Related Research Articles

The Fraser Valley is a geographical region in southwestern British Columbia, Canada and northwestern Washington State. It starts just west of Hope in a narrow valley encompassing the Fraser River and ends at the Pacific Ocean stretching from the North Shore Mountains, opposite the city of Vancouver BC, to just south of Bellingham, Washington.

The Chehalis people or Tsihalis are a native people of western Washington state in the United States. They should not be confused with the similarly named Chehalis First Nation of the Sts'Ailes people along the Harrison River in the Fraser Valley area of British Columbia.

Chilliwack is a city in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Chilliwack is surrounded by mountains and home to recreational areas such as Cultus Lake and Chilliwack Lake Provincial Parks. There are numerous outdoor activities in the area in which to participate, including hiking, rock climbing, mountain biking horseback riding, whitewater kayaking, camping, fishing, golf, and paragliding. Chilliwack is known for its annual corn harvest, and is home to the Province's second largest independent bookstore The Book Man. The Fraser Valley Regional District is headquartered in Chilliwack, which is the Fraser Valley's second-largest city, after Abbotsford.

Highway 9, the Agassiz-Rosedale Highway, is a north-south route in the eastern part of the Fraser Valley. It acts as the last connection between the Trans Canada Highway and the Lougheed Highway eastbound before Hope, and is the main access to the resort village of Harrison Hot Springs. The highway first opened in 1953, originally going between Yale Road in Rosedale and Highway 7, with a ferry across the Fraser River. A bridge for Highway 9 across the Fraser opened in 1956. When the section of Highway 1 east of Chilliwack opened in 1961, Highway 9 was extended south to a junction with the new Highway 1 alignment, which replaced Yale Road as the main route between Chilliwack and Hope.

The Chinook salmon is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name chavycha (чавыча).

Shuswap Lake is a lake located in the southern interior of British Columbia, Canada that drains via the Little Shuswap River into Little Shuswap Lake. Little Shuswap Lake is the source of the South Thompson River, a branch of the Thompson River, a tributary of the Fraser River. It is at the heart of a region known as the Columbia Shuswap or "the Shuswap", noted for its recreational lakeshore communities including the city of Salmon Arm. The name "Shuswap" is derived from the Shuswap or Secwepemc First Nations people, the most northern of the Interior Salish peoples, whose territory includes the Shuswap. The Shuswap call themselves /ʃǝxwépmǝx/ in their own language, which is called /ʃǝxwepmǝxtʃín/.

The Stó꞉lō, alternately written as Sto꞉lo, Stó:lô, or Stó:lõ, historically as Staulo or Stahlo, and historically known and commonly referred to in ethnographic literature as the Fraser River Indians or Lower Fraser Salish, are a group of First Nations peoples inhabiting the Fraser Valley and lower Fraser Canyon of British Columbia, Canada, part of the loose grouping of Coast Salish nations. Stó꞉lō is the Halqemeylem word for "river", so the Stó꞉lō are the river people. The first documented reference to these people as "the Stó꞉lō" occurs in Catholic Oblate missionary records from the 1880s. Prior to this, references were primarily to individual tribal groups such as Matsqui, Ts’elxweyeqw, or Sumas.
The Chehalis River is located in the southwest corner of British Columbia, Canada near the city of Chilliwack. It flows south-eastward out of the Douglas Ranges of the Coast Mountains, draining into the Harrison River.

Harrison Hot Springs is a village located at the southern end of Harrison Lake in the Fraser Valley of British Columbia. It is a member of the Fraser Valley Regional District; its immediate neighbour is the District of Kent, which includes the town of Agassiz. It is a resort community known for its hot springs and has a population of just over 1500 people. It is named after Benjamin Harrison, a former deputy governor for the Hudson's Bay Company.

Harrison Lake is the largest lake in the southern Coast Mountains of Canada, being about 250 square kilometres (95 mi²) in area. It is about 60 km (37 mi) in length and at its widest almost 9 km (5.6 mi) across. Its southern end, at the resort community of Harrison Hot Springs, is c. 95 km east of downtown Vancouver. East of the lake are the Lillooet Ranges while to the west are the Douglas Ranges. The lake is the last of a series of large north-south glacial valleys tributary to the Fraser along its north bank east of Vancouver, British Columbia. The others to the west are the Chehalis, Stave, Alouette, Pitt, and Coquitlam Rivers. Harrison Lake is a natural lake, not man-made. The lake is supplied primarily from the Lillooet River, which flows into the lake at the northernmost point.

Barry Penner, is a Canadian licensed lawyer and former politician in the province of British Columbia. He served as a Member of the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia (MLA) for Chilliwack-Hope for 16 years. He also served as Attorney General of British Columbia, Deputy House Leader (2005–2009), Minister of Environment and Minister of Aboriginal Relations and Reconciliation. Barry has also served as chair of the board of directors for the government-owned Insurance Corporation of British Columbia.

The District of Kent is a district municipality located 116 kilometres (72 mi) east of Vancouver, British Columbia. Part of the Fraser Valley Regional District, Kent consists of several communities, the largest and most well-known being Agassiz—the only town in the municipality—Harrison Mills, Kilby, Mount Woodside, Kent Prairie, Sea Bird Island and Ruby Creek. Included within the municipality's boundaries are several separately-governed Indian reserves, including the Seabird Island First Nation's reserves on and around the island of the same name.

Agassiz is a small community located in the Eastern Fraser Valley region of British Columbia, Canada, about 97 kilometres east of Vancouver and 24 kilometres north-east of the city of Chilliwack. The only town within the jurisdiction of the District Municipality of Kent, it contains the majority of Kent's population.

Harrison Mills, formerly Carnarvon and also Harrison River, is an agricultural farming and tourism-based community in the District of Kent west of Agassiz, British Columbia. The community is a part of the Fraser Valley Regional District. Harrison Mills is home to the British Columbia Heritage Kilby Museum and Campground.
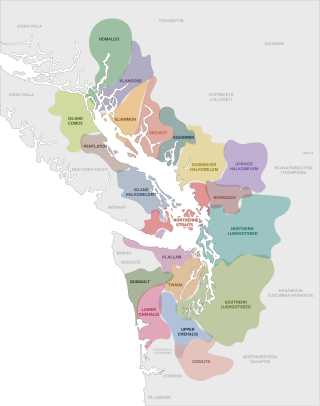
The Coast Salish is a group of ethnically and linguistically related Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, living in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. states of Washington and Oregon. They speak one of the Coast Salish languages. The Nuxalk nation are usually included in the group, although their language is more closely related to Interior Salish languages.
The Sts'ailes Nation formerly known as Chehalis First Nation is the band government of the Sts'Ailes people, whose territories lie between Deroche and Agassiz, British Columbia. The Sts'Alies are a Halkomelem-speaking people but are distinct historically and politically from the surrounding Sto:lo peoples.

Chilliwack Transit System operates the public transportation system for the City of Chilliwack in the Upper Fraser Valley of British Columbia, Canada. Funding is provided under a partnership between the city and BC Transit, the provincial agency which plans and manages municipal transit systems. handyDART provides door-to-door transportation for people whose disability prevents them from using conventional bus service.
The New Westminster Indian Band is an Indian Act band government based at suite 105 – 3680 Rae Avenue in Vancouver, British Columbia. The band administration uses the unofficial name "Qayqayt First Nation" in its public communication. The New Westminster Indian Band is one of the smallest First Nations in Canada and the only one registered without a land base.
Harrison Hill (622m) is a small mountain located at the confluence of the Harrison and Fraser Rivers in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia, Canada. Harrison Knob (~225m) is a prominent shoulder to the east of the main peak of Harrison Hill. Harrison Hill and Harrison Knob are on the north side of the Fraser opposite Chilliwack, Harrison Knob overlooks the confluence directly, Harrison Hill itself separates the Fraser downstream from that confluence and overlooks on its north Harrison Bay, a large, shallow lake-like sidewater of the Harrison River, while at its western foot is the community of Lake Errock. At its eastern foot, just below Harrison Knob, had been the formerly large sawmill town of Harrison Mills, which spanned both sides of the Harrison and was served by the mainline of the Canadian Pacific Railway, which runs along the north side of the mountain's base. The Indian Reserves of the Scowlitz First Nation are at the western end of Harrison Bay and at its outlet at its eastern end, while the reserve of the Chehalis First Nation is along its north shore, and Kilby is on its east shore.
References
- ↑ "Welcome." Sts'ailes. Retrieved 13 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "Sts'ailes Band." British Columbia Assembly of First Nations. Retrieved 13 Aug 2013.
- ↑ "Sts'ailes." SFU Stepping Stones. Retrieved 13 Aug 2013.
- 1 2 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-01-03. Retrieved 2017-01-03.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-01-03. Retrieved 2017-01-03.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Who we are | STS'ailes Band". Archived from the original on 2013-07-18. Retrieved 2017-01-03.
- ↑ Chilliwack court dismisses fisheries charge against former Sts'ailes chief, Paul J. Henderson, Chilliwack Times, August 29, 2016 Chilliwack court dismisses fisheries charge against former Sts'ailes chief