Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are genetically engineered chromosomes derived from the DNA of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is then ligated into a bacterial plasmid. By inserting large fragments of DNA, from 100–1000 kb, the inserted sequences can be cloned and physically mapped using a process called chromosome walking. This is the process that was initially used for the Human Genome Project, however due to stability issues, YACs were abandoned for the use of bacterial artificial chromosome

A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multidomain enzymes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain.
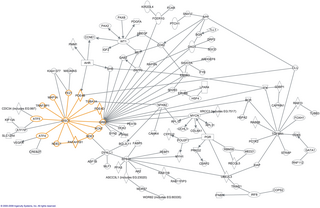
In molecular biology, an interactome is the whole set of molecular interactions in a particular cell. The term specifically refers to physical interactions among molecules but can also describe sets of indirect interactions among genes.

Hans Victor Westerhoff is a Dutch biologist and biochemist who is professor of synthetic systems biology at the University of Amsterdam and AstraZeneca professor of systems biology at the University of Manchester. Currently he is a Chair of AstraZeneca and a director of the Manchester Centre for Integrative Systems Biology.
Gerald Mayer Rubin is an American biologist, notable for pioneering the use of transposable P elements in genetics, and for leading the public project to sequence the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Related to his genomics work, Rubin's lab is notable for development of genetic and genomics tools and studies of signal transduction and gene regulation. Rubin also served as a vice president of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (2003–2020) and founding executive director of its Janelia Research Campus.
Richard I. Morimoto is a Japanese American molecular biologist. He is the Bill and Gayle Cook Professor of Biology and Director of the Rice Institute for Biomedical Research at Northwestern University.

Christopher Paul Ponting is a British computational biologist, specializing in the evolution and function of genes and genomes. He is currently Chair of Medical Bioinformatics at the University of Edinburgh and group leader in the MRC Human Genetics Unit. He is also an Associate Faculty member of the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, a Fellow of the Academy of Medical Sciences, member of the European Molecular Biology Organisation and Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. His research focuses on long noncoding RNA function and evolution, on single cell biology and on disease genomics. Outside of science, Chris is an amateur novelist and wrote an unpublished, science fiction novel about engineered viruses.

Douglas Bruce Kell is a British biochemist and Professor of Systems Biology in the Institute of Systems, Molecular and Integrative Biology at the University of Liverpool. He was previously at the School of Chemistry at the University of Manchester, based in the Manchester Institute of Biotechnology (MIB) where he founded and led the Manchester Centre for Integrative Systems Biology (MCISB). He served as chief executive officer (CEO) of the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) from 2008 to 2013.
Robot Scientist is a laboratory robot created and developed by a group of scientists including Ross King, Kenneth Whelan, Ffion Jones, Philip Reiser, Christopher Bryant, Stephen Muggleton, Douglas Kell, Emma Byrne and Steve Oliver.
Bernhard Örn Pálsson is the Galletti Professor of Bioengineering and an adjunct professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Gerard Ian Evan FRS, FMedSci is a British biologist and, since May 2022, Professor of Cancer Biology at King's College London and a principal group leader in the Francis Crick Institute. Prior to this he was Sir William Dunn Professor of Biochemistry and Head of Biochemistry at the University of Cambridge (2009-2022).

Ross Donald King is a Professor of Machine Intelligence at Chalmers University of Technology.
Norman William Paton is a Professor in the Department of Computer Science at the University of Manchester in the UK where he co-leads the Information Management Group (IMG) with Carole Goble.

Stephen Robert Pettifer is a Professor in the Department of Computer Science at the University of Manchester in England.

Julian Parkhill is Professor of Bacterial Evolution in the Department of Veterinary Medicine at the University of Cambridge. He previously served as head of pathogen genomics at the Wellcome Sanger Institute.

Peter D. Keightley is a British geneticist who is Professor of Evolutionary Genetics at the Institute of Evolutionary Biology in School of Biological Sciences at the University of Edinburgh.
David S. Broomhead was a British mathematician specialising in dynamical systems and was professor of applied mathematics at the School of Mathematics, University of Manchester.

Peter Malcolm Colman is the head of the structural biology division at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research in Melbourne, Australia.

Robin Campbell Allshire is a British academic who is Professor of Chromosome Biology at University of Edinburgh and a Wellcome Trust Principal Research Fellow. His research group at the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell Biology focuses on the epigenetic mechanisms governing the assembly of specialised domains of chromatin and their transmission through cell division.

Peter Karl Sorger is a systems and cancer biologist and Otto Krayer Professor of Systems Pharmacology in the Department of Systems Biology at Harvard Medical School. Sorger is the founding head of the Harvard Program in Therapeutic Science (HiTS), director of its Laboratory of Systems Pharmacology (LSP), and co-director of the Harvard MIT Center for Regulatory Science. He was previously a Professor of Biology and Biological Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology where he co-founded its program on Computational and Systems Biology (CSBi). Sorger is known for his work in the field of systems biology and for having helped launch the field of computational and systems pharmacology. His research focuses on the molecular origins of cancer and approaches to accelerate the development of new medicines. Sorger teaches Principles and Practice of Drug Development at Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard University.