
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR).
In aviation, visual flight rules (VFR) are a set of regulations under which a pilot operates an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minima, i.e., in visual meteorological conditions (VMC), as specified in the rules of the relevant aviation authority. The pilot must be able to operate the aircraft with visual reference to the ground, and by visually avoiding obstructions and other aircraft.

Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airspace. The primary purpose of ATC is to prevent collisions, organize and expedite the flow of traffic in the air, and provide information and other support for pilots.
Aviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Articles related to aviation include:

Centennial Airport is a public use airport owned by the Arapahoe County Public Airport Authority in the Denver-Aurora metropolitan area, 15 nautical miles southeast of downtown Denver, Colorado, United States. Located in Dove Valley, a census designated place in Arapahoe County, the airport's runways extend into Douglas County.
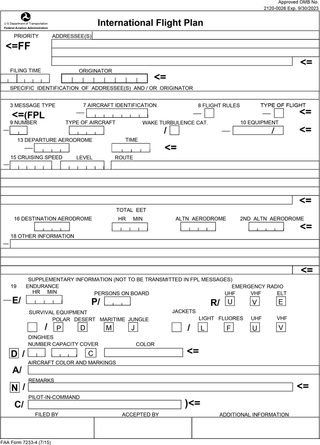
Flight plans are documents filed by a pilot or flight dispatcher with the local Air Navigation Service Provider prior to departure which indicate the plane's planned route or flight path. Flight plan format is specified in ICAO Doc 4444. They generally include basic information such as departure and arrival points, estimated time en route, alternate airports in case of bad weather, type of flight, the pilot's information, number of people on board, and information about the aircraft itself. In most countries, flight plans are required for flights under IFR, but may be optional for flying VFR unless crossing international borders. Flight plans are highly recommended, especially when flying over inhospitable areas such as water, as they provide a way of alerting rescuers if the flight is overdue. In the United States and Canada, when an aircraft is crossing the Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ), either an IFR or a special type of VFR flight plan called a DVFR flight plan must be filed. For IFR flights, flight plans are used by air traffic control to initiate tracking and routing services. For VFR flights, their only purpose is to provide needed information should search and rescue operations be required, or for use by air traffic control when flying in a "Special Flight Rules Area."

A flight service station (FSS) is an air traffic facility that provides information and services to aircraft pilots before, during, and after flights, but unlike air traffic control (ATC), is not responsible for giving instructions or clearances or providing separation. They do, however, relay clearances from ATC for departure or approaches. The people who communicate with pilots from an FSS are referred to as flight service specialists.

In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing, or to a point from which a landing may be made visually. These approaches are approved in the European Union by EASA and the respective country authorities and in the United States by the FAA or the United States Department of Defense for the military. The ICAO defines an instrument approach as "a series of predetermined maneuvers by reference to flight instruments with specific protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if landing is not completed, to a position at which holding or en route obstacle clearance criteria apply."

Flight planning is the process of producing a flight plan to describe a proposed aircraft flight. It involves two safety-critical aspects: fuel calculation, to ensure that the aircraft can safely reach the destination, and compliance with air traffic control requirements, to minimise the risk of midair collision. In addition, flight planners normally wish to minimise flight cost through the appropriate choice of route, height, and speed, and by loading the minimum necessary fuel on board. Air Traffic Services (ATS) use the completed flight plan for separation of aircraft in air traffic management services, including tracking and finding lost aircraft, during search and rescue (SAR) missions.

The Canada Flight Supplement (CFS) is a joint civil/military publication and is a supplement of the Aeronautical Information Publication. It is the nation's official airport directory. It contains information on all registered Canadian and certain Atlantic aerodromes and certified airports.

Area navigation is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from the beacons. This can conserve flight distance, reduce congestion, and allow flights into airports without beacons. Area navigation used to be called "random navigation", hence the acronym RNAV.

Perth Airport is a general-aviation airport located at New Scone, 3 nautical miles northeast of Perth, Scotland. The airport is used by private and business aircraft, and for pilot training. There are no commercial scheduled flights from the airport.

In aviation, a standard terminal arrival route (STAR) is a published flight procedure followed by aircraft on an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan just before reaching a destination airport.
An aeronautical chart is a map designed to assist in the navigation of aircraft, much as nautical charts do for watercraft, or a roadmap does for drivers. Using these charts and other tools, pilots are able to determine their position, safe altitude, best route to a destination, navigation aids along the way, alternative landing areas in case of an in-flight emergency, and other useful information such as radio frequencies and airspace boundaries. There are charts for all land masses on Earth, and long-distance charts for trans-oceanic travel.
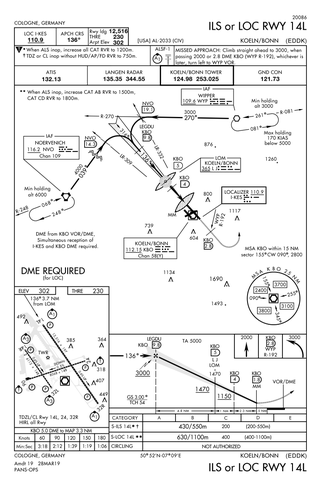
Approach plates are the printed or digital charts of instrument approach procedures that pilots use to fly instrument approaches during instrument flight rules (IFR) operations. Each country maintains its own instrument approach procedures according to International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards.

San Martin Airport — formerly Q99 — is a public non-towered airport located 1 mi (1.6 km) east of San Martin, serving Santa Clara County, California, United States. This general aviation airport covers 179 acres (72 ha) and has one runway. A self-service fueling facility offers 94UL aviation gasoline continuously. Jet-A fuel is available from a full-service truck during FBO operating hours, and major airframe and powerplant service are available. San Martin Aviation is the fixed-base operator (FBO) at South County, serving aviation fuels and aircraft & hangar maintenance.

In aviation, a visual approach is an approach to a runway at an airport conducted under instrument flight rules (IFR) but where the pilot proceeds by visual reference and clear of clouds to the airport. The pilot must at all times have either the airport or the preceding aircraft in sight. This approach must be authorized and under the control of the appropriate air traffic control (ATC) facility. The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) definition adds that the visual approach can commence when "either part or all of an instrument approach is not completed", varying only slightly from the Federal Aviation Administration regulation and is essentially identical.
The Cape TRACON (K90) is a radar approach facility located at Joint Base Cape Cod, Massachusetts next to the airfield for Coast Guard Air Station Cape Cod. It is operated by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).

ForeFlight is an electronic flight bag for iOS and iPadOS devices designed to assist pilots and corporate flight departments with flight planning. It includes information about facilities such as airports, NAVAIDs, and air traffic control facilities. It also aids pilots in tasks including flight planning, weather monitoring, and document management, as well as an electronic logbook to help pilots record flight time. The United States, Canada, and Europe are supported regions. The company was founded in 2007 and has since been purchased by Boeing.

Obstacle departure procedure (ODP) is a type of departure procedure that provides obstruction clearance via the least onerous route from an airport to an appropriate en-route structure. Pilots can fly ODPs without prior clearance unless assigned a standard instrument departure or radar vectored by air traffic controllers.
















