
Indonesia's transport system has been shaped over time by the economic resource base of an archipelago with thousands of islands, and the distribution of its more than 200 million people concentrated mainly on a single island, Java.

The Autostrade are roads forming the Italian national system of motorways. The total length of the system is about 6,758 kilometres (4,199 mi). In North and Central Italy, the Autostrade mainly consists of tollways managed by Autostrade per l'Italia, a holding company controlled by Cassa Depositi e Prestiti. Other operators include ASTM, ATP, and Autostrade Lombarde in the north-west; Autostrada del Brennero, A4 Holding, Concessioni Autostradali Venete, and Autovie Venete in the north-east; Strada dei Parchi, SALT, SAT, and Autocisa in the center; and CAS in the south.

The Jakarta–Bogor–Ciawi Toll Road is the first toll road in Indonesia. Construction of the highway began in 1973, and it was officially opened on 9 March 1978.

Speed limits in the United States are set by each state or territory. States have also allowed counties and municipalities to enact typically lower limits. Highway speed limits can range from an urban low of 25 mph (40 km/h) to a rural high of 85 mph (137 km/h). Speed limits are typically posted in increments of five miles per hour (8 km/h). Some states have lower limits for trucks, some also have night and/or minimum speed limits.

A speed limit is the limit of speed allowed by law for road vehicles, usually the maximum speed allowed. Occasionally, there is a minimum speed limit. Advisory speed limits also exist, which are recommended but not mandatory speeds. Speed limits are commonly set by the legislative bodies of national or local governments.

The Jakarta–Cikampek Toll Road or Japek toll road is an expressway that was inaugurated in 1988. The highway links Jakarta with cities to its east in the province of West Java, in Indonesia.

Speed limits in the Philippines are specified in Republic Act No. 4136, or the Land Transportation and Traffic Code of the Philippines, which took effect on its approval on June 20, 1964. The act covers a number of areas other areas than speed limits, and was amended regarding some of those areas by Republic Act No. 10930, which was approved on August 2, 2017. As of 30 July 2022, RA 4136 is listed as current by the Land Transportation Office of the Philippines.

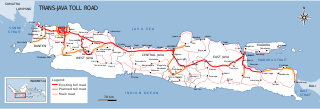
The Trans-Java Toll Road is a tolled expressway network that runs from Port of Merak in Cilegon, the main link between the island of Sumatra and Java, to Banyuwangi, the eastern end of the island in Indonesia and the main link between the island of Java and Bali. It mainly runs through the northern coast of the island, except for the section between Semarang and Surabaya, where it runs through the centre and south of the island. It runs through five of the six provinces on the island of Java, connecting the major cities of Jakarta, Cirebon, Semarang, Solo, and Surabaya. The toll road is the land transportation backbone of the island and is the most important toll road network of the country. The toll road has a total length of 1,167 kilometres (725 mi).
Jakarta Outer Ringroad 2 or JORR 2 is an under-construction toll road circling the Greater Jakarta area, running roughly parallel with the Jakarta Outer Ring Road in Indonesia. This toll road will connect Soekarno-Hatta International Airport to Cilincing, crossing Tangerang, South Tangerang, Depok, Bekasi, Bekasi Regency. and North Jakarta. It is expected to be able to relieve the traffic of other toll roads in the Greater Jakarta area.
Cileunyi-Sumedang-Dawuan Toll Road or Cisumdawu Toll Road is a toll road in West Java, Indonesia, which is currently under construction and expected to complete by 2022. This will be the only toll road in Indonesia that has two tunnel length of 472 metres (1,549 ft) each and a diameter of 14 metres (46 ft) in Section II. The toll road will pass through Cileunyi, Tanjung Sari, Sumedang, Cimalaka, Legok, Ujung Jaya and Kertajati. This toll road will connect Padaleunyi Toll Road with Palimanan-Kanci Toll Road. The toll road will connect Bandung with Kertajati International Airport, which opened in 2018.
Surabaya–Mojokerto Toll Road or Sumo Toll Road, is a part of Trans-Java toll road in Java, Indonesia, that length of the toll road is 36.1 kilometres.
Balikpapan–Samarinda Toll Road or Balsam Toll Road is an expressway which is constructed to connect Balikpapan with Samarinda of East Kalimantan, Indonesia as well as the proposed new capital city of the country.
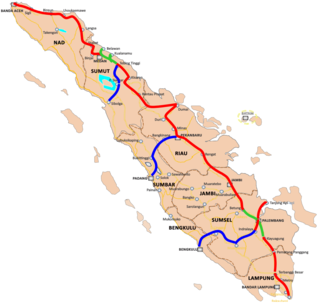
Trans-Sumatra Toll Road is an under-construction tolled expressway stretching across Sumatra Island in Indonesia from the northern tip of Banda Aceh to the southern tip of Bakauheni. This toll road was originally planned to connect to the established toll road system of Java through the now cancelled Sunda Strait Bridge. The toll road is to include supporting corridors connecting the cities of Padang, Bengkulu, and Sibolga on the western coast of the island to the main corridors stretching across the more populated eastern coast. State construction company Hutama Karya has been given a government-granted monopoly to operate the network.
Purwakarta–Bandung–Cileunyi Toll Road or shortened as Purbaleunyi Toll Road is a toll road in Indonesia, connecting Purwakarta Regency, West Bandung, Cimahi and the city and regency of Bandung.
Antasari-Depok, also known as the Depok-Antasari or Desari Toll Road is a highway in Java, Indonesia, connecting South Jakarta with Sawangan, Depok and Bojong Gede, Bogor.

Surabaya–Gempol Toll Road is a toll road in East Java, Indonesia. This 37 kilometers (23 mi) highway connects Surabaya City in the north with Porong in the south. This toll road passes Surabaya and Sidoarjo. It is part of the Trans-Java Expressway. The original length of this toll road from Surabaya to Gempol was 43 kilometers (27 mi) long, but the 6 kilometers (3.7 mi) part of this toll road is closed due to the overflow of Lapindo Mudflow that has inundated the Porong–Gempol section of the Surabaya–Gempol toll road since 2006.
Cengkang-Batu Ceper-Kunciran Toll Road is a toll road, which runs from Cengkareng to Kunciran in Greater Jakarta, Indonesia. This toll road is part of the Jakarta Outer Ring Road 2 network that will connect Soekarno-Hatta International Airport to Cilincing. The toll road will be connected to the Jakarta-Tangerang Toll Road, Kunciran-Serpong Toll Road, as well as Prof. Dr. Ir. Soedijatmo Toll Road.
Manado-Bitung Toll Road is a toll road that connects Manado and Bitung, two largest cities of North Sulawesi province in the island of Sulawesi, Indonesia. This toll road serves as the main access road to Bitung Special Economic Zone (SEZ) and Bitung International Hub Port.

Kayu Agung–Palembang–Betung Toll Road or Kapal Betung/Kapalbetung Toll Road is a 111.7-kilometre-long (69.4 mi) tolled expressway, which is part of Trans-Sumatra Toll Road. The toll road is managed by PT Waskita Sriwijaya Tol stretching from the township of Kayu Agung, passing through the major city of Palembang, and terminating at the township of Betung. The toll road connects Lampung–Palembang corridor with the Palembang–Jambi corridor of Trans-Sumatra Toll Road network.
Krian–Legundi–Bunder–Manyar Toll Road is a toll road that links Krian in Sidoarjo Regency with Manyar in Gresik Regency in East Java. The toll road is planned to be connected with Tuban–Gresik Toll Road at north and Surabaya–Mojokerto Toll Road at south. This toll road was designed to link industrial areas in Surabaya metropolitan area. The connectivity of KLBM Toll Road and Sumo Toll Road is expected to boost investment in Gresik Regency.










