
The Subaru Forester is a compact crossover SUV that has been manufactured by Subaru since 1997. The first generation was built on the platform of the Impreza in the style of a taller station wagon, a style that continued to the second generation, while the third-generation model onwards moved towards a crossover SUV design. A performance model was available for the second-generation Forester in Japan as the Forester STi.

The Subaru Outback is an automotive nameplate used by the Japanese automaker Subaru for two different SUV-themed vehicles: a Legacy-derived crossover station wagon, the Outback, and an Impreza-derived off-road themed hatchback, the Outback Sport (1994–2011).

A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and, in many instances, additional gear ranges.

Quattro is the trademark used by the automotive brand Audi to indicate that all-wheel drive (AWD) technologies or systems are used on specific models of its automobiles.

A transfer case is an intermediate gearbox that transfers power from the transmission of a motor vehicle to the driven axles of four-wheel-drive, all-wheel-drive, and other multi-axled on- and off-road machines. A part of the vehicle's drivetrain, it employs drive shafts to mechanically deliver motive power. The transfer case also synchronizes the difference between the rotation of the front and rear wheels, and may contain one or more sets of low range gears for off-road use.

The Subaru Alcyone SVX, marketed outside Japan as the Subaru SVX, is a two-door, front-engine, all- or front-wheel drive coupé manufactured and marketed by Subaru from 1991 to 1996 over a single generation.
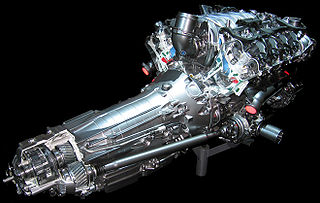
4Matic is the marketing name of an all-wheel drive system developed by Mercedes-Benz. It is designed to increase traction in slippery conditions. With the introduction of the 2017 E 63 S sedan, Mercedes-AMG announced a performance-oriented variant of the system called AMG Performance 4MATIC+.

A drive wheel is a wheel of a motor vehicle that transmits force, transforming torque into tractive force from the tires to the road, causing the vehicle to move. The powertrain delivers enough torque to the wheel to overcome stationary forces, resulting in the vehicle moving forwards or backwards.
Torque steer is the unintended influence of engine torque on the steering, especially in front-wheel-drive vehicles. For example, during heavy acceleration, the steering may pull to one side, which may be disturbing to the driver. The effect is manifested either as a tugging sensation in the steering wheel, or a veering of the vehicle from the intended path. Torque steer is directly related to differences in the forces in the contact patches of the left and right drive wheels. The effect becomes more evident when high torques are applied to the drive wheels because of a high overall reduction ratio between the engine and wheels, high engine torque, or some combination of the two. Torque steer is distinct from steering kickback.
ATTESA is a four-wheel drive system used in some automobiles produced by the Japanese automaker Nissan, including some models under its luxury marque Infiniti.
Super Handling-All Wheel Drive (SH-AWD) is a full-time, fully automatic, all-wheel drive traction and handling system, which combines front-rear torque distribution control with independently regulated torque distribution to the left and right rear wheels. This way the system freely distributes the optimum amount of torque to all four wheels according to the driving conditions. The system was announced in April 2004, and was introduced in the North American market in the second generation 2005 model year Acura RL, and in Japan as the fourth generation Honda Legend.
ControlTrac four-wheel drive is the brand name of a selectable automatic full-time four-wheel drive system offered by Ford Motor Company. The four-wheel drive system was designed and developed at BorgWarner under its TorqTransfer Systems division in the mid 1980s. BorgWarner calls the system Torque-On-Demand (TOD). ControlTrac was the first automatic system to use software control and no planetary or bevel geared center differential. Instead of a planetary or bevel geared center differential, the system uses a variable intelligent locking center multi-disc differential.
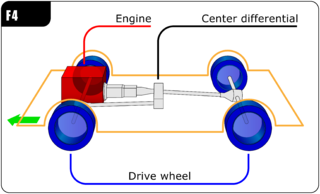
In automotive design, an F4, or front-engine, four-wheel drive (4WD) layout places the internal combustion engine at the front of the vehicle and drives all four roadwheels. This layout is typically chosen for better control on many surfaces, and is an important part of rally racing, as well as off-road driving. In terms of racing purposes, whether it be on-road or off-road, can be described as follows,
A team that pursues the Weak LS4WD architecture will minimize the development cost of the front-wheel drive system at the expense of having a larger rear powertrain. The Weak architecture produces a vehicle with a large powersplit between the front and rear powertrains, while the Strong architecture recommends a vehicle with more similar power and torque requirements for the front and rear.

The first generation Subaru Legacy is a mid-size family car / wagon developed by Fuji Heavy Industries. The Legacy was an all new model, and was considered a notable departure from Subaru products in the past.

The second-generation Subaru Legacy was marketed in Japan from October 1993, and July 1994 marked the second generation in North America with a full body and chassis revision. The exterior was designed by Olivier Boulay in 1991, during his tenure at Subaru. The tail light appearance on both the sedan and wagon was influenced by the taillights on the SVX.

Subaru launched the third generation Japanese and world-market Legacy in June 1998, while the North American model was introduced in May 1999 for the 2000 model year. In all markets except for the United States, production lasted through 2002, with a limited production Blitzen model sold mid-cycle under the 2003 model year in Japan. Production in the United States lasted through 2004.

Individual-wheel drive (IWD) is a wheeled vehicle with a drivetrain that allows all wheels to receive torque from several motors independent of each other. The term was coined to identify those electric vehicles whereby each wheel is driven by its own individual electric motor, as opposed to conventional differentials.
Torque vectoring is a technology employed in automobile differentials that has the ability to vary the torque to each half-shaft with an electronic system; or in rail vehicles which achieve the same using individually motored wheels. This method of power transfer has recently become popular in all-wheel drive vehicles. Some newer front-wheel drive vehicles also have a basic torque vectoring differential. As technology in the automotive industry improves, more vehicles are equipped with torque vectoring differentials. This allows for the wheels to grip the road for better launch and handling.

The second generation of the Subaru Impreza compact car was introduced in 2000 and manufactured up to 2007 by Subaru in Ota, Gunma, Japan, in both sedan and five-door wagon bodystyles, as well as two intermediate facelifts throughout its lifespan.














