
HMS Beagle was a Cherokee-class 10-gun brig-sloop of the Royal Navy, one of more than 100 ships of this class. The vessel, constructed at a cost of £7,803, was launched on 11 May 1820 from the Woolwich Dockyard on the River Thames. Later reports say the ship took part in celebrations of the coronation of King George IV of the United Kingdom, passing under the old London Bridge, and was the first rigged man-of-war afloat upriver of the bridge. There was no immediate need for Beagle, so she "lay in ordinary", moored afloat but without masts or rigging. She was then adapted as a survey barque and took part in three survey expeditions.

The Challenger expedition of 1872–1876 was a scientific programme that made many discoveries to lay the foundation of oceanography. The expedition was named after the naval vessel that undertook the trip, HMS Challenger.

Sir Charles Wyville Thomson was a Scottish natural historian and marine zoologist. He served as the chief scientist on the Challenger expedition; his work there revolutionized oceanography and led to his being knighted.

Kaikō was a remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) built by the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC) for exploration of the deep sea. Kaikō was the second of only five vessels ever to reach the bottom of the Challenger Deep, as of 2019. Between 1995 and 2003, this 10.6 ton unmanned submersible conducted more than 250 dives, collecting 350 biological species, some of which could prove to be useful in medical and industrial applications. On 29 May 2003, Kaikō was lost at sea off the coast of Shikoku Island during Typhoon Chan-Hom, when a secondary cable connecting it to its launcher at the ocean surface broke.

The United Kingdom Hydrographic Office (UKHO) is the UK's agency for providing hydrographic and marine geospatial data to mariners and maritime organisations across the world. The UKHO is a trading fund of the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and is located in Taunton, Somerset, with a workforce of approximately 900 staff.

HMS Challenger was a Pearl-class corvette of the Royal Navy launched on 13 February 1858 at the Woolwich Dockyard. She served the flagship of the Australia Station between 1866 and 1870.

HMS Tamar was a Royal Navy troopship built by the Samuda Brothers at Cubitt Town, London, and launched in Britain in 1863. She served as a supply ship from 1897 to 1941, and gave her name to the shore station HMS Tamar in Hong Kong.
Thomas Henry Tizard was an English oceanographer, hydrographic surveyor, and navigator.
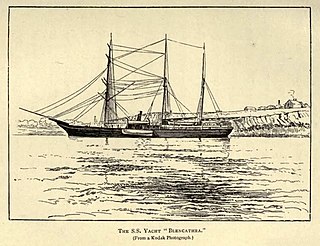
The Philomel-class gunvesselHMS Newport was launched in Wales in 1867. Having become the first ship to pass through the Suez Canal, she was sold in 1881 and renamed Pandora II. She was purchased again in about 1890 and renamed Blencathra, taking part in expeditions to the north coast of Russia. She was bought in 1912 by Georgy Brusilov for use in his ill-fated 1912 Arctic expedition to explore the Northern Sea Route, and was named Svyataya Anna, after Saint Anne. The ship became firmly trapped in ice; only two members of the expedition, Valerian Albanov and Alexander Konrad, survived. The ship has never been found.

Podophorus is an extinct genus of plants in the grass family. The only known species is Podophorus bromoides, which was native to Robinson Crusoe Island in the South Pacific Ocean. This is one of the Juan Fernández Islands, part of the Republic of Chile. The plant was last collected in the wild in the mid-19th century and is now considered extinct. A genetic analysis of the type material found it to be most closely related to Megalachne, also endemic to the Juan Fernández archipelago. This clade was in turn found to be nested within a paraphyletic Festuca, most closely related to F. pampeana of South America.

Typhlodaphne platamodes is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Borsoniidae.

Puncturella agger is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Fissurellidae, the keyhole limpets.
Coralliophila aedonia is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Muricidae, the murex snails or rock snails.
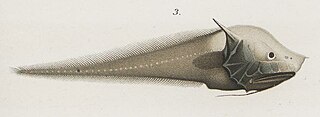
The bony-eared assfish is a bathypelagic species of cusk-eel found in tropical and sub-tropical oceans at depths of from 1,171 to 4,415 metres. It has been found as far north as Queen Charlotte Sound off British Columbia's coast. This species grows to a length of 37.5 centimetres (14.8 in) SL. The larvae are similar in overall form to the related gargoyle cusk, but have elongated 3rd, 4th, and 5th pectoral-fin rays.

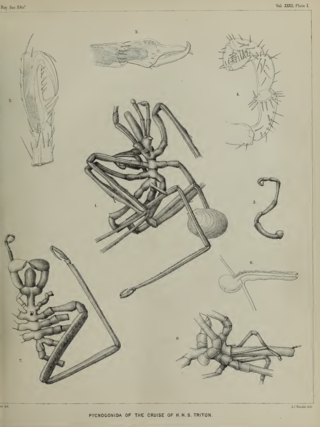
Ocean dredging was an oceanography technique introduced in the nineteenth century and developed by naturalist Edward Forbes. This form of dredging removes substrate and fauna specifically from the marine environment. Ocean dredging techniques were used on the HMS Challenger expeditions as a way to sample marine sediment and organisms.

Johan Hjalmar Théel was a Swedish zoologist and university professor.

Symplegma is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Styelidae.

Caulophacus elegans is a species of glass sponges belonging to the subfamily Lanuginellinae. The type specimen has been found in Central Kuroshio Current, near Japan.
Geodia cooksoni is a sponge species in the family Geodiidae. The species was first described by British scientist William Johnson Sollas in 1888 under the name Cydonium cooksoni. It is found in the waters of the Pacific Ocean around the Galápagos Islands.

Sycozoa pulchra, is a sea squirt in the family Holozoidae, first described by William Abbott Herdman in 1886 as Colella pulchra. The taxonomic decision which determined the name, Sycozoa pulchra, and the species' synonymy was given by Patricia Kott in 1990.


















