Uniform California Earthquake Rupture Forecast, Version 3, or UCERF3, is the latest official earthquake rupture forecast (ERF) for the state of California, superseding UCERF2. It provides authoritative estimates of the likelihood and severity of potentially damaging earthquake ruptures in the long- and near-term. Combining this with ground motion models produces estimates of the severity of ground shaking that can be expected during a given period, and of the threat to the built environment. This information is used to inform engineering design and building codes, planning for disaster, and evaluating whether earthquake insurance premiums are sufficient for the prospective losses. A variety of hazard metrics can be calculated with UCERF3; a typical metric is the likelihood of a magnitude M 6.7 earthquake in the 30 years since 2014.
Lisa D. White is an American geologist and director of Education and Outreach at the University of California Museum of Paleontology. White is a former professor of geosciences and associate dean of the College of Science and Engineering at San Francisco State University. She was elected to the California Academy of Sciences in 2000 and as a Fellow of the Geological Society of America in 2009. White was awarded her PhD in 1989 from the University of California, Santa Cruz. In 2022 the National Center for Science Education (NCSE) presented White with the 2022 "Friend of Darwin" award.
Christie D. Rowe is a Professor of Geology at McGill University. She holds a Canada Research Chair in Earthquake Geology and was awarded the 2017 Geological Association of Canada W. W. Hutchison Medal.

Emily E. Brodsky is a Professor of Earth Sciences at the University of California, Santa Cruz. She studies the fundamental physical properties of earthquakes, as well as the seismology of volcanoes and landslides. In 2023, she was elected to the National Academy of Sciences.
Joan S. Gomberg is a research geophysicist at the United States Geological Survey. She serves as an adjunct professor at the University of Washington. She is interested in subduction zone science, and studies how earthquakes trigger each other and how faults can slip. Gomberg is a Fellow of the American Geophysical Union. She was the first person to demonstrate how dynamic stress associated with seismic waves can trigger other earthquakes.

The Cascadia Region Earthquake Science Center (CRESCENT) is a research and educational collaboration between public and private universities, government agencies, and non-profits. The stated mission of the center is to (i) carry out basic and applied science research on earthquake hazards at the Cascadia Subduction Zone, (ii) promote access to careers in the geosciences, especially amongst minoritized individuals, and (iii) form partnerships between researchers and organizations in charge of response and planning for earthquake hazards.
Deborah Kuchnir Fygenson is an American biophysicist who is a professor at the University of California, Santa Barbara. She is interested in the physics of soft matter, and how DNA origami can be used to position spin centres for quantum technologies.










