
A fossil is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood, oil, coal, and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the fossil record.

Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.

An exoskeleton is the external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to the internal skeleton (endoskeleton) of, for example, a human. In usage, some of the larger kinds of exoskeletons are known as "shells". Examples of animals with exoskeletons include insects such as grasshoppers and cockroaches, and crustaceans such as crabs and lobsters, as well as the shells of certain sponges and the various groups of shelled molluscs, including those of snails, clams, tusk shells, chitons and nautilus. Some animals, such as the tortoise and turtle, have both an endoskeleton and an exoskeleton.

Taphonomy is the study of how organisms decay and become fossilized or preserved in the paleontological record. The term taphonomy was introduced to paleontology in 1940 by Soviet scientist Ivan Efremov to describe the study of the transition of remains, parts, or products of organisms from the biosphere to the lithosphere.

A trace fossil, also ichnofossil, is a fossil record of biological activity but not the preserved remains of the plant or animal itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, which are the fossilized remains of parts of organisms' bodies, usually altered by later chemical activity or mineralization. The study of such trace fossils is ichnology and is the work of ichnologists.

Micropaleontology is the branch of paleontology (palaeontology) that studies microfossils, or fossils that require the use of a microscope to see the organism, its morphology and its characteristic details.

Paleoecology is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs a variety of fields including paleontology, ecology, climatology and biology.

The Florissant Formation is a sedimentary geologic formation outcropping around Florissant, Teller County, Colorado. The formation is noted for the abundant and exceptionally preserved insect and plant fossils that are found in the mudstones and shales. Based on argon radiometric dating, the formation is Eocene in age and has been interpreted as a lake environment. The fossils have been preserved because of the interaction of the volcanic ash from the nearby Thirtynine Mile volcanic field with diatoms in the lake, causing a diatom bloom. As the diatoms fell to the bottom of the lake, any plants or animals that had recently died were preserved by the diatom falls. Fine layers of clays and muds interspersed with layers of ash form "paper shales" holding beautifully-preserved fossils. The Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument is a national monument established to preserve and study the geology and history of the area.

In geology, petrifaction or petrification is the process by which organic material becomes a fossil through the replacement of the original material and the filling of the original pore spaces with minerals. Petrified wood typifies this process, but all organisms, from bacteria to vertebrates, can become petrified. Petrifaction takes place through a combination of two similar processes: permineralization and replacement. These processes create replicas of the original specimen that are similar down to the microscopic level.

Fossil collecting is the collection of fossils for scientific study, hobby, or profit. Fossil collecting, as practiced by amateurs, is the predecessor of modern paleontology and many still collect fossils and study fossils as amateurs. Professionals and amateurs alike collect fossils for their scientific value. A commercial trade in fossils has also long existed, with some of this being practised illegally.
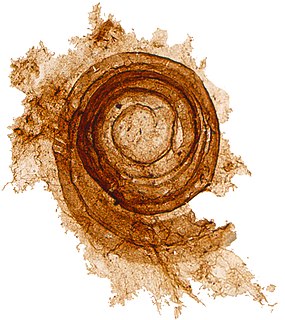
A microfossil is a fossil that is generally between 0.001 mm and 1 mm in size, the visual study of which requires the use of light or electron microscopy. A fossil which can be studied with the naked eye or low-powered magnification, such as a hand lens, is referred to as a macrofossil.

Paleopedology is the discipline that studies soils of past geological eras, from quite recent (Quaternary) to the earliest periods of the Earth's history. Paleopedology can be seen either as a branch of soil science (pedology) or of paleontology, since the methods it uses are in many ways a well-defined combination of the two disciplines.
Absolute dating is the process of determining an age on a specified chronology in archaeology and geology. Some scientists prefer the terms chronometric or calendar dating, as use of the word "absolute" implies an unwarranted certainty of accuracy. Absolute dating provides a numerical age or range, in contrast with relative dating, which places events in order without any measure of the age between events.

Relative dating is the science of determining the relative order of past events, without necessarily determining their absolute age. In geology, rock or superficial deposits, fossils and lithologies can be used to correlate one stratigraphic column with another. Prior to the discovery of radiometric dating in the early 20th century, which provided a means of absolute dating, archaeologists and geologists used relative dating to determine ages of materials. Though relative dating can only determine the sequential order in which a series of events occurred, not when they occurred, it remains a useful technique. Relative dating by biostratigraphy is the preferred method in paleontology and is, in some respects, more accurate. The Law of Superposition, which states that older layers will be deeper in a site than more recent layers, was the summary outcome of 'relative dating' as observed in geology from the 17th century to the early 20th century.

Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly by rivers but also by dust carried by wind and by the flow of glaciers into the sea. Additional deposits come from marine organisms and chemical precipitation in seawater, as well as from underwater volcanoes and meteorite debris.
The Burgess Shale of British Columbia is famous for its exceptional preservation of mid-Cambrian organisms. Around 69 other sites have been discovered of a similar age, with soft tissues preserved in a similar, though not identical, fashion. Additional sites with a similar form of preservation are known from the Ediacaran and Ordovician periods.

A microbial mat is a multi-layered sheet of microorganisms, mainly bacteria and archaea, and also just bacterial. Microbial mats grow at interfaces between different types of material, mostly on submerged or moist surfaces, but a few survive in deserts. A few are found as endosymbionts of animals.

Small carbonaceous fossils (SCFs) are sub-millimetric organic remains of organisms preserved in sedimentary strata.
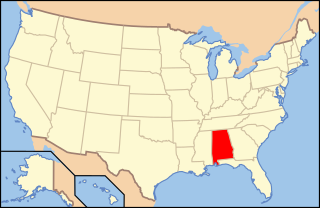
Paleontology in Alabama refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Alabama. Pennsylvanian plant fossils are common, especially around coal mines. During the early Paleozoic, Alabama was at least partially covered by a sea that would end up being home to creatures including brachiopods, bryozoans, corals, and graptolites. During the Devonian the local seas deepened and local wildlife became scarce due to their decreasing oxygen levels.

Egg taphonomy is the study of the decomposition and fossilization of eggs. The processes of egg taphonomy begin when the egg either hatches or dies. Eggshell fragments are robust and can often travel great distances before burial. More complete egg specimens gradually begin to fill with sediment, which hardens as minerals precipitate out of water percolating through pores or cracks in the shell. Throughout the fossilization process the calcium carbonate composing the eggshell generally remains unchanged, allowing scientists to study its original structure. However, egg fossils buried under sediments at great depth can be subjected to heat, pressure and chemical processes that can alter the structure of its shell through a process called diagenesis.















