In biochemistry, isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed. The general form of such a reaction is as follows:

Fuculose or 6-deoxy-tagatose is a ketohexose deoxy sugar. Fuculose is involved in the process of sugar metabolism. l-Fuculose can be formed from l-fucose by l-fucose isomerase and converted to L-fuculose-1-phosphate by l-fuculose kinase.
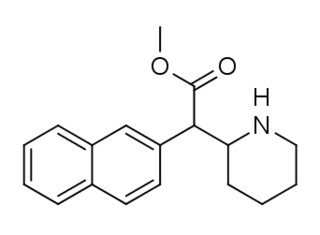
HDMP-28 or methylnaphthidate is a piperidine based stimulant drug, closely related to methylphenidate, but with the benzene ring replaced by naphthalene. It is a potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor, with several times the potency of methylphenidate and a short duration of action, and is a structural isomer of another potent dopamine reuptake inhibitor, N,O-Dimethyl-4-(2-naphthyl)piperidine-3-carboxylate. It has been sold as a designer drug since around 2015.

Enediynes are organic compounds containing two triple bonds and one double bond.

Sorbinil (INN) is an aldose reductase inhibitor being investigated for treatment of diabetic complications including neuropathy and retinopathy. Aldose reductase is an enzyme present in lens and brain that removes excess glucose by converting it to sorbitol. Sorbitol accumulation can lead to the development of cataracts in the lens and neuropathy in peripheral nerves. Sorbinil has been shown to inhibit aldose reductase in human brain and placenta and calf and rat lens. Sorbinil reduced sorbitol accumulation in rat lens and sciatic nerve of diabetic rats orally administered 0.25 mg/kg sorbinil.
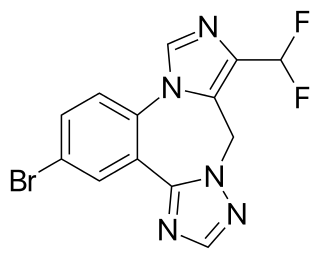
Ro4938581 is a nootropic drug invented in 2009 by a team working for Hoffmann-La Roche, which acts as a subtype-selective inverse agonist at the α5 subtype of the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor. It has good selectivity for the α5 subtype and did not produce convulsant or anxiogenic effects in animal studies, making it a promising potential nootropic. Ro4938581 and a related derivative basmisanil have subsequently been investigated for the alleviation of cognitive dysfunction in Down syndrome.
Elaiomycin is an antimicrobial chemical compound, classified as an conjugated azoxyalkene, which was first isolated from Streptomyces in 1954. A laboratory synthesis of elaiomycin was reported in 1977.
Gliflozins are a class of drugs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes (T2D). They act by inhibiting sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2), and are therefore also called SGLT-2 inhibitors. The efficacy of the drug is dependent on renal excretion and prevents glucose from going into blood circulation by promoting glucosuria. The mechanism of action is insulin independent.

In enzymology, a xylose isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of D-xylose and D-xylulose. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases interconverting aldoses and ketoses. The isomerase has now been observed in nearly a hundred species of bacteria. Xylose-isomerases are also commonly called fructose-isomerases due to their ability to interconvert glucose and fructose. The systematic name of this enzyme class is D-xylose aldose-ketose-isomerase. Other names in common use include D-xylose isomerase, D-xylose ketoisomerase, and D-xylose ketol-isomerase.
Streptomyces bobili is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from garden soil. Streptomyces bobili produces aclacinomycin A, aclacinomycin B, aclacinomycin M, aclacinomycin S, aclacinomycin Y, cinerubin A, cinerubin B, sulfurmycin A, sulfurmycin B, sulfurmycin C, sulfurmycin D, sulfurmycin F, ferrimycin A1 and ferrimycin A2.
Streptomyces griseoloalbus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces griseoloalbus produces grisein.
Streptomyces lusitanus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces lusitanus produces 7-chlortetracycline, naphthyridinomycin, cyanocycline B, N-desmethylnaphthyridinomycin and tetracycline.
Streptomyces microflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces microflavus produces nemadectin, fattiviracin A1, milbemycin and deoxyuridines. Streptomyces microflavus also produces the ionophore valinomycin. Streptomyces microflavus is also known to cause potato common scab disease in Korea.
Streptomyces murinus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces murinus produces the actinomycin X complex and glucose isomerase Streptomyces murinus can be used for its production of glucose isomerase in the food industry. Streptomyces murinus produces lankamycin and lankacidin.
Streptomyces nashvillensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces nashvillensis produces tetrodecamycin and bellenamine.
Streptomyces rubiginosus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces rubiginosus produces glucose isomerase. glucose isomerase from Streptomyces rubiginosus can be used to texture fish and meat products.
Streptomyces varsoviensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces varsoviensis produces oxytetracycline and hygrobafilomycin.

C-1027 or lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks.
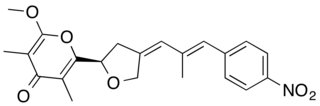
Aureothin is a natural product of a cytotoxic shikimate-polyketide antibiotic with the molecular formula C22H23NO6. Aureothin is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces thioluteus that illustrates antitumor, antifungal, and insecticidal activities and the new aureothin derivatives can be antifungal and antiproliferative. In addition, aureothin, a nitro compound from Streptomyces thioluteus, was indicated to have pesticidal activity against the bean weevil by interfering with mitochondrial respiratory complex II.
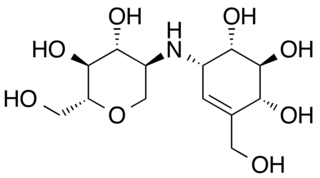
Salbostatin is an antibiotic and trehalase inhibitor with the molecular formula C13H23O8. Salbostatin is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces albus.








