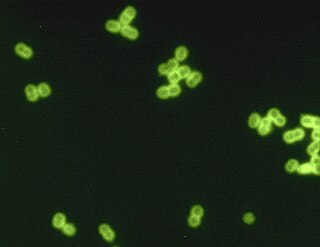
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic or beta-hemolytic, facultative anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not form spores and are non motile. As a significant human pathogenic bacterium S. pneumoniae was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies.

Lactococcus lactis is a Gram-positive bacterium used extensively in the production of buttermilk and cheese, but has also become famous as the first genetically modified organism to be used alive for the treatment of human disease. L. lactis cells are cocci that group in pairs and short chains, and, depending on growth conditions, appear ovoid with a typical length of 0.5 - 1.5 µm. L. lactis does not produce spores (nonsporulating) and are not motile (nonmotile). They have a homofermentative metabolism, meaning they produce lactic acid from sugars. They've also been reported to produce exclusive L-(+)-lactic acid. However, reported D-(−)-lactic acid can be produced when cultured at low pH. The capability to produce lactic acid is one of the reasons why L. lactis is one of the most important microorganisms in the dairy industry. Based on its history in food fermentation, L. lactis has generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, with few case reports of it being an opportunistic pathogen.
Streptococcus bovis is a species of Gram-positive bacteria that in humans is associated with urinary tract infections, endocarditis, sepsis, and colorectal cancer. S. gallolyticus is commonly found in the alimentary tract of cattle, sheep, and other ruminants, and may cause ruminal acidosis or feedlot bloat. It is also associated with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, a frequent complication occurring in patients affected by cirrhosis. Equivalence with Streptococcus equinus has been contested.
Streptococcus sanguinis, formerly known as Streptococcus sanguis, is a Gram-positive facultative anaerobic coccus species of bacteria and a member of the Viridans Streptococcus group. S. sanguinis is a normal inhabitant of the healthy human mouth where it is particularly found in dental plaque, where it modifies the environment to make it less hospitable for other strains of Streptococcus that cause cavities, such as Streptococcus mutans.
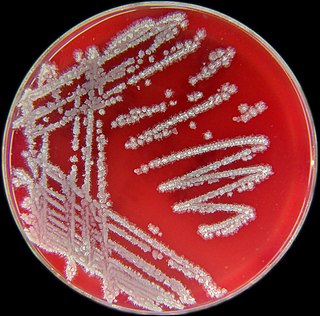
Bacillus licheniformis is a bacterium commonly found in the soil. It is found on bird feathers, especially chest and back plumage, and most often in ground-dwelling birds and aquatic species.
Streptococcus equinus is a Gram-positive, nonhemolytic, nonpathogenic, lactic acid bacterium of the genus Streptococcus. It is the principal Streptococcus found in the alimentary canal of a horse, and makes up the majority of the bacterial flora in horse feces. S. equinus is seldom found in humans. Equivalence with Streptococcus bovis has been contested.

Streptococcus dysgalactiae is a gram positive, beta-haemolytic, coccal bacterium belonging to the family Streptococcaceae. It is capable of infecting both humans and animals, but is most frequently encountered as a commensal of the alimentary tract, genital tract, or less commonly, as a part of the skin flora. The clinical manifestations in human disease range from superficial skin-infections and tonsillitis, to severe necrotising fasciitis and bacteraemia. The incidence of invasive disease has been reported to be rising. Several different animal species are susceptible to infection by S. dysgalactiae, but bovine mastitis and infectious arthritis in lambs have been most frequently reported.
Streptococcus zooepidemicus is a Lancefield group C streptococcus that was first isolated in 1934 by P. R. Edwards, and named Animal pyogens A. It's a mucosal commensal and opportunistic pathogen that infects several animals and humans, but most commonly isolated from the uterus of mares. It's a subspecies of Streptococcus equi, a contagious upper respiratory tract infection of horses, and shares greater than 98% DNA homology, as well as many of the same virulence factors.

Maqsudul Alam was a Bangladeshi-born life-science scientist who is known for his work on genome sequencing. His work on genome sequencing started with bacteria Idiomarina loihiensis in 2003. He came into the focus of Bangladeshi people after his work on genome sequencing of tosha jute in 2010, white jute in 2013 and jute attacking fungus in 2012.
In molecular biology, Streptococcus sRNAs are small RNAs produced by species of Streptococcus bacteria. Several screens have identified numerous sRNAs in different species and strains of Streptococcus including S. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae and S.mutans. The function of most of these is currently unknown, however a few have been characterised including FasX small RNA. Many sRNAs have roles in pathogenesis.

Lancefield grouping is a system of classification that classifies catalase-negative Gram-positive cocci based on the carbohydrate composition of bacterial antigens found on their cell walls. The system, created by Rebecca Lancefield, was historically used to organize the various members of the family Streptococcaceae, which includes the genera Lactococcus and Streptococcus, but now is largely superfluous due to explosive growth in the number of streptococcal species identified since the 1970s. However, it has retained some clinical usefulness even after the taxonomic changes, and as of 2018, Lancefield designations are still often used to communicate medical microbiological test results in the United States.
Roseobacter litoralis is a species of aerobic pink-pigmented bacteria. It contains Bacteriochlorophyll a. It contains spheroidenone, does not synthesize bacteriochlorophyll anaerobically, but shows aerobic phototrophic activity. Cells are ovoid or rod-shaped and motile by subpolar flagella. R. litoralis does not reduce nitrate, while R. dentrificans does.
Thermacetogenium phaeum is a bacterium, the type species of its genus. It is strictly anaerobic, thermophilic, syntrophic and acetate-oxidizing. Its cells are gram-positive, endospore-forming and rod-shaped. Its type strain is PBT. It has a potential biotechnological role.
Cronobacter turicensis is a bacterium. It is usually food-borne and pathogenic. It is named after Turicum, the Latin name of Zurich, as the type strain originates from there. Its type strain is strain 3032. This strain was first isolated from a fatal case of neonatal meningitis. C. Turicensis strains are indole negative but malonate, dulcitol and methyl-α-D-glucopyranoside positive.
Pelobacter carbinolicus is a species of bacteria that ferments 2,3-butanediol and acetoin. It is Gram-negative, strictly anaerobic and non-spore-forming. Gra Bd 1 is the type strain. Its genome has been sequenced.
Helicobacter canadensis is a bacterium in the Helicobacteraceae family, Campylobacterales order, first isolated from humans with diarrhea. Its genome has been sequenced.
Geobacter psychrophilus is a Fe(III)-reducing bacterium. It is Gram-negative, slightly curved, rod-shaped and motile via means of monotrichous flagella. Its type strain is P35T.
Methylophaga thalassica is an obligately methylotrophic, Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, motile, rod-shaped bacteria. Its type strain is ATCC 33146.





