
The Actinomycetota are a phylum of mostly Gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to soil systems. In soil they help to decompose the organic matter of dead organisms so the molecules can be taken up anew by plants. While this role is also played by fungi, Actinomycetota are much smaller and likely do not occupy the same ecological niche. In this role the colonies often grow extensive mycelia, like a fungus would, and the name of an important order of the phylum, Actinomycetales, reflects that they were long believed to be fungi. Some soil actinomycetota live symbiotically with the plants whose roots pervade the soil, fixing nitrogen for the plants in exchange for access to some of the plant's saccharides. Other species, such as many members of the genus Mycobacterium, are important pathogens.

Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinobacteria and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinobacteria, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin.

Streptomyces griseus is a species of bacteria in the genus Streptomyces commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other streptomycetes, S. griseus strains are well known producers of antibiotics and other such commercially significant secondary metabolites. These strains are known to be producers of 32 different structural types of bioactive compounds. Streptomycin, the first antibiotic ever reported from a bacterium, comes from strains of S. griseus. Recently, the whole genome sequence of one of its strains had been completed.
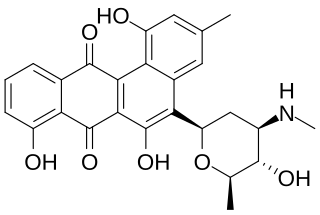
Mayamycin is a cytotoxic polyketide isolated from a marine Streptomyces.
Streptomyces thermocarboxydovorans is a streptomycete bacterium species. It is moderately thermophilic and carboxydotrophic, with type strain AT52.
Streptomyces thermocarboxydus is a streptomycete bacterium species. It is moderately thermophilic and carboxydotrophic, with type strain AT37.
Naphthomycins are a group of closely related antimicrobial chemical compounds isolated from Streptomyces. They are considered a subclass of ansamycins.
Streptomyces antibioticus is a gram-positive bacterium discovered in 1941 by Nobel-prize-winner Selman Waksman and H. Boyd Woodruff. Its name is derived from the Greek "strepto-" meaning "twisted", alluding to this genus' chain-like spore production, and "antibioticus", referring to this species' extensive antibiotic production. Upon its first characterization, it was noted that S. antibioticus produces a distinct soil odor.
Streptomyces cavourensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Italy. Streptomyces cavourensis produces flavensomycin.
Streptomyces collinus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Baden in Germany. Streptomyces collinus produces ansatrienin A2, ansatrienin A3, ansatrienin B, naphthomycin A, collinomycine, toromycin, streptocollin, kirromycin and rubromycine.
Streptomyces diastaticus is an alkaliphilic and thermophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces diastaticus produces oligomycin A, oligomycin C, rimocidin and the leukotriene-A4 hydrolase-inhibitor 8(S)-amino-2(R)-methyl-7-oxononanoic acid. Streptomyces diastaticus also produces gougerotin and the antibiotic ruticin.
Streptomyces diastatochromogenes is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces diastatochromogenes produces polyketomycin, concanamycin A, concanamycin B, concanamycin C, momofulvenone A, azdimycin, toyocamycin and oligomycins.
Streptomyces griseoruber is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Japan. Streptomyces griseoruber produces beromycin, actinomycin D, gombapyrone A, gombapyrone B, gombapyrone C, gombapyrone D and rhodomycins
Streptomyces microflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces microflavus produces nemadectin, fattiviracin A1, milbemycin and deoxyuridines. Streptomyces microflavus also produces the ionophore valinomycin. Streptomyces microflavus is also known to cause potato common scab disease in Korea.
Streptomyces pseudovenezuelae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from lead polluted soil in China. Streptomyces pseudovenezuelae produces chloramphenicol and setomimycin.
Streptomyces sanglieri is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from a hay meadow. Streptomyces sanglieri produces the antibiotic lactonamycin Z.
Streptomyces seoulensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Korea. Streptomyces seoulensis produces lipoamide dehydrogenase.
Streptomyces staurosporininus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from hay meadow soil from the Cockle Park Experimental Farm in Northumberland in the United Kingdom. Streptomyces staurosporininus produces the antibiotic, staurosporine.
Streptomyces violaceusniger is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces violaceusniger has antifungal activity. Streptomyces violaceusniger produces isoafricanol and spirofungin.
Streptomyces lasiicapitis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from the head of the ant Lasius fuliginosus. Streptomyces lasiicapitis produces the antibiotic kanchanamycin.



