
Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have very large genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Different strains of the same species may colonize very diverse environments.

Glufosinate is a naturally occurring broad-spectrum herbicide produced by several species of Streptomyces soil bacteria. Glufosinate is a non-selective, contact herbicide, with some systemic action. Plants may also metabolize bialaphos and phosalacine, other naturally occurring herbicides, directly into glufosinate. The compound irreversibly inhibits glutamine synthetase, an enzyme necessary for the production of glutamine and for ammonia detoxification, giving it antibacterial, antifungal and herbicidal properties. Application of glufosinate to plants leads to reduced glutamine and elevated ammonia levels in tissues, halting photosynthesis and resulting in plant death.

Streptomyces griseus is a species of bacteria in the genus Streptomyces commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other streptomycetes, S. griseus strains are well known producers of antibiotics and other such commercially significant secondary metabolites. These strains are known to be producers of 32 different structural types of bioactive compounds. Streptomycin, the first antibiotic ever reported from a bacterium, comes from strains of S. griseus. Recently, the whole genome sequence of one of its strains had been completed.

Streptomyces hygroscopicus is a bacterial species in the genus Streptomyces. It was first described by Hans Laurits Jensen in 1931.

Common scab is a plant disease of root and tuber crops caused by a small number of Streptomyces species, specifically S. scabies, S. acidiscabies, S. turgidiscabies and others. Common scab mainly affects potato, but can also cause disease on radish, parsnip, beet, and carrot. This plant disease is found wherever these vegetables are grown.
Streptomyces thermocarboxydovorans is a streptomycete bacterium species. It is moderately thermophilic and carboxydotrophic, with type strain AT52.
Streptomyces thermocarboxydus is a streptomycete bacterium species. It is moderately thermophilic and carboxydotrophic, with type strain AT37.
Streptomyces cinnamoneus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Japan. Streptomyces cinnamoneus produces duramycin A, duramycin B, duramycin C, carbomycin, cinnomycin and fungichromin.
Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Daghestan in Russia. Streptomyces cyaneofuscatus can be used for valinomycin biosynthesis.
Streptomyces iakyrus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil Streptomyces iakyrus produces actinomycin G2, actinomycin G3, actinomycin G4, actinomycin G5, actinomycin G6, iakirine I, iakirine II and iakirine III.
Streptomyces ipomoeae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from rot from potatoes. Streptomyces ipomoeae produces thaxtomin C and ipomycin. Streptomyces ipomoeae can cause soft rot disease on sweet potatoes.
Streptomyces rochei is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces rochei produces borrelidin, butyrolactol A, butyrolactol B, uricase and streptothricin. Streptomyces rochei has antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici and Aspergillus fumigatus. Streptomyces rochei produces moenomycin and bambermycin. Streptomyces rochei produces amicetin A, amicetin B, amicetin C and streptolin. Streptomyces rochei produces endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase mithramycin, amicetin, bamicetin, and plicacetin.
Streptomyces violarus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Egypt. It is a mesophilic bacterium that produces antibiotic compounds.
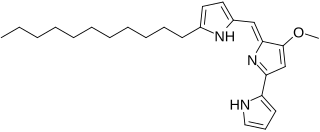
Undecylprodigiosin is an alkaloid produced by some Actinomycetes bacteria. It is a member of the prodiginines group of natural products and has been investigated for potential antimalarial activity.
Streptomyces altiplanensis is an alkalitolerant bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Salar del Huasco in the Atacama Desert.
Streptomyces dangxiongensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China.
Streptomyces fodineus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from a mine. Streptomyces fodineus has antifungal properties.
Streptomyces cadmiisoli is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil which was contaminated with cadmium.
Streptomyces cyaneochromogenes is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces.
Streptomyces inhibens is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from rhizospheric soil of a wheat plant from the Northeast Agricultural University.





