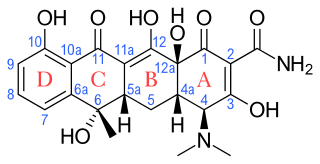Oxytetracycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic, the second of the group to be discovered.

Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota, and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 700 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have very large genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Different strains of the same species may colonize very diverse environments.
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotic compounds that have a common basic structure and are either isolated directly from several species of Streptomyces bacteria or produced semi-synthetically from those isolated compounds. Tetracycline molecules comprise a linear fused tetracyclic nucleus to which a variety of functional groups are attached. Tetracyclines are named after their four ("tetra-") hydrocarbon rings ("-cycl-") derivation ("-ine"). They are defined as a subclass of polyketides, having an octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide skeleton and are known as derivatives of polycyclic naphthacene carboxamide. While all tetracyclines have a common structure, they differ from each other by the presence of chloro, methyl, and hydroxyl groups. These modifications do not change their broad antibacterial activity, but do affect pharmacological properties such as half-life and binding to proteins in serum.

Streptomyces griseus is a species of bacteria in the genus Streptomyces commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other streptomycetes, S. griseus strains are well known producers of antibiotics and other such commercially significant secondary metabolites. These strains are known to be producers of 32 different structural types of bioactive compounds. Streptomycin, the first antibiotic ever reported from a bacterium, comes from strains of S. griseus. Recently, the whole genome sequence of one of its strains had been completed.
Streptomyces rimosus is a bacterium species in the genus Streptomyces.
Streptomyces albidoflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Poland. Streptomyces albidoflavus produces dibutyl phthalate and streptothricins.
Streptomyces albofaciens is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which produces oxytetracycline, spiramycin, albopeptin A, albopeptin B and alpomycin.
Streptomyces alboflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which produces oxytetracycline, tetracycline and desertomycin A.
Streptomyces bikiniensis is a bacterium species from the genus Streptomyces which has isolated from soil from the island Bikini atoll. Streptomyces bikiniensis produces streptomycin II and carboxypeptidase.
Streptomyces cinnamoneus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Japan. Streptomyces cinnamoneus produces duramycin A, duramycin B, duramycin C, carbomycin, cinnomycin and fungichromin.
Streptomyces diastaticus is an alkaliphilic and thermophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces diastaticus produces oligomycin A, oligomycin C, rimocidin and the leukotriene-A4 hydrolase-inhibitor 8(S)-amino-2(R)-methyl-7-oxononanoic acid. Streptomyces diastaticus also produces gougerotin and diastaphenazine and the antibiotic ruticin.
Streptomyces halstedii is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from deeper soil layers. Streptomyces halstedii produces magnamycin B, vicenistatin deltamycin A2, deltamycin A3, bafilomycin B1 and bafilomycin C1. Streptomyces halstedii also produces complex antifungal antibiotics like oligomycins and the antibiotics anisomycin and sinefungin.
Streptomyces hiroshimensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces hiroshimensis produces the red pigment prodigiosin.
Streptomyces nogalater is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces nogalater produces nogalamycin.
Streptomyces platensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces platensis produces oxytetracycline, platensimycin, migrastatin, isomigrastatin, platencin, dorrigocin A, dorrigocin B and terramycine.
Streptomyces rochei is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces rochei produces borrelidin, butyrolactol A, butyrolactol B, uricase and streptothricin. Streptomyces rochei has antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici and Aspergillus fumigatus. Streptomyces rochei produces moenomycin and bambermycin. Streptomyces rochei produces amicetin A, amicetin B, amicetin C and streptolin. Streptomyces rochei produces endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase mithramycin, amicetin, bamicetin, and plicacetin.
Streptomyces speibonae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Cape Town in South Africa. Streptomyces speibonae produces the antibiotic oxytetracycline.
Streptomyces violaceoruber is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces violaceoruber produces protoactinorhodin, kendomycin, phospholipase A2, granaticin and methylenomycin A.
Streptomyces virginiae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces virginiae produces actithiazic acid, virginiamycins and cycloserine. Streptomyces virginiae also produces monensin A, monensin B, monensin C, monensin D, actithiazic acid.
Streptomyces viridosporus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces viridosporus produces sistomycine and lignin peroxidase. Streptomyces viridosporus can degrade lignin and humic acids. Streptomyces viridosporus also produces moenomycin A, a component of bambermycin.