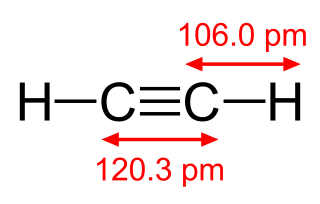
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2 and structure H−C≡C−H. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.

In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula CnH2n−2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic.

Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilized remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin calx "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone.

In chemistry, a carbide usually describes a compound composed of carbon and a metal. In metallurgy, carbiding or carburizing is the process for producing carbide coatings on a metal piece.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.

The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure.

Calcium carbide, also known as calcium acetylide, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of CaC2. Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene and calcium cyanamide.

Thorium dioxide (ThO2), also called thorium(IV) oxide, is a crystalline solid, often white or yellow in colour. Also known as thoria, it is mainly a by-product of lanthanide and uranium production. Thorianite is the name of the mineralogical form of thorium dioxide. It is moderately rare and crystallizes in an isometric system. The melting point of thorium oxide is 3300 °C – the highest of all known oxides. Only a few elements (including tungsten and carbon) and a few compounds (including tantalum carbide) have higher melting points. All thorium compounds, including the dioxide, are radioactive because there are no stable isotopes of thorium.
In chemistry, an acetylide is a compound that can be viewed as the result of replacing one or both hydrogen atoms of acetylene (ethyne) HC≡CH by metallic or other cations. Calcium carbide is an important industrial compound, which has long been used to produce acetylene for welding and illumination. It is also a major precursor to vinyl chloride. Other acetylides are reagents in organic synthesis.
Carbothermic reactions involve the reduction of substances, often metal oxides (O2-), using carbon (C) as the reducing agent. The reduction is usually conducted in the electric arc furnace or reverberatory furnace, depending on the metal ore. These chemical reactions are usually conducted at temperatures of several hundred degrees Celsius. Such processes are applied for production of the elemental forms of many elements. The ability of metals to participate in carbothermic reactions can be predicted from Ellingham diagrams.

Kipp's apparatus, also called a Kipp generator, is an apparatus designed for preparation of small volumes of gases. It was invented around 1844 by the Dutch pharmacist Petrus Jacobus Kipp and widely used in chemical laboratories and for demonstrations in schools into the second half of the 20th century.
Strontium boride (SrB6) is an inorganic compound. At room temperature, it appears as a crystalline black powder. Closer examination reveals slightly translucent dark red crystals capable of scratching quartz. It is very stable and has a high melting point and density. Although not thought to be toxic, it is an irritant to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.

Strontium carbonate (SrCO3) is the carbonate salt of strontium that has the appearance of a white or grey powder. It occurs in nature as the mineral strontianite.

Group 2 organometallic chemistry refers to the organic derivativess of any group 2 element. It is a subtheme to main group organometallic chemistry. By far the most common group 2 organometallic compounds are the magnesium-containing Grignard reagents which are widely used in organic chemistry. Other organometallic group 2 compounds are typically limited to academic interests.
Dilithium acetylide is an organometallic compound with the formula Li2C2. It is typically derived by double deprotonation of acetylene. X-ray crystallography confirms the presence of C≡C subunits attached to lithium, resulting in a polymeric structure. Li2C2 is one of an extensive range of lithium-carbon compounds, which include the lithium-rich Li4C, Li6C2, Li8C3, Li6C3, Li4C3, Li4C5, and the graphite intercalation compounds LiC6, LiC12, and LiC18. It is an intermediate compound produced during radiocarbon dating procedures.
Uranyl carbonate refers to the inorganic compound with the formula UO2CO3. Also known by its mineral name rutherfordine, this material consists of uranyl (UO22+) and carbonate (CO32-). Like most uranyl salts, the compound is a polymeric, each uranium(VI) center being bonded to eight O atoms. Hydrolysis products of rutherfordine are also found in both the mineral and organic fractions of coal and its fly ash and is the main component of uranium in mine tailing seepage water.
In organometallic chemistry, a transition metal alkyne complex is a coordination compound containing one or more alkyne ligands. Such compounds are intermediates in many catalytic reactions that convert alkynes to other organic products, e.g. hydrogenation and trimerization.
Platinum tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula PtF
4. In the solid state, the compound features platinum(IV) in octahedral coordination geometry.

Barium carbide is a chemical compound in the carbide family having the chemical formula BaC2.















