
Eswatini is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the African Union, the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa, and the Southern African Development Community. Currently, the Kingdom of Eswatini maintains 11 embassies along with 15 consulates and other representations around the world, while there are five embassies in Eswatini as well as 14 consulates and other representations.

The President's Emergency Plan For AIDS Relief is a United States governmental initiative to address the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and help save the lives of those suffering from the disease, primarily in Africa.

Ghana – United States relations have generally been friendly since Ghana's independence, except for a period of strained relations during the later years of the Nkrumah regime. Ghana was the first country to which United States Peace Corps volunteers were sent in 1961. Ghana and the United States are signatories to twenty agreements and treaties covering such matters as agricultural commodities, aviation, defense, economic and technical cooperation, education, extradition, postal matters, telecommunications, and treaty obligations. The refusal of the United States to join the International Cocoa Agreement, given Ghana's heavy dependence on cocoa exports to earn hard currency, is the most serious bilateral issue between the two countries.

The transition from a one-party state to a multi-party democracy significantly strengthened the already cordial U.S. relationship with Malawi. Significant numbers of Malawians study in the United States. The United States has an active Peace Corps program, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Health and Human Servicess, and an Agency for International Development (USAID) mission in Malawi.

The diplomatic relationship between the United States of America and Zambia can be characterized as warm and cooperative. Several U.S. administrations cooperated closely with Zambia's first president, Kenneth Kaunda, in hopes of facilitating solutions to the conflicts in Rhodesia (Zimbabwe), Angola, and Namibia. The United States works closely with the Zambian Government to defeat the HIV/AIDS pandemic that is ravaging Zambia, to promote economic growth and development, and to effect political reform needed to promote responsive and responsible government. The United States is also supporting the government's efforts to root out corruption. Zambia is a beneficiary of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA). The U.S. Government provides a variety of technical assistance and other support that is managed by the Department of State, U.S. Agency for International Development, Millennium Challenge Account (MCA) Threshold Program, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Treasury, Department of Defense, and Peace Corps. The majority of U.S. assistance is provided through the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), in support of the fight against HIV/AIDS.
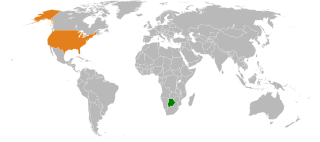
Botswana–United States relations are the international relations between Botswana and the United States.
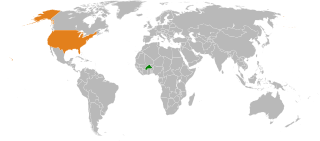
Burkina Faso–United States relations are the international relations between Burkina Faso and the United States. The relations are good but subject to strains in the past because of the Compaoré government's past involvement in arms trading and other sanctions-breaking activity.

Cameroon–United States relations are international relations between Cameroon and the United States.

Dominica–United States relations are bilateral relations between the Commonwealth of Dominica and the United States of America.

Gambian–American relations are bilateral relations between the Gambia and the United States.
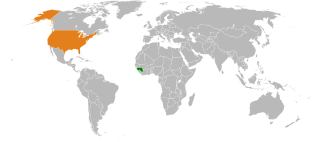
Guinea – United States relations are bilateral relations between Guinea and the United States.

Guyana–United States relations are the bilateral relations between the Co-operative Republic of Guyana and the United States of America.
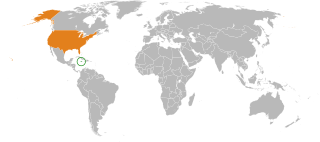
Jamaica–United States relations are bilateral relations between Jamaica and the United States.

Lesotho–United States relations are bilateral relations between the Kingdom of Lesotho and the United States of America.

Namibia – United States relations are bilateral relations between Namibia and the United States.
Nigeria–United States relations are bilateral relations between the Federal Republic of Nigeria and the United States of America. Nigeria and the United States have long been close allies.

Togo–United States relations are bilateral relations between Togo and the United States.
Uganda – United States relations are bilateral relations between Uganda and the United States.
HIV/AIDS in Eswatini was first reported in 1986 but has since reached epidemic proportions due in large part to cultural beliefs which discourage safe-sex practices. Coupled with a high rate of co-infection with tuberculosis, life expectancy has halved in the first decade of the millennium. Eswatini has the highest prevalence of HIV as percentage of population in the world as of 2016 (27.2%).
Seed Global Health, formerly known as Global Health Service Corps, is a non-profit organization started in 2011 which helps to provide nursing and medical training support in resource-limited countries. Seed Global Health collaborates with the Peace Corps to create the Global Health Service Partnership (GHSP). This program has established the first "Peace Corps for doctors and nurses". Since launch, GHSP has had 97 volunteers train more than 8,300 students in 5 African countries.

The United States Department of State (DOS), commonly referred to as the State Department, is the federal executive department that advises the President and conducts international relations. Equivalent to the foreign ministry of other countries, it was established in 1789 as the nation's first executive department. The current Secretary of State is Mike Pompeo, who ascended to the office in April 2018 after Rex Tillerson resigned.
The U.S. Bilateral Relations Fact Sheets, also known as the Background Notes, are a series of works by the United States Department of State. These publications include facts about the land, people, history, government, political conditions, economy, and foreign relations of independent states, some dependencies, and areas of special sovereignty. The series is available online through the State Department's website.






























