The banjo is a stringed instrument with a thin membrane stretched over a frame or cavity to form a resonator. The membrane is typically circular, in modern forms usually made of plastic, originally of animal skin.

The classical guitar, also known as Spanish guitar, is a member of the guitar family used in classical music and other styles. An acoustic wooden string instrument with strings made of gut or nylon, it is a precursor of the modern steel-string acoustic and electric guitars, both of which use metal strings. Classical guitars derive from instruments such as the lute, the vihuela, the gittern, which evolved into the Renaissance guitar and into the 17th and 18th-century baroque guitar. Today's modern classical guitar was established by the late designs of the 19th-century Spanish luthier, Antonio Torres Jurado.

The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted and typically has six or twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A guitar pick may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant hollow chamber on the guitar, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.

In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner.

Clawhammer, sometimes called down-picking, overhand, or most commonly known as frailing, is a distinctive banjo playing style and a common component of American old-time music. The style likely descends from that of West African lutes, such as the akonting which are also the direct ancestors of the banjo.

A guitar pick is a plectrum used for guitars. Picks are generally made of one uniform material, such as some kind of plastic, rubber, felt, tortoiseshell, wood, metal, glass, tagua, thermosetting plastic or stone. They are often shaped in an acute isosceles triangle with the two equal corners rounded and the third corner less rounded. They are used to strum chords or to sound individual notes on a guitar.
The fingerboard is an important component of most stringed instruments. It is a thin, long strip of material, usually wood, that is laminated to the front of the neck of an instrument. The strings run over the fingerboard, between the nut and bridge. To play the instrument, a musician presses strings down to the fingerboard to change the vibrating length, changing the pitch. This is called stopping the strings. Depending on the instrument and the style of music, the musician may pluck, strum or bow one or more strings with the hand that is not fretting the notes. On some instruments, notes can be sounded by the fretting hand alone, such as with hammer ons, an electric guitar technique.

The Appalachian dulcimer is a fretted string instrument of the zither family, typically with three or four strings, originally played in the Appalachian region of the United States. The body extends the length of the fingerboard, and its fretting is generally diatonic.
Rasgueado is a guitar finger strumming technique commonly associated with flamenco guitar music. It is also used in classical and other fingerstyle guitar picking techniques. The rasgueado is executed using the fingers of the strumming hand in rhythmically precise, and often rapid, strumming patterns. The important characteristic of this strumming style is the fingernail (outer) side of the finger tips is also used, and in such case, in reverse of the way it is done when the fleshy side of the finger tips is used, namely downward and upward (thumb).

Fingerstyle guitar is the technique of playing the guitar or bass guitar by plucking the strings directly with the fingertips, fingernails, or picks attached to fingers, as opposed to flatpicking. The term "fingerstyle" is something of a misnomer, since it is present in several different genres and styles of music—but mostly, because it involves a completely different technique, not just a "style" of playing, especially for the guitarist's picking/plucking hand. The term is often used synonymously with fingerpicking except in classical guitar circles, although fingerpicking can also refer to a specific tradition of folk, blues and country guitar playing in the US. The terms "fingerstyle" and "fingerpicking" are also applied to similar string instruments such as the banjo.

The tar is a long-necked, waisted lute family instrument, used by many cultures and countries including Iran, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Armenia, Georgia, Tajikistan, Turkey, and others near the Caucasus and Central Asia regions. The older and more complete name of the tār is čahārtār or čārtār, meaning in Persian "four string",. This is in accordance with a practice common in Persian-speaking areas of distinguishing lutes on the basis of the number of strings originally employed. Beside the čārtār, these include the dotār, setār, pančtār, and šaštār or šeštār.
Downpicking, sometimes referred to as down-stroke picking, is a technique used by musicians on plucked string instruments in which the player moves the plectrum, or pick in a downward motion, relative to the position of the instrument, against one or more of the strings to make them vibrate. If down-strokes are played without the addition of upstrokes, the tip of the pick never comes in contact with the strings as the hand moves back up to repeat the down-stroke.

The jarana jarocha is a guitar-shaped fretted stringed instrument from the southern region of the state of Veracruz, Mexico. Typically strung with 8 strings in 5 courses, usually arranged in two single outer strings with three double-courses in between. The strings are usually nylon, although they were gut in the past. The body is somewhat narrower than a guitar because of its direct lineage from the Spanish baroque guitar of the sixteenth century. Sometimes mistaken for a ukulele, the jarana jarocha comes in at least five sizes, the smallest being the chaquiste, somewhat smaller than a soprano ukulele; then the mosquito, about the size of a soprano ukulele; the 'primera', about the size of a concert ukulele; the 'segunda', in length between a tenor and a baritone ukulele; and the 'tercera', somewhat longer than the baritone ukulele. Some luthiers are building jaranas of a size they label "tercerola" or "jarana cuarta", but there is some discussion as to whether these represent a distinct size or are merely particularly large variations of the standard tercera.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to guitars:

In classical guitar, the right hand is developed in such a way that it can sustain two, three, and four voice harmonies while also paying special attention to tone production. The index (i), middle (m), and ring (a) fingers are generally used to play the melody, while the thumb (p) accompanies in the bass register adding harmony and produces a comparable texture and effect to that of the piano. The classical guitar is a solo polyphonic instrument.

A flamenco guitar is a guitar similar to a classical guitar, but with lower action, thinner tops and less internal bracing. It usually has nylon strings, like the classical guitar, but it generally possesses a livelier, more gritty sound compared to the classical guitar. It is used in toque, the guitar-playing part of the art of flamenco.
An acoustic guitar is a musical instrument in the string family. When a string is plucked, its vibration is transmitted from the bridge, resonating throughout the top of the guitar. It is also transmitted to the side and back of the instrument, resonating through the air in the body, and producing sound from the sound hole. While the original, general term for this stringed instrument is guitar, the retronym 'acoustic guitar' – often used to indicate the steel stringed model – distinguishes it from an electric guitar, which relies on electronic amplification. Typically, a guitar's body is a sound box, of which the top side serves as a sound board that enhances the vibration sounds of the strings. In standard tuning the guitar's six strings are tuned (low to high) E2 A2 D3 G3 B3 E4.

Kroncong is the name of a ukulele-like instrument and an Indonesian musical style that typically makes use of the kroncong. A kroncong orchestra or ensemble traditionally consists of a flute, a violin, at least one, but usually a pair of kroncongs, a cello in Pizzicato style, string bass in pizzicato style, and a vocalist. Kroncong originated as an adaptation of a Portuguese musical tradition, brought by sailors to Indonesian port cities in the 16th century. By the late 19th century, kroncong reached popular music status throughout the Indonesian archipelago.

The Mexican vihuela is a guitar-like string instrument from 19th-century Mexico with five strings and typically played in mariachi groups.

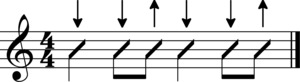
Guitar picking is a group of hand and finger techniques a guitarist uses to set guitar strings in motion to produce audible notes. These techniques involve plucking, strumming, brushing, etc. Picking can be done with: