
The Faboideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Fabaceae or Leguminosae. An acceptable alternative name for the subfamily is Papilionoideae, or Papilionaceae when this group of plants is treated as a family.

Diplotropis is a genus of trees found in Brazil and parts of northern Argentina.

Camoensia is a genus of 2 species of lianas in the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, native to the Gulf of Guinea, Africa. C. scandens is cultivated as an ornamental plant; it has one of the largest leguminous flowers, up to 20 cm across. The genus has classically been assigned to the tribe Sophoreae, but was recently assigned to its own monophyletic tribe, Camoensieae, on the basis of molecular phylogenetic evidence. Species of Camoensia are known to produce quinolizidine alkaloids, consistent with their placement in the genistoid clade.

Centrolobium is a Neotropical genus of legume in the family Fabaceae, assigned to the informal monophyletic Pterocarpus clade of the Dalbergieae. The genus comprises mostly large trees to 30 m tall, characterised by an abundance of orange peltate glands that cover most parts of the plant, and fruits that are large winged samaras to 30 cm long with a spiny basal seed chamber.

Leptolobium is a small Neotropical genus of plants in the family Fabaceae, with ten species currently recognized. With the exception of Leptolobium panamense, which occurs in tropical forests from northwestern South America to Mexico, all species of Leptolobium are restricted to South America and most diverse in Brazil. Most Leptolobium species have been traditionally included in AcosmiumSchott (Fabaceae), but both genera have been recently distinguished based on several vegetative and reproductive traits.
Guianodendron praeclarum is a South American legume endemic to the Guiana Shield. It is the only member of the genus Guianodendron. It has been segregated from Acosmium based on its unique combination of vegetative and floral traits, and it is related to Diplotropis.It is the only member of the genus Guianodendron.

Bowdichia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae.

Hymenolobium is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It was formerly assigned to the tribe Dalbergieae, but recent molecular phylogenetic evidence has placed it in a unique clade named the Andira clade.
Leucomphalos is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, found in west Africa. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. Leucomphalos was traditionally assigned to the tribe Sophoreae; however, recent molecular phylogenetic analyses reassigned Leucomphalos to the Baphieae tribe.
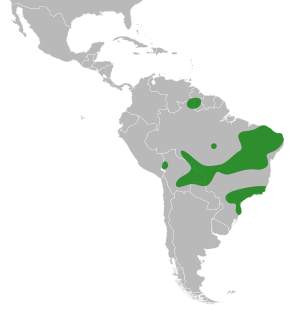
Luetzelburgia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It was traditionally assigned to the tribe Sophoreae, mainly on the basis of flower morphology; recent molecular phylogenetic analyses assigned Luetzelburgia into an informal, monophyletic clade called the "vataireoids". Keys for the different species of Luetzelburgia have been published.

The tribe Brongniartieae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae, primarily found in tropical regions of the Americas and in Australia The members of this tribe consistently form a monophyletic clade in molecular phylogenetic analyses. The tribe does not currently have a node-based definition, but morphological synapomorphies have been identified:
"stamens united by filaments in an adaxially open tube; anthers alternately long and basifixed, short and versatile; anther connective inconspicuous; septa present between seeds in pods; aril lateral lobe present and fitting into heel of funicle; fine red glandular processes present in axils; and pollen tricolporate with opercula and no definite endoaperture."

The tribe Dalbergieae is an early-branching clade within the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae. Within that subfamily, it belongs to an unranked clade called the dalbergioids. It was recently revised to include many genera formerly placed in tribes Adesmieae and Aeschynomeneae and to be included in a monophyletic group informally known as the dalbergioids sensu lato. The members of this tribe have a distinctive root nodule morphology, often referred to as an "aeschynomenoid" or "dalbergioid" nodule.

The tribe Podalyrieae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae.

Leptolobieae is a Neotropical, early-branching monophyletic clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae or Papilionaceae that are mostly found in South America.

The tribe Amburaneae is one of the subdivisions of the plant family Fabaceae. It has been circumscribed to include the following genera, which used to be placed in tribes Sophoreae and Swartzieae:
The Andira clade is a predominantly Neotropical, monophyletic clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae. The members of this clade were formerly included in tribe Dalbergieae, but this placement was questioned due to differences in wood anatomy and fruit, seed, seedling, floral, and vegetative characters. Recent molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown that they belong to a unique evolutionary lineage. It is predicted to have diverged from the other legume lineages in the late Eocene).

The Genistoids are one of the major radiations in the plant family Fabaceae. Members of this phylogenetic clade are primarily found in the Southern hemisphere. Some genera are pollinated by birds. The genistoid clade is consistently resolved as monophyletic in molecular phylogenetic analyses. It is estimated to have arisen 56.4 ± 0.2 million years ago. A node-based definition for the genistoids is: "the MRCA of Poecilanthe parviflora and Lupinus argenteus." One morphological synapomorphy has been tentatively identified: production of quinolizidine alkaloids. Some genera also accumulate pyrrolizidine. A new genus, to be segregated from Clathrotropis, has also been proposed to occupy an undetermined position within the genistoid clade.
Meso-Papilionoideae is a monophyletic clade of the flowering plant subfamily Faboideae that includes the majority of papilionoid legumes. This clade is consistently resolved in molecular phylogenies. It contains many agronomically important genera, including Arachis (peanut), Cicer (chickpea), Glycine (soybean), Medicago (alfalfa), Phaseolus, Trifolium (clover), Vicia (vetch), and Vigna.
Bowringia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, found in west Africa. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It was named after Sir John Bowring and his son, J. C. Bowring for their botanical work in China. Bowringia was traditionally assigned to the tribe Sophoreae; however, recent molecular phylogenetic analyses reassigned Bowringia to the Baphieae tribe.












