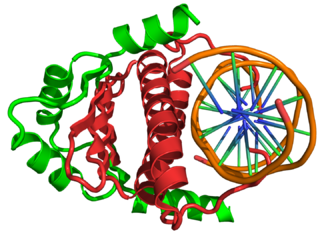
In the field of molecular biology, myocyte enhancer factor-2 (Mef2) proteins are a family of transcription factors which through control of gene expression are important regulators of cellular differentiation and consequently play a critical role in embryonic development. In adult organisms, Mef2 proteins mediate the stress response in some tissues. Mef2 proteins contain both MADS-box and Mef2 DNA-binding domains.

Transcription factor GATA-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GATA4 gene.

Paired box gene 8, also known as PAX8, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PAX8 gene.

Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 2 also known as pituitary homeobox 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PITX2 gene.

Homeobox protein Nkx-2.5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NKX2-5 gene.

Transcription factor GATA-6, also known as GATA-binding factor 6 (GATA6), is protein that in humans is encoded by the GATA6 gene. The gene product preferentially binds (A/T/C)GAT(A/T)(A) of the consensus binding sequence.
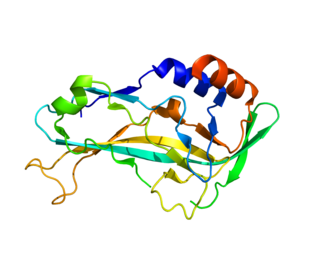
T-box transcription factor TBX5, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX5 gene. Abnormalities in the TBX5 gene can result in altered limb development, Holt-Oram syndrome, Tetra-amelia syndrome, and cardiac and skeletal problems.

Insulin gene enhancer protein ISL-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ISL1 gene.

T-box transcription factor TBX3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX3 gene.

Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 2 (HEY2) also known as cardiovascular helix-loop-helix factor 1 (CHF1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HEY2 gene.

Homeobox protein OTX2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OTX2 gene.
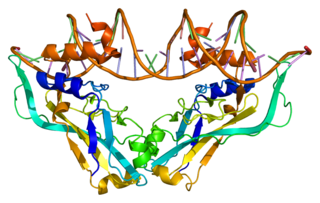
T-box transcription factor 2 Tbx2 is a transcription factor that is encoded by the Tbx2 gene on chromosome 17q21-22 in humans. This gene is a member of a phylogenetically conserved family of genes that share a common DNA-binding domain, the T-box. Tbx2 and Tbx3 are the only T-box transcription factors that act as transcriptional repressors rather than transcriptional activators, and are closely related in terms of development and tumorigenesis. This gene plays a significant role in embryonic and fetal development through control of gene expression, and also has implications in various cancers. Tbx2 is associated with numerous signaling pathways, BMP, TGFβ, Wnt, and FGF, which allow for patterning and proliferation during organogenesis in fetal development.

ZIC3 is a member of the Zinc finger of the cerebellum (ZIC) protein family.

Heart- and neural crest derivatives-expressed protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HAND1 gene.

Heart- and neural crest derivatives-expressed protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HAND2 gene.

Zinc finger protein ZFPM2, i.e. zinc finger protein, FOG family member 2, but also termed Friend of GATA2, Friend of GATA-2, FOG2, or FOG-2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZFPM2 and in mice by the Zfpm2 gene.

Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family, member A2, also known as ALDH1A2 or retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (RALDH2), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALDH1A2 gene.

Protein Jumonji is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JARID2 gene. JARID2 is a member of the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase superfamily.
Neural crest cells are multipotent cells required for the development of cells, tissues and organ systems. A subpopulation of neural crest cells are the cardiac neural crest complex. This complex refers to the cells found amongst the midotic placode and somite 3 destined to undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transformation and migration to the heart via pharyngeal arches 3, 4 and 6.
tinman, or tin is an Nk2-homeobox containing transcription factor first isolated in Drosophila flies. The human homolog is the Nkx2-5 gene. tinman is expressed in the precardiac mesoderm and is responsible for the differentiation, proliferation, and specification of cardiac progenitor cells. This gene is named after the character Tin Woodman who lacks a heart, as flies with nonfunctional tinman genes have cardiac deformities.



















