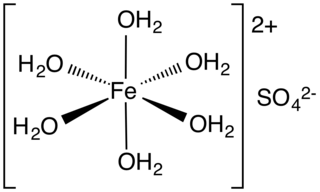
Iron(II) sulfate (British English: iron(II) sulphate) or ferrous sulfate denotes a range of salts with the formula FeSO4·xH2O. These compounds exist most commonly as the heptahydrate (x = 7) but are known for several values of x. The hydrated form is used medically to treat iron deficiency, and also for industrial applications. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol (vitriol is an archaic name for sulfate), the blue-green heptahydrate (hydrate with 7 molecules of water) is the most common form of this material. All the iron(II) sulfates dissolve in water to give the same aquo complex [Fe(H2O)6]2+, which has octahedral molecular geometry and is paramagnetic. The name copperas dates from times when the copper(II) sulfate was known as blue copperas, and perhaps in analogy, iron(II) and zinc sulfate were known respectively as green and white copperas.
Automatic process control in continuous production processes is a combination of control engineering and chemical engineering disciplines that uses industrial control systems to achieve a production level of consistency, economy and safety which could not be achieved purely by human manual control. It is implemented widely in industries such as oil refining, pulp and paper manufacturing, chemical processing and power generating plants.

The Souders–Brown equation has been a tool for obtaining the maximum allowable vapor velocity in vapor–liquid separation vessels. It has also been used for the same purpose in designing trayed fractionating columns, trayed absorption columns and other vapor–liquid-contacting columns.

In theoretical particle physics, maximally helicity violating amplitudes (MHV) are amplitudes with n massless external gauge bosons, where n–2 gauge bosons have a particular helicity and the other two have the opposite helicity. These amplitudes are called MHV amplitudes, because at tree level, they violate helicity conservation to the maximum extent possible. The tree amplitudes in which all gauge bosons have the same helicity or all but one have the same helicity vanish.
Trichophaea is a genus of fungi in the family Pyronemataceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1885 by French pharmacist Jean Louis Émile Boudier in 1885.

Parascutellinia is a genus of fungi in the family Pyronemataceae. It was circumscribed by mycologist Mirko Svrček in 1975, with P. violacea as the type species.

Chlorosplenium is a genus of fungi in the family Dermateaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Elias Magnus Fries in 1849.

Cudoniella is a genus of fungi in the family Helotiaceae. The genus contains an estimated 30 species. Cudoniella was circumscribed by mycologist Pier Andrea Saccardo in 1889.

Ombrophila is a genus of fungi in the Helotiaceae family. The genus contains 11 species. Elias Fries circumscribed Ombrophila in 1849.

Suillus lakei, commonly known as the matte Jack, Lake's bolete, or the western painted Suillus, is a species of fungus in the Suillaceae family. It is characterized by the distinctive reddish-brown tufted fibers or small scales on the cap, and the presence of a woolly veil on the stem. The caps can reach diameters of up to 15 cm (5.9 in), while the stems are between 6 to 12 cm long and usually 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) thick. On the underside of the cap is a layer of spongy yellow to yellow-brown angular pores; these pores are covered with a whitish partial veil when young. A mycorrhizal fungus, S. lakei grows in association with Douglas fir, and can be found where this tree occurs. It is native to northwestern North America, but has been introduced to Europe, South America, and New Zealand. The mushroom is edible, but opinions vary considerably as to its quality.

Pseudotomentella is a genus of corticioid fungi in the family Thelephoraceae. The genus was described by Czech mycologist Mirko Svrček in 1958.
Richard William George Dennis, Ph.D., was an English mycologist and plant pathologist.
František Kotlaba is a Czech botanist and mycologist.
Jan Švrček is a Czech professional ice hockey defenceman. He played with HC Sparta Prague in the Czech Extraliga during the 2010–11 Czech Extraliga season.

Xenasmatella is a genus of corticioid fungi in the order Polyporales. Circumscribed by German mycologist Franz Oberwinkler in 1966, the widespread genus contains 14 species.

Peziza fimeti is a species of ascomycete fungus belonging to the family Pezizaceae. Found in Europe and North America, the fungus grows on cow dung. It produces small, light brown, cup-shaped fruit bodies up to 2 cm (0.8 in) in diameter. The asci are cylindrical, with dimensions of up to 280 µm long and 18 µm in diameter. The spores are ellipsoid and measure 8 by 16 µm.
Lukáš Švrček is a professional Slovak footballer who currently plays for Fortuna Liga club MFK Skalica as a midfielder.
Egon Horak is an Austrian mycologist who has described more than 1000 species of fungi, including many from the Southern Hemisphere, particularly New Zealand and South America. He was an executive editor of the scientific journal Sydowia from 1975 to 1989, and a member of the editorial board afterwards.

Scutellinia subhirtella is a species of fungus belonging to the family Pyronemataceae. It was described as new to science in 1971 by Czech mycologist Mirko Svrček from specimens collected in the former Czechoslovakia. The yellowish-red to red fruitbodies of the fungus measure 2–5 mm (0.1–0.2 in) in diameter. Spores are hyaline (translucent), ellipsoid, and measure 18–22 by 12–14 μm.

The Level is a British crime drama, which began broadcasting on ITV on 30 September 2016. The six-part series focuses on DS Nancy Devlin, a detective with the National Crime Division, who is assigned to Brighton CID to investigate the murder of Frank Le Saux, a corrupt businessman with whom she has been associated in the past. Having been present at the scene of the murder, Nancy struggles to keep her involvement in the case a secret, whilst working under the watchful eye of boss DCI Michelle Newman. The series was predominantly filmed in and around the streets of Brighton. The series received consistent viewing figures throughout its run, and actress Karla Crome has suggested the possibility of a second series.













